Alberta
With spending restraint, Alberta can re-introduce a rainy-day fund worth $9.8 billion by 2025/26

From the Fraser Institute
It’s Time to Get Off the Resource Revenue Rollercoaster: Re-establishing the Alberta Sustainability Fund
With spending restraint, Alberta can re-introduce a rainy-day fund worth $9.8 billion by 2025/26 that could help insulate the province’s budget from swings in resource revenue, finds a new study published by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Alberta has an ongoing fiscal problem fueled by volatile resource revenues, but reintroducing a rainy-day fund, based on the previously successful Alberta Sustainability Fund, would help get Alberta off this resource revenue rollercoaster and stabilize provincial finances for the long-term,” said Tegan Hill, associate director of Alberta policy at the Fraser Institute and co-author of There’s time to get off the resource revenue rollercoaster: Re-establishing the Alberta Sustainability Fund.
Alberta governments typically include all resource revenue in the budget, meaning that during periods of relatively high resource revenue, the province enjoys budget surpluses but faces pressure to increase spending, and when resource revenues decline, with comparatively high levels of spending, the province’s finances turn to deficits.
Consider that amid the windfall in resource revenue, in Budget 2023, the Alberta government increased cumulative spending by $10.1 billion from 2022/23 through 2024/25 compared to the 2022 Mid-Year Fiscal update just three months earlier.
Rather than continue to spend relatively high one-time resource revenue, the Alberta government can use this opportunity to stabilize provincial finances over the long-term.
By limiting resource revenue included the budget to a stable amount, it will thereby limit the amount of money available for annual spending. Any resource revenue above the set stable amount would be automatically saved in a rainy-day fund to be withdrawn to maintain that stable amount in years with relatively low resource revenue, thus, helping to avoid budget deficits.
The study calculates that with spending restraint Alberta can fund a rainy-day fund worth $9.8 billion by 2025/26.
“The rainy-day fund could be implemented all while still maintaining a balanced budget for Alberta,” Hill said.

Summary
- Alberta’s volatile resource revenues are fueling its ongoing fiscal problem. The provincial government typically includes all resource revenue in its budget. When resource revenue is relatively high, the province enjoys budget surpluses but faces pressure to increase spending; when resource revenues drop, spending remains high and the province turns to deficits.
- Despite efforts to better manage Alberta’s finances, the Smith government is largely repeating past mistakes by increasing spending during a period of relatively high resource revenue.
- In the 2022 mid-year update, the Smith government increased the plan for nominal program spending from Budget 2022 every year from 2022/23 through 2024/25 for a cumulative increase of $5.9 billion. In Budget 2023, the Smith government increased the plan further with a cumulative increase of $10.1 billion from 2022/23 through 2024/25 compared to the 2022 mid-year update.
- Rather than spend all of the resource revenue in years when it is relatively high, the Alberta government should use this opportunity to stabilize provincial finances over the long-term by re-introducing a rainy-day account based on the earlier Alberta Sustainability Fund (ASF).
- To do so, it would limit the resource revenue included the budget to a stable amount, thereby limiting the amount of money available for annual spending. Any resource revenue above the set stable amount would be automatically saved in the ASF to be withdrawn to maintain that stable amount in years with relatively low resource revenue. The government could implement the ASF while maintaining a balanced budget and without an annual reduction in nominal spending.
- Based on 2023 budget projections, with spending restraint, the provincial government could re-introduce an ASF worth $9.8 billion by 2025/26.
Authors:
Alberta
‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Multilateral designs lift more energy with a smaller environmental footprint
A “weird and wonderful” drilling innovation in Alberta is helping producers tap more oil and gas at lower cost and with less environmental impact.
With names like fishbone, fan, comb-over and stingray, “multilateral” wells turn a single wellbore from the surface into multiple horizontal legs underground.
“They do look spectacular, and they are making quite a bit of money for small companies, so there’s a lot of interest from investors,” said Calin Dragoie, vice-president of geoscience with Calgary-based Chinook Consulting Services.
Dragoie, who has extensively studied the use of multilateral wells, said the technology takes horizontal drilling — which itself revolutionized oil and gas production — to the next level.
“It’s something that was not invented in Canada, but was perfected here. And it’s something that I think in the next few years will be exported as a technology to other parts of the world,” he said.
Dragoie’s research found that in 2015 less than 10 per cent of metres drilled in Western Canada came from multilateral wells. By last year, that share had climbed to nearly 60 per cent.
Royalty incentives in Alberta have accelerated the trend, and Saskatchewan has introduced similar policy.
Multilaterals first emerged alongside horizontal drilling in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dragoie said. But today’s multilaterals are longer, more complex and more productive.
The main play is in Alberta’s Marten Hills region, where producers are using multilaterals to produce shallow heavy oil.
Today’s average multilateral has about 7.5 horizontal legs from a single surface location, up from four or six just a few years ago, Dragoie said.
One record-setting well in Alberta drilled by Tamarack Valley Energy in 2023 features 11 legs stretching two miles each, for a total subsurface reach of 33 kilometres — the longest well in Canada.
By accessing large volumes of oil and gas from a single surface pad, multilaterals reduce land impact by a factor of five to ten compared to conventional wells, he said.
The designs save money by skipping casing strings and cement in each leg, and production is amplified as a result of increased reservoir contact.
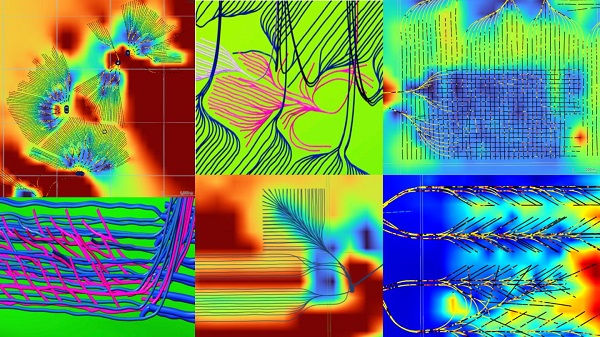
Here are examples of multilateral well design. Images courtesy Chinook Consulting Services.
Parallel
Fishbone
Fan
Waffle
Stingray
Frankenwells
Alberta
Alberta to protect three pro-family laws by invoking notwithstanding clause

