Health
World Health Organization negotiating to take control “when the next event with pandemic potential strikes”

From Dr. John Campbell on Youtube
British Health Researcher Dr. John Campbell is raising the alarm about the latest moves by the World Health Organization to consolidate authority over governments all around the world.
As argued in UK Parliament, the World Health Organization is asking for a vast transfer of power and some MP’s are very much in favour of ceding power to the WHO.
In this video, Dr. Campbell outlines new regulations countries are currently negotiating to hand over vast new responsibilities to the WHO. The treaties would put the World Health Organization in charge – not just of the global health response, but of what information is shared, and how that information is shared. The regulations would also allow the WHO to take control not just in the event of a health emergency, but in the event of any emergency that could potentially impact public health.
From the commentary notes of Dr. John Campbell.
Countries from around the world are currently working on negotiating and/or amending two international instruments, which will help the world be better prepared when the next event with pandemic potential strikes.
The Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB) https://inb.who.int to draft and negotiate a convention, agreement or other international instrument to strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness and response (commonly known as the Pandemic Accord).
Amendments to the International Health Regulations https://www.who.int/teams/ihr/working…) https://apps.who.int/gb/wgihr/pdf_fil… to amend the current International Health Regulations (2005) https://apps.who.int/gb/wgihr/ https://www.who.int/publications/i/it… 66 2005 articles
Underlined and bold = proposal to add text
Strikethrough = proposal to delete existing text (cut and paste does not copy strike through so I’ve put them in comic sans)
Article 1 Definitions
“standing recommendation” means non-binding advice issued by WHO
“temporary recommendation” means non-binding advice issued by WHO
Article 2 Scope and purpose including through health systems
readiness and resilience in ways that are commensurate with and restricted to public health risk – all risks – with a potential to impact public health,
Article 3 Principles
The implementation of these Regulations shall be with full respect for the dignity, human rights and fundamental freedoms of persons
Article 4 Responsible authorities
each State Party should inform WHO about the establishment of its National Competent Authority responsible for overall implementation of the IHR that will be recognized and held accountable
Article 5 Surveillance
the State Party may request a further extension not exceeding two years from the Director-General,
who shall make the decision refer the issue to World Health Assembly which will then take a decision on the same
WHO shall collect information regarding events through its surveillance activities
Article 6 Notification
No sharing of genetic sequence data or information shall be required under these Regulations.
Article 9: Other Reports
reports from sources other than notifications or consultations
Before taking any action based on such reports, WHO shall consult with and attempt to obtain verification from the State Party in whose territory the event is allegedly occurring
Article 10 Verification
whilst encouraging the State Party to accept the offer of collaboration by WHO, taking into account the views of the State Party concerned.
Article 11 Exchange of information
WHO shall facilitate the exchange of information between States Parties and ensure that the Event Information Site For National IHR Focal Points offers a secure and reliable platform
Parties referred to in those provisions, shall not make this information generally available to other States Parties, until such time as when: (e) WHO determines it is necessary that such information be made available to other States Parties to make informed, timely risk assessments.
Addictions
Why B.C.’s new witnessed dosing guidelines are built to fail
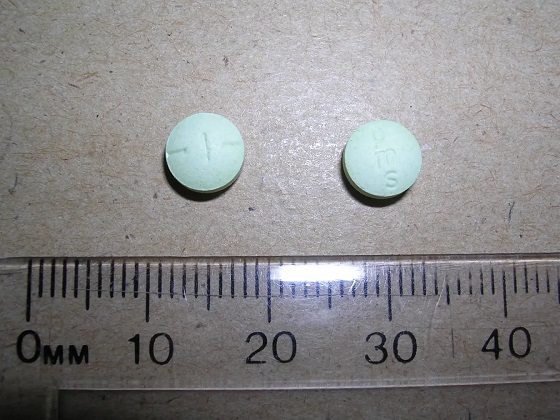
Photo by Acceptable at English Wikipedia, ‘Two 1 mg pills of Hydromorphone, prescribed to me after surgery.’ [Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons]
By Alexandra Keeler
B.C. released new witnessed dosing guidelines for safer supply opioids. Experts say they are vague, loose and toothless
This February, B.C pledged to reintroduce witnessed dosing to its controversial safer supply program.
Safer supply programs provide prescription opioids to people who use drugs. Witnessed dosing requires patients to consume those prescribed opioids under the supervision of a health-care professional, rather than taking their drugs offsite.
The province said it was reintroducing witnessed dosing to “prevent the diversion of prescribed opioids and hold bad actors accountable.”
But experts are saying the government’s interim guidelines, released April 29, are fundamentally flawed.
