Alberta
The way forward for energy development? Cenovus commits to building hundreds of homes in communities closest to their oil sands operations

From Cenovus Energy
Our Indigenous Housing program, the largest community investment initiative in Cenovus’s history, is aimed at addressing one of the most pressing issues facing Indigenous communities in Canada – the lack of adequate housing that is forcing many families to live in overcrowded and unsafe conditions.
The program involves a plan to commit $10 million per year for at least five years to build much-needed new homes in six First Nations and Métis communities closest to our oil sands operations in northern Alberta, with the potential to extend the project to 10 years. We see this initiative as an important way to contribute to reconciliation with Indigenous peoples.
We also plan to work with the communities to develop training programs, so that local residents can participate in the building and maintenance of the new homes.
The communities that are part of this program are:
- Beaver Lake Cree Nation
- Chard Métis (Local 218)
- Chipewyan Prairie Dene First Nation
- Cold Lake First Nations
- Conklin Métis (Local 193)
- Heart Lake First Nation
More information including comments from the surrounding communities
Cenovus to help address Indigenous housing crisis in northern Alberta
Project aims to provide about 200 new homes as well as jobs and training opportunities
Cenovus Energy Inc. has launched a major initiative aimed at addressing one of the most pressing issues facing Indigenous communities in Canada – the lack of adequate housing that is forcing many families to live in overcrowded and unsafe conditions. Cenovus is committing $10 million per year for five years to build much-needed new homes in six First Nations and Métis communities closest to its oil sands operations in northern Alberta, with the potential to extend the project to 10 years. The company sees this initiative as an important way to contribute to reconciliation with Indigenous peoples.
“Investing in Indigenous communities near our operations and ensuring they share in the benefits of resource development has always been part of how we do business. Today, we see an opportunity to step up and do more,” said Alex Pourbaix, Cenovus President & Chief Executive Officer. “We can’t solve the Indigenous housing crisis by ourselves, but through this initiative, we have the opportunity to significantly improve the lives of many families currently living in overcrowded and unsafe conditions.”
Developed as part of Cenovus’s recent 10th anniversary celebration, the housing initiative is the single largest community investment in the company’s history. It’s a testament to the strong positive relationships Cenovus has built over many years working with Indigenous communities near its Christina Lake and Foster Creek oil sands projects. Cenovus has met with leaders from Beaver Lake Cree Nation, Chard Métis (Local 218), Chipewyan Prairie Dene First Nation, Cold Lake First Nations, Conklin Métis (Local 193) and Heart Lake First Nation to begin planning the implementation of the housing program starting this year.
Cenovus plans to work with leaders from the six communities to determine the most effective ways of delivering new homes based on the specific needs of each community. It’s anticipated the communities will be able to build about 200 new houses in total over five years. Cenovus will also work with the communities to develop training programs, so that local residents can participate in the building and maintenance of the new homes. This will potentially create valuable education and employment opportunities for them in the long term. Depending on the success of the initiative, including meeting Cenovus’s performance expectations, the company may consider extending the program to 10 years with a total investment amount of $100 million.
“In addition to creating training and employment opportunities and funding the construction of new houses, Cenovus will also work with communities to raise awareness about the Indigenous housing shortage and help advocate for solutions,” said Pourbaix. “Communities have done an admirable job in managing their housing with limited resources. But this is a complex issue that will require new ideas and collaboration among many stakeholders. We hope to inspire other companies, governments and organizations to get involved.”
Separately, Cenovus has engaged its Indigenous Inclusion Advisory Committee, created in 2017 and comprised of senior leaders from various company functions, to help increase Indigenous inclusion in the company’s business. Since its inception in 2009, Cenovus has signed nine long-term benefits agreements with Indigenous communities near its oil sands operations and spent almost $3 billion with Indigenous owned and operated businesses. On January 9, 2020, Cenovus announced ambitious new targets in four environmental, social and governance (ESG) focus areas, including Indigenous engagement, climate & greenhouse gas emissions, land & wildlife, and water stewardship. A significant element of the Indigenous engagement ESG target commits Cenovus to spend at least an additional $1.5 billion with Indigenous businesses through 2030. Cenovus also continues to provide scholarships to Indigenous youth who are pursuing a full-time degree, diploma or certified trade program. More than 190 scholarships have been awarded since the Indigenous scholarship program started in 2013.
Shirley Paradis, Councillor, Beaver Lake Cree Nation
“Beaver Lake Cree Nation has always had housing issues. We’re at a capacity where we are trying to keep up with families’ needs. The most crucial thing is understanding that we have help now. Cenovus is stepping forward and saying: ‘We’re here to help, how do we help your community?’ There is going to be a sigh of relief for us.”
Justin Herman, CEO, Chard Métis (Local 218)
“What I am taking away from Cenovus’s announcement about the new housing initiative – it’s absolutely amazing and groundbreaking, and I hope it sets a precedent for the rest of the industry to follow the lead of Cenovus. We are excited and honoured to be part of this housing initiative.”
Vern Janvier, Chief, Chipewyan Prairie Dene First Nation
“We’re getting to the point where we have two families living in one house, and in some cases three. On top of the houses that are in disrepair, we have demand for another 50 houses. That’s how it builds up on us. And that’s just our reserve.”
Roger Marten, Chief, Cold Lake First Nations
“We have about 3,000 band members and only 300 homes. So, the crisis is always there and is always ongoing. The relationship has always been a great one with Cenovus; they have always listened and try to do the best they can to help us along the way.”
Val Quintal, Board member, Conklin Resource Development Advisory Committee, representing Conklin Métis (Local 193)
“Housing is a critical need for Conklin, and we are so pleased that Cenovus has come forward to help our community address this issue.”
Curtis Monias, Chief, Heart Lake First Nation
“I am really excited for Heart Lake. I look forward to working with all the surrounding communities, with industry, and I’m excited to build homes back home for my people.”
Alberta
Alberta bill would protect freedom of expression for doctors, nurses, other professionals

