Economy
Oil prices fall under pressure as global supply surges

This article supplied by Troy Media.
OPEC output, weak demand and global politics are flooding the market. Experts warn an oil supply glut could hit by 2026
Global oil markets are bracing for a long-term downturn, driven by rising supply, softening demand and mounting economic headwinds.
Brent crude closed Friday at US$66.68 per barrel, down 76 cents or 1.1 per cent. West Texas Intermediate dropped 89 cents to US$62.68, a 1.4
per cent decline. While markets initially hoped an interest rate cut by the U.S. Federal Reserve might boost consumption, oversupply concerns have taken the wheel.
The International Energy Agency now projects a market surplus of 3.3 million barrels per day (bpd) by 2026 if current policies remain in place. Global supply is expected to rise by 2.7 million bpd in 2025 and another 2.1 million in 2026, while demand will grow by just 700,000 bpd annually.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration echoes the concern. Its latest ShortTerm Energy Outlook forecasts global petroleum and other liquid fuels production to average 105.5 million bpd in 2025, climbing to 106.6 million bpd in 2026. Consumption will lag at 103.8 million and 105.1 million bpd, respectively.
Adding to the unease, U.S. distillate stockpiles—diesel, jet fuel and other products held in storage— unexpectedly rose by four million barrels,
suggesting that more fuel is going unused and demand is starting to stall.
Beyond market fundamentals, some of the bearish pressure is also political. OPEC, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is increasing production—partly shielded by U.S. President Donald Trump’s push for lower domestic fuel prices, a priority that influences how much pressure Washington applies to oil-producing nations.
The White House has made clear it wants energy affordability, giving oil producers the political cover to keep pumping without fear of retaliation.
Geopolitical dynamics are compounding the supply picture. A recent thaw in U.S.–China relations reduced the likelihood of secondary sanctions over Chinese imports of Russian crude. Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping are expected to meet at the upcoming Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit at the end of October.
Markets took comfort in Trump’s silence on Chinese oil purchases, seeing it as a signal that confrontation is off the table, at least for now.
India continues to buy Russian oil, and the European Union’s latest sanctions package lacks the strength to provoke a firmer U.S. response. Together, these factors are helping keep Russian barrels in global circulation.
Elsewhere, Iraq appears close to resuming crude exports from its Kurdistan region to Turkey, adding yet another stream of supply to an already saturated market.
On top of all this, the upcoming refinery turnaround season—a routine drop in crude demand as refineries shut down for maintenance—will temporarily reduce consumption even further.
In short, all the major levers are pulling in the same direction: lower prices.
And while that may seem like good news for consumers, the ripple effects are far more serious. Canadians may welcome cheaper gas in the near term, but the implications go far beyond the pump.
A prolonged downturn could hit investment in Alberta’s oil sands, Newfoundland and Labrador’s offshore sector, and Saskatchewan’s oil-producing regions—each of them key drivers of provincial revenue and the Canadian economy. Lower prices mean reduced royalties, which fund everything from health care to infrastructure.
Non-renewable resource revenues—primarily from oil and gas—remain a significant source of income for these provinces. In Alberta, they are forecast to account for roughly 21.5 per cent of total government revenue in 2025–26. In Newfoundland and Labrador, oil royalties alone are projected to contribute about 15 per cent of the province’s revenue. Even in Saskatchewan, where potash and uranium also play a role, oil and gas revenues make up a substantial share of the 12.8 per cent of income tied to non-renewable resources.
These figures underscore just how exposed provincial finances remain to global oil price movements.
That pullback in investment could also slow hiring and capital spending, with ripple effects across energy-dependent regions. Pension funds and institutional investors with heavy exposure to oil and gas may feel the sting as well.
At the national level, the consequences could be far-reaching. Canada’s oil and gas extraction sector alone accounts for about 3.2 per cent of GDP, according to the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers. Broader estimates that include investment, supply chains and related industries place the sector’s total contribution at around 6.4 per cent, based on previous Canadian Energy Centre analysis.
Lower crude prices tend to weaken the Canadian dollar, slow investment in big projects, and cut into export earnings. That can drag down GDP growth, shrink government revenues, and affect job markets even outside the oil patch.
In a country where energy exports still drive much of the economy, a prolonged slump could have wide-reaching fiscal and economic consequences.
Investors, governments and energy workers alike should brace for impact—the oil market isn’t just cooling, it’s being flooded.
Toronto-based Rashid Husain Syed is a highly regarded analyst specializing in energy and politics, particularly in the Middle East. In addition to his contributions to local and international newspapers, Rashid frequently lends his expertise as a speaker at global conferences. Organizations such as the Department of Energy in Washington and the International Energy Agency in Paris have sought his insights on global energy matters.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country
Alberta
Federal budget: It’s not easy being green