“These guidelines — just as any guidelines for safer supply — do not align with addiction medicine best practices, period,” said Dr. Leonara Regenstreif, a primary care physician specializing in substance use disorders. Regenstreif is a founding member of Addiction Medicine Canada, an advocacy group that represents 23 addiction specialists.
Addiction physician Dr. Michael Lester, who is also a founding member of the group, goes further.
“Tweaking a treatment protocol that should not have been implemented in the first place without prior adequate study is not much of an advancement,” he said.
Witnessed dosing
Initially, B.C.’s safer supply program was generally administered through witnessed dosing. But in 2020, to facilitate access amidst pandemic restrictions, the province moved to “take-home dosing,” allowing patients to take their prescription opioids offsite.
After pandemic restrictions were lifted, the province did not initially return to witnessed dosing. Rather, it did so only recently, after a bombshell government report alleged more than 60 B.C. pharmacies were boosting sales by encouraging patients to fill unnecessary opioid prescriptions. This incentivized patients to sell their medications on the black market.
B.C.’s interim guidelines, developed by the BC Centre on Substance Use at the government’s request, now require all new safer supply patients to begin with witnessed dosing.
But for existing patients, the guidelines say prescribers have discretion to determine whether to require witnessed dosing. The guidelines define an existing patient as someone who was dispensed prescription opioids within the past 30 days.
The guidelines say exemptions to witnessed dosing are permitted under “extraordinary circumstances,” where witnessed dosing could destabilize the patient or where a prescriber uses “best clinical judgment” and determines diversion risk is “very low.”
Holes
Clinicians say the guidelines are deliberately vague.
Regenstreif described them as “wordy, deliberately confusing.” They enable prescribers to carry on as before, she says.
Lester agrees. Prescribers would be in compliance with these guidelines even if “none of their patients are transferred to witnessed dosing,” he said.
In his view, the guidelines will fail to meet their goal of curbing diversion.
And without witnessed dosing, diversion is nearly impossible to detect. “A patient can take one dose a day and sell seven — and this would be impossible to detect through urine testing,” Lester said.
He also says the guidelines do not remove the incentive for patients to sell their drugs to others. He cites estimates from Addiction Medicine Canada that clients can earn up to $20,000 annually by selling part of their prescribed supply.
“[Prescribed safer supply] can function as a form of basic income — except that the community is being flooded with addictive and dangerous opioids,” Lester said.
Regenstreif warns that patients who had been diverting may now receive unnecessarily high doses. “Now you’re going to give people a high dose of opioids who don’t take opioids,” she said.
She also says the guidelines leave out important details on adjusting doses for patients who do shift from take-home to witnessed dosing.
“If a doctor followed [the guidelines] to the word, and the patient followed it to the word, the patient would go into withdrawal,” she said.
The guidelines assume patients will swallow their pills under supervision, but many crush and inject them instead, Regenstreif says. Because swallowing is less potent, a higher dose may be needed.
“None of that is accounted for in this document,” she said.
Survival strategy
Some harm reduction advocates oppose a return to witnessed dosing, saying it will deter people from accessing a regulated drug supply.
Some also view diversion as a life-saving practice.
Diversion is “a harm reduction practice rooted in mutual aid,” says a 2022 document developed by the National Safer Supply Community of Practice, a group of clinicians and harm reduction advocates.
The group supports take-home dosing as part of a broader strategy to improve access to safer supply medications. In their document, they say barriers to accessing safer supply programs necessitate diversion among people who use drugs — and that the benefits of diversion outweigh the risks.
However, the risks — and harms — of diversion are mounting.
People can quickly develop a tolerance to “safer” opioids and then transition to more dangerous substances. Some B.C. teenagers have said the prescription opioid Dilaudid was a stepping stone to them using fentanyl. In some cases, diversion of these drugs has led to fatal overdoses.
More recently, a Nanaimo man was sentenced to prison for running a highly organized drug operation that trafficked diverted safer supply opioids. He exchanged fentanyl and other illicit drugs for prescription pills obtained from participants in B.C.’s safer supply program.
Recovery
Lester, of Addiction Medicine Canada, believes clinical discretion has gone too far. He says take-home dosing should be eliminated.
“Best practices in addiction medicine assume physicians prescribing is based on sound and thorough research, and ensuring that their prescribing does not cause harm to the broader community, as well as the patient,” he said.
“[Safer supply] for opioids fails in both these regards.”
He also says safer supply should only be offered as a short-term bridge to patients being started on proven treatments like buprenorphine or methadone, which help reduce drug cravings and manage withdrawal symptoms.
B.C.’s witnessed dosing guidelines say prescribers can discuss such treatment options with patients. However, the guidelines remain neutral on whether safer supply is intended as a transitional step toward longer-term treatment.