From LifeSiteNews
Premier Danielle Smith said her government will use a constitutional tool to defend a ban on transgender surgery for minors and stopping men from competing in women’s sports.
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith said her government will use a rare constitutional tool, the notwithstanding clause, to ensure three bills passed this year — a ban on transgender surgery for minors, stopping men from competing in women’s sports, and protecting kids from extreme aspects of the LGBT agenda — stand and remain law after legal attacks from extremist activists.
Smith’s United Conservative Party (UCP) government stated that it will utilize a new law, Bill 9, to ensure that laws passed last year remain in effect.
“Children deserve the opportunity to grow into adulthood before making life-altering decisions about their gender and fertility,” Smith said in a press release sent to LifeSiteNews and other media outlets yesterday.
“By invoking the notwithstanding clause, we’re ensuring that laws safeguarding children’s health, education and safety cannot be undone – and that parents are fully involved in the major decisions affecting their children’s lives. That is what Albertans expect, and that is what this government will unapologetically defend.”
Alberta Justice Minister and Attorney General Mickey Amery said that the laws passed last year are what Albertans voted for in the last election.
“These laws reflect an overwhelming majority of Albertans, and it is our responsibility to ensure that they will not be overturned or further delayed by activists in the courts,” he noted.
“The notwithstanding clause reinforces democratic accountability by keeping decisions in the hands of those elected by Albertans. By invoking it, we are providing certainty that these protections will remain in place and that families can move forward with clarity and confidence.”
The Smith government said the notwithstanding clause will apply to the following pieces of legislation:
-
Bill 26, the Health Statutes Amendment Act, 2024, prohibits both gender reassignment surgery for children under 18 and the provision of puberty blockers and hormone treatments for the purpose of gender reassignment to children under 16.
-
Bill 27, the Education Amendment Act, 2024, requires schools to obtain parental consent when a student under 16 years of age wishes to change his or her name or pronouns for reasons related to the student’s gender identity, and requires parental opt-in consent to teaching on gender identity, sexual orientation or human sexuality.
-
Bill 29, the Fairness and Safety in Sport Act, requires the governing bodies of amateur competitive sports in Alberta to implement policies that limit participation in women’s and girls’ sports to those who were born female.”
Bill 26 was passed in December of 2024, and it amends the Health Act to “prohibit regulated health professionals from performing sex reassignment surgeries on minors.”
As reported by LifeSiteNews, pro-LGBT activist groups, with the support of Alberta’s opposition New Democratic Party (NDP), have tried to stop the bill via lawsuits. It prompted the Smith government to appeal a court injunction earlier this year blocking the province’s ban on transgender surgeries and drugs for gender-confused minors.
Last year, Smith’s government also passed Bill 27, a law banning schools from hiding a child’s pronoun changes at school that will help protect kids from the extreme aspects of the LGBT agenda.
Bill 27 will also empower the education minister to, in effect, stop the spread of extreme forms of pro-LGBT ideology or anything else to be allowed to be taught in schools via third parties.
Bill 29, which became law last December, bans gender-confused men from competing in women’s sports, the first legislation of its kind in Canada. The law applies to all school boards, universities, and provincial sports organizations.
Alberta’s notwithstanding clause is like all other provinces’ clauses and was a condition Alberta agreed to before it signed onto the nation’s 1982 constitution.
It is meant as a check to balance power between the court system and the government elected by the people. Once it is used, as passed in the legislature, a court cannot rule that the “legislation which the notwithstanding clause applies to be struck down based on the Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the Alberta Bill of Rights, or the Alberta Human Rights Act,” the Alberta government noted.
While Smith has done well on some points, she has still been relatively soft on social issues of importance to conservatives , such as abortion, and has publicly expressed pro-LGBT views, telling Jordan Peterson earlier this year that conservatives must embrace homosexual “couples” as “nuclear families.”
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta to protect three pro-family laws by invoking notwithstanding clause
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada is failing dismally at our climate goals. We’re also ruining our economy.
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoCDC’s Autism Reversal: Inside the Collapse of a 25‑Year Public Health Narrative
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoBREAKING: CDC quietly rewrites its vaccine–autism guidance
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days ago‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoCocaine, Manhunts, and Murder: Canadian Cartel Kingpin Prosecuted In US
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoBREAKING: Globalist Climate Conference Bursts Into Flames
-

 Business10 hours ago
Business10 hours agoNew airline compensation rules could threaten regional travel and push up ticket prices