From LifeSiteNews
‘Peterson’s law,’ named for Canadian psychologist Jordan Peterson, was introduced by Alberta Premier Danielle Smith.
Alberta’s Conservative government introduced a new law that will set “clear expectations” for professional regulatory bodies to respect freedom of speech on social media and online for doctors, nurses, engineers, and other professionals.
The new law, named “Peterson’s law” after Canadian psychologist Jordan Peterson, who was canceled by his regulatory body, was introduced Thursday by Alberta Premier Danielle Smith.
“Professionals should never fear losing their license or career because of a social media post, an interview, or a personal opinion expressed on their own time,” Smith said in a press release sent to media and LifeSiteNews.
“Alberta’s government is restoring fairness and neutrality so regulators focus on competence and ethics, not policing beliefs. Every Albertan has the right to speak freely without ideological enforcement or intimidation, and this legislation makes that protection real.”
The law, known as Bill 13, the Regulated Professions Neutrality Act, will “set clear expectations for professional regulatory bodies to ensure professionals’ right to free expression is protected.”
According to the government, the new law will “Limit professional regulatory bodies from disciplining professionals for expressive off-duty conduct, except in specific circumstances such as threats of physical violence or a criminal conviction.”
It will also restrict mandatory training “unrelated to competence or ethics, such as diversity, equity, and inclusion training.”
Bill 13, once it becomes law, which is all but guaranteed as Smith’s United Conservative Party (UCP) holds a majority, will also “create principles of neutrality that prohibit professional regulatory bodies from assigning value, blame or different treatment to individuals based on personally held views or political beliefs.”
As reported by LifeSiteNews, Peterson has been embattled with the College of Psychologists of Ontario (CPO) after it mandated he undergo social media “training” to keep his license following posts he made on X, formerly Twitter, criticizing Trudeau and LGBT activists.
He recently noted how the CPO offered him a deal to “be bought,” in which the legal fees owed to them after losing his court challenge could be waived but only if he agreed to quit his job as a psychologist.
Early this year, LifeSiteNews reported that the CPO had selected Peterson’s “re-education coach” for having publicly opposed the LGBT agenda.
The Alberta government directly referenced Peterson’s (who is from Alberta originally) plight with the CPO, noting “the disciplinary proceedings against Dr. Jordan Peterson by the College of Psychologists of Ontario, demonstrate how regulatory bodies can extend their reach into personal expression rather than professional competence.”
“Similar cases involving nurses, engineers and other professionals revealed a growing pattern: individuals facing investigations, penalties or compulsory ideological training for off-duty expressive conduct. These incidents became a catalyst, confirming the need for clear legislative boundaries that protect free expression while preserving professional standards.”
Alberta Minister of Justice and Attorney General Mickey Amery said regarding Bill 13 that the new law makes that protection of professionals “real and holds professional regulatory bodies to a clear standard.”
Last year, Peterson formally announced his departure from Canada in favor of moving to the United States, saying his birth nation has become a “totalitarian hell hole.”