Regenstreif says this neutrality undermines care.
“[M]ost patients I’ve seen with opioid use disorder don’t want to have [this disorder],” she said. “They would rather be able to set goals and do other things.”
Oversight gaps
Currently, about 3,900 people in B.C. participate in the safer supply program — down from 5,200 in March 2023.
The B.C. government has not provided data on how many have been transitioned to witnessed dosing. Investigative journalist Rob Shaw recently reported that these data do not exist.
“The government … confirmed recently they don’t have any mechanism to track which ‘safe supply’ participants are witnessed and which [are] not,” said Elenore Sturko, a Conservative MLA for Surrey-Cloverdale, who has been a vocal critic of safer supply.
“Without a public report and accountability there can be no confidence.”
The BC Centre on Substance Use, which developed the interim guidelines, says it does not oversee policy decisions or data tracking. It referred Canadian Affairs’ questions to B.C.’s Ministry of Health, which has yet to clarify whether it will track and publish transition data. The ministry did not respond to requests for comment by deadline.
B.C. has also not indicated when or whether it will release final guidelines.
Regenstreif says the flawed guidelines mean many people may be misinformed, discouraged or unsupported when trying to reduce their drug use and recover.
“We’re not listening to people with lived experience of recovery,” she said.
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle
Brownstone Institute
Net Zero: The Mystery of the Falling Fertility

From the Brownstone Institute
By
If you want to argue that a mysterious factor X is responsible for the drop in fertility, you will have to explain (1) why the factor affected only the vaccinated, and (2) why it started affecting them at about the time of vaccination.
In January 2022, the number of children born in the Czech Republic suddenly decreased by about 10%. By the end of 2022, it had become clear that this was a signal: All the monthly numbers of newborns were mysteriously low.
In April 2023, I wrote a piece for a Czech investigative platform InFakta and suggested that this unexpected phenomenon might be connected to the aggressive vaccination campaign that had started approximately 9 months before the drop in natality. Denik N – a Czech equivalent of the New York Times – immediately came forward with a “devastating takedown” of my article, labeled me a liar and claimed that the pattern can be explained by demographics: There were fewer women in the population and they were getting older.
To compare fertility across countries (and time), the so-called Total Fertility Rate (TFR) is used. Roughly speaking, it is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime. TFR is independent of the number of women and of their age structure. Figure 1 below shows the evolution of TFR in several European countries between 2001 and 2023. I selected countries that experienced a similar drop in TFR in 2022 as the Czech Republic.

So, by the end of 2023, the following two points were clear:
- The drop in natality in the Czech Republic in 2022 could not be explained by demographic factors. Total fertility rate – which is independent of the number of women and their age structure – dropped sharply in 2022 and has been decreasing ever since. The data for 2024 show that the Czech TFR has decreased further to 1.37.
- Many other European countries experienced the same dramatic and unexpected decrease in fertility that started at the beginning of 2022. I have selected some of them for Figure 1 but there are more: The Netherlands, Norway, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Sweden. On the other hand, there are some countries that do not show a sudden drop in TFR, but rather a steady decline over a longer period (e.g. Belgium, France, UK, Greece, or Italy). Notable exceptions are Bulgaria, Spain, and Portugal where fertility has increased (albeit from very low numbers). The Human Fertility Project database has all the numbers.
This data pattern is so amazing and unexpected that even the mainstream media in Europe cannot avoid the problem completely. From time to time, talking heads with many academic titles appear and push one of the politically correct narratives: It’s Putin! (Spoiler alert: The war started in February 2022; however, children not born in 2022 were not conceived in 2021). It’s the inflation caused by Putin! (Sorry, that was even later). It’s the demographics! (Nope, see above, TFR is independent of the demographics).
Thus, the “v” word keeps creeping back into people’s minds and the Web’s Wild West is ripe with speculation. We decided not to speculate but to wrestle some more data from the Czech government. For many months, we were trying to acquire the number of newborns in each month, broken down by age and vaccination status of the mother. The post-socialist health-care system of our country is a double-edged sword: On one hand, the state collects much more data about citizens than an American would believe. On the other hand, we have an equivalent of the FOIA, and we are not afraid to use it. After many months of fruitless correspondence with the authorities, we turned to Jitka Chalankova – a Czech Ron Johnson in skirts – who finally managed to obtain an invaluable data sheet.
To my knowledge, the datasheet (now publicly available with an English translation here) is the only officially released dataset containing a breakdown of newborns by the Covid-19 vaccination status of the mother. We requested much more detailed data, but this is all we got. The data contains the number of births per month between January 2021 and December 2023 given by women (aged 18-39) who were vaccinated, i.e., had received at least one Covid vaccine dose by the date of delivery, and by women who were unvaccinated, i.e., had not received any dose of any Covid vaccine by the date of delivery.
