In Ottawa they call it “arm’s-length.” Out in the real world, people call it duck-and-cover. At Meeting No. 6 of the House of Commons transport committee, MPs confronted a simple, damning timeline: Transport Canada’s top non-partisan official was warned six weeks before the public announcement that BC Ferries would award a four-ship contract to a Chinese state-owned yard. Yet the former transport minister, Chrystia Freeland, told Parliament she was “shocked.” Those two facts do not coexist in nature. One is true, or the other is not.
There’s an even bigger betrayal hiding in plain sight. In the last election, this Liberal government campaigned on a Canada-first message—jobs here, supply chains here, steel here. And then, when it actually mattered, they watched a billion-dollar ferry order sail to a PRC state yard with no Canadian-content requirement attached to the federal financing. So much for “Canada first.” Turns out it was “Canada… eventually,” after the press release.
Conservatives put the revelation on the record and asked the only question that matters in a democracy: what did the minister know and when did she know it? The documents they cite don’t suggest confusion; they suggest choreography—ministerial staff emailing the Prime Minister’s Office on how to manage the announcement rather than stop the deal that offshored Canadian work to a Chinese state firm.
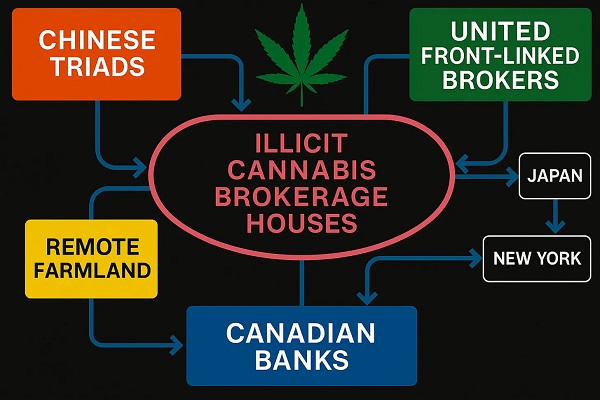
Follow the money and it gets worse. A federal Crown lender—the Canada Infrastructure Bank—underwrote $1 billion for BC Ferries and attached no Canadian-content requirement to the financing. In plain English: taxpayers took the risk, Beijing got the jobs. The paper trail presented to MPs is smothered in black ink—hundreds of pages of redactions—with one stray breadcrumb: a partially visible BC Hydro analysis suggesting roughly half a billion dollars in B.C. terminal upgrades to make the “green” ferry plan work. You’re not supposed to see that. You almost didn’t.
How did the government side respond? With a jurisdictional shrug. We’re told, over and over, that BC Ferries is a provincial, arm’s-length corporation; the feds didn’t pick the yard, don’t run the procurement, and therefore shouldn’t be blamed. That line is convenient, and in a technical sense it’s tidy. But it wilts under heat. The federal lender is still federal. The money is still public. If “arm’s-length” means “no accountability,” it’s not a governance model—it’s a get-out-of-jail-free card.
The fallback argument is economic fatalism: no Canadian shipyards bid, we’re told; building here would have taken longer and cost “billions” more. Maybe that’s true, maybe it isn’t—but it’s the sort of claim that demands evidence, not condescension. Because the last time Canadians heard this script, the same political class promised that global supply chains were efficient, cheap and safe. Then reality happened. If domestic capacity is too weak to compete, that’s not an argument for outsourcing permanently; it’s an indictment of the people who let that capacity atrophy. And if you swear “Canada first” on the campaign trail, you don’t bankroll “China first” from the Treasury bench.
Even the process looked like a master class in delay. The committee repeatedly suspended to “circulate” and “review” lengthy motions, while edits ricocheted across the witness list. There were pushes to pare back which ministers would appear at all, and counter-moves to tuck sensitive testimony behind closed doors. In the end, members nudged toward a compromise—Public Safety in open session, other national-security witnesses in camera—but the pattern was unmistakable: every procedural minute spent on choreography was a minute not spent on the timeline.
And after all that stalling, here’s who they’re hauling in—because even Ottawa’s fog machine couldn’t hide the paper trail forever.
They moved to recall Chrystia Freeland herself—the minister who claimed to be “shocked” after her own department had a six-week head start. She’s the centerpiece witness, and rightly so.
On the security front, the Public Safety Minister is slated for an hour in public, followed by an hour with officials, while the national-security reviewers will give their evidence in camera—translation: the part you most want to hear will happen behind closed doors.
Industry voices are on deck too: Seaspan (the transcript garbles it as “C-Span”), Irving Shipbuilding, plus labour and trade heavyweights—the BC Ferries & Marine Workers’ Union, BC Building Trades, the BC Federation of Labour, the Shipyard General Workers Federation, and the Canadian steel producers—the people who can say, under oath, exactly what Ottawa knew and when the alarm bells rang.
They even tacked on Ontario shipyards via a “friendly amendment”—because apparently no one thought to ask central Canada’s yards until the story blew up.
And then the hedge: Liberals worked the amendments to pare back which ministers would face the lights—especially Revenue and Labour—prompting Conservatives to call the move “intolerable.” In other words, invite the easy witnesses, bury the consequential ones. The fight over those two remained live at that point.
So yes, the committee will finally hear from the people who matter—Freeland, Public Safety, shipyards, unions, steel. But notice the choreography: showcase the safe bits in public, tuck the sensitive parts out of view, and keep chipping away at the ministerial witness list. That’s not transparency; that’s stage management with a security badge.
Strip away the talking points and what remains are questions no serious government would duck. When did the minister learn the contract was going to China? What did her office tell the PMO and when? Why did a federal loan—the leverage Ottawa actually controls—carry zero requirement to build any of it here? And why are the documents that might answer those questions buried under redactions thick enough to pave a road?
Canadians are not children. They understand that ferries are essential and that delays are costly. They also understand something else: when a government runs on Canada first and then cheers from the dock as the jobs steam away, that’s not “arm’s-length.” That’s arm’s-length accountability—which is to say, none. Until the emails are unredacted and Chrystia Freeland answers the timeline under oath, the government’s position amounts to this: trust us, the money’s independent, the decisions were someone else’s, and the facts you’re not allowed to see fully vindicate us. Sure. And the check is in the mail.