Alberta
‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
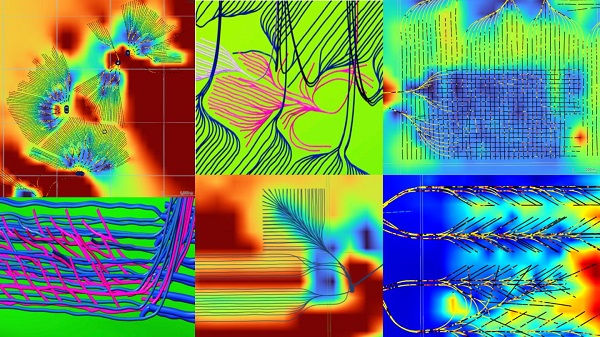
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Multilateral designs lift more energy with a smaller environmental footprint
A “weird and wonderful” drilling innovation in Alberta is helping producers tap more oil and gas at lower cost and with less environmental impact.
With names like fishbone, fan, comb-over and stingray, “multilateral” wells turn a single wellbore from the surface into multiple horizontal legs underground.
“They do look spectacular, and they are making quite a bit of money for small companies, so there’s a lot of interest from investors,” said Calin Dragoie, vice-president of geoscience with Calgary-based Chinook Consulting Services.
Dragoie, who has extensively studied the use of multilateral wells, said the technology takes horizontal drilling — which itself revolutionized oil and gas production — to the next level.
“It’s something that was not invented in Canada, but was perfected here. And it’s something that I think in the next few years will be exported as a technology to other parts of the world,” he said.
Dragoie’s research found that in 2015 less than 10 per cent of metres drilled in Western Canada came from multilateral wells. By last year, that share had climbed to nearly 60 per cent.
Royalty incentives in Alberta have accelerated the trend, and Saskatchewan has introduced similar policy.
Multilaterals first emerged alongside horizontal drilling in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dragoie said. But today’s multilaterals are longer, more complex and more productive.
The main play is in Alberta’s Marten Hills region, where producers are using multilaterals to produce shallow heavy oil.
Today’s average multilateral has about 7.5 horizontal legs from a single surface location, up from four or six just a few years ago, Dragoie said.
One record-setting well in Alberta drilled by Tamarack Valley Energy in 2023 features 11 legs stretching two miles each, for a total subsurface reach of 33 kilometres — the longest well in Canada.
By accessing large volumes of oil and gas from a single surface pad, multilaterals reduce land impact by a factor of five to ten compared to conventional wells, he said.
The designs save money by skipping casing strings and cement in each leg, and production is amplified as a result of increased reservoir contact.
Here are examples of multilateral well design. Images courtesy Chinook Consulting Services.
Parallel
Fishbone
Fan
Waffle
Stingray
Frankenwells
-

 Carbon Tax6 hours ago
Carbon Tax6 hours agoCarney fails to undo Trudeau’s devastating energy policies
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoNew airline compensation rules could threaten regional travel and push up ticket prices
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWill the Port of Churchill ever cease to be a dream?
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoMove over Soviet Russia: UK Police Make 10,000 Arrests Over “Offensive” Online Speech
-

 Digital ID2 days ago
Digital ID2 days agoRoblox to Mandate Facial and ID Verification
-

 Business2 hours ago
Business2 hours agoBudget 2025: Ottawa Fakes a Pivot and Still Spends Like Trudeau
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe numbers Canada uses to set policy don’t add up
-

 armed forces13 hours ago
armed forces13 hours agoCanada At Risk Of Losing Control Of Its Northern Territories