Furthermore, the numbers of births per month by women vaccinated by one or more doses during pregnancy were provided. This enabled us to estimate the number of women who were vaccinated before conception. Then, we used open data on the Czech population structure by age, and open data on Covid vaccination by day, sex, and age.
Combining these three datasets, we were able to estimate the rates of successful conceptions (i.e., conceptions that led to births nine months later) by preconception vaccination status of the mother. Those interested in the technical details of the procedure may read Methods in the newly released paper. It is worth mentioning that the paper had been rejected without review in six high-ranking scientific journals. In Figure 2, we reprint the main finding of our analysis.

Figure 2 reveals several interesting patterns that I list here in order of importance:
- Vaccinated women conceived about a third fewer children than would be expected from their share of the population. Unvaccinated women conceived at about the same rate as all women before the pandemic. Thus, a strong association between Covid vaccination status and successful conceptions has been established.
- In the second half of 2021, there was a peak in the rate of conceptions of the unvaccinated (and a corresponding trough in the vaccinated). This points to rather intelligent behavior of Czech women, who – contrary to the official advice – probably avoided vaccination if they wanted to get pregnant. This concentrated the pregnancies in the unvaccinated group and produced the peak.
- In the first half of 2021, there was significant uncertainty in the estimates of the conception rates. The lower estimate of the conception rate in the vaccinated was produced by assuming that all women vaccinated (by at least one dose) during pregnancy were unvaccinated before conception. This was almost certainly true in the first half of 2021 because the vaccines were not available prior to 2021. The upper estimate was produced by assuming that all women vaccinated (by at least one dose) during pregnancy also received at least one dose before conception. This was probably closer to the truth in the second part of 2021. Thus, we think that the true conception rates for the vaccinated start close to the lower bound in early 2021 and end close to the upper bound in early 2022. Once again, we would like to be much more precise, but we have to work with what we have got.
Now that the association between Covid-19 vaccination and lower rates of conception has been established, the one important question looms: Is this association causal? In other words, did the Covid-19 vaccines really prevent women from getting pregnant?
The guardians of the official narrative brush off our findings and say that the difference is easily explained by confounding: The vaccinated tend to be older, more educated, city-dwelling, more climate change aware…you name it. That all may well be true, but in early 2022, the TFR of the whole population dropped sharply and has been decreasing ever since.
So, something must have happened in the spring of 2021. Had the population of women just spontaneously separated into two groups – rednecks who wanted kids and didn’t want the jab, and city slickers who didn’t want kids and wanted the jab – the fertility rate of the unvaccinated would indeed be much higher than that of the vaccinated. In that respect, such a selection bias could explain the observed pattern. However, had this been true, the total TFR of the whole population would have remained constant.
But this is not what happened. For some reason, the TFR of the whole population jumped down in January 2022 and has been decreasing ever since. And we have just shown that, for some reason, this decrease in fertility affected only the vaccinated. So, if you want to argue that a mysterious factor X is responsible for the drop in fertility, you will have to explain (1) why the factor affected only the vaccinated, and (2) why it started affecting them at about the time of vaccination. That is a tall order. Mr. Occam and I both think that X = the vaccine is the simplest explanation.
What really puzzles me is the continuation of the trend. If the vaccines really prevented conception, shouldn’t the effect have been transient? It’s been more than three years since the mass vaccination event, but fertility rates still keep falling. If this trend continues for another five years, we may as well stop arguing about pensions, defense spending, healthcare reform, and education – because we are done.
We are in the middle of what may be the biggest fertility crisis in the history of mankind. The reason for the collapse in fertility is not known. The governments of many European countries have the data that would unlock the mystery. Yet, it seems that no one wants to know.
Author
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoMark Carney’s Fiscal Fantasy Will Bankrupt Canada
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoCharity Campaigns vs. Charity Donations
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoTemporary Alberta grid limit unlikely to dampen data centre investment, analyst says
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days agoCanada’s New Border Bill Spies On You, Not The Bad Guys
-
 Daily Caller20 hours ago
Daily Caller20 hours ago‘Strange Confluence Of Variables’: Mike Benz Wants Transparency Task Force To Investigate What Happened in Butler, PA
-

 Uncategorized2 days ago
Uncategorized2 days agoCNN’s Shock Climate Polling Data Reinforces Trump’s Energy Agenda
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoPreston Manning: Three Wise Men from the East, Again
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoTrump DOJ dismisses charges against doctor who issued fake COVID passports