From Resource Works
Canada’s climate rethink signals shift from green idealism to pragmatic prosperity.
Bill Gates raised some eyebrows last week – and probably the blood pressure of climate activists – when he published a memo calling for a “strategic pivot” on climate change.
In his memo, the Microsoft founder, whose philanthropy and impact investments have focused heavily on fighting climate change, argues that, while global warming is still a long-term threat to humanity, it’s not the only one.
There are other, more urgent challenges, like poverty and disease, that also need attention, he argues, and that the solution to climate change is technology and innovation, not unaffordable and unachievable near-term net zero policies.
“Unfortunately, the doomsday outlook is causing much of the climate community to focus too much on near-term emissions goals, and it’s diverting resources from the most effective things we should be doing to improve life in a warming world,” he writes.
Gates’ memo is timely, given that world leaders are currently gathered in Brazil for the COP30 climate summit. Canada may not be the only country reconsidering things like energy policy and near-term net zero targets, if only because they are unrealistic and unaffordable.
It could give some cover for Canadian COP30 delegates, who will be at Brazil summit at a time when Prime Minister Mark Carney is renegotiating his predecessor’s platinum climate action plan for a silver one – a plan that contains fewer carbon taxes and more fossil fuels.
It is telling that Carney is not at COP30 this week, but rather holding a summit with Alberta Premier Danielle Smith.
The federal budget handed down last week contains kernels of the Carney government’s new Climate Competitiveness Strategy. It places greater emphasis on industrial strategy, investment, energy and resource development, including critical minerals mining and LNG.
Despite his Davos credentials, Carney is clearly alive to the fact it’s a different ballgame now. Canada cannot afford a hyper-focus on net zero and the green economy. It’s going to need some high octane fuel – oil, natural gas and mining – to prime Canada’s stuttering economic engine.
The prosperity promised from the green economy has not quite lived up to its billing, as a recent Fraser Institute study reveals.
Spending and tax incentives totaling $150 billion over a decade by Ottawa, B.C, Ontario, Alberta and Quebec created a meagre 68,000 jobs, the report found.
“It’s simply not big enough to make a huge difference to the overall performance of the economy,” said Jock Finlayson, chief economist for the Independent Contractors and Business Association and co-author of the report.
“If they want to turn around what I would describe as a moribund Canadian economy…they’re not going to be successful if they focus on these clean, green industries because they’re just not big enough.”
There are tentative moves in the federal budget and Climate Competitiveness Strategy to recalibrate Canada’s climate action policies, though the strategy is still very much in draft form.
Carney’s budget acknowledges that the world has changed, thanks to deglobalization and trade strife with the U.S.
“Industrial policy, once seen as secondary to market forces, is returning to the forefront,” the budget states.
Last week’s budget signals a shift from regulations towards more investment-based measures.
These measures aim to “catalyse” $500 billion in investment over five years through “strengthened industrial carbon pricing, a streamlined regulatory environment and aggressive tax incentives.”
There is, as-yet, no commitment to improve the investment landscape for Alberta’s oil industry with the three reforms that Alberta has called for: scrapping Bill C-69, a looming oil and gas emissions cap and a West Coast oil tanker moratorium, which is needed if Alberta is to get a new oil pipeline to the West Coast.
“I do think, if the Carney government is serious about Canada’s role, potentially, as an global energy superpower, and trying to increase our exports of all types of energy to offshore markets, they’re going to have to revisit those three policy files,” Finlayson said.
Heather Exner-Pirot, director of energy, natural resources and environment at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, said she thinks the emissions cap at least will be scrapped.
“The markets don’t lie,” she said, pointing to a post-budget boost to major Canadian energy stocks. “The energy index got a boost. The markets liked it. I don’t think the markets think there is going to be an emissions cap.”
Some key measures in the budget for unlocking investments in energy, mining and decarbonization include:
- incentives to leverage $1 trillion in investment over the next five years in nuclear and wind power, energy storage and grid infrastructure;
- an expansion of critical minerals eligible for a 30% clean technology manufacturing investment tax credit;
- $2 billion over five years to accelerate critical mineral production;
- tax credits for turquoise hydrogen (i.e. hydrogen made from natural gas through methane pyrolysis); and
- an extension of an investment tax credit for carbon capture utilization and storage through to 2035.
As for carbon taxes, the budget promises “strengthened industrial carbon pricing.”
This might suggest the government’s plan is to simply simply shift the burden for carbon pricing from the consumer entirely onto industry. If that’s the case, it could put Canadian resource industries at a disadvantage.
“How do we keep pushing up the carbon price — which means the price of energy — for these industries at a time when the United States has no carbon pricing at all?” Finlayson wonders.
Overall, Carney does seem to be moving in the right direction in terms of realigning Canada’s energy and climate policies.
“I think this version of a Liberal government is going to be more focused on investment and competitiveness and less focused around the virtue-signaling on climate change, even though Carney personally has a reputation as somebody who cares a lot about climate change,” Finlayson said.
“It’s an awkward dance for them. I think they are trying to set out a different direction relative to the Trudeau years, but they’re still trying to hold on to the Trudeau climate narrative.”
Pictured is Mark Carney at COP26 as UN Special Envoy on Climate Action and Finance. He is not at COP30 this week. UNRIC/Miranda Alexander-Webber
Resource Works News
Business
Carney government needs stronger ‘fiscal anchors’ and greater accountability

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Grady Munro
Following the recent release of the Carney government’s first budget, Fitch Ratings (one of the big three global credit rating agencies) issued a warning that the “persistent fiscal expansion” outlined in the budget—characterized by high levels of spending, borrowing and debt accumulation—will erode the health of Canada’s finances and could lead to a downgrade in Canada’s credit rating.
Here’s why this matters. Canada’s credit rating impacts the federal government’s cost of borrowing money. If the government’s rating gets downgraded—meaning Canadian federal debt is viewed as an increasingly risky investment due to fiscal mismanagement—it will likely become more expensive for the government to borrow money, which ultimately costs taxpayers.
The cost of borrowing (i.e. the interest paid on government debt) is a significant part of the overall budget. This year, the federal government will spend a projected $55.6 billion on debt interest, which is more than one in every 10 dollars of federal revenue, and more than the government will spend on health-care transfers to the provinces. By 2029/30, interest costs will rise to a projected $76.1 billion or more than one in every eight dollars of revenue. That’s taxpayer money unavailable for programs and services.
Again, if Canada’s credit rating gets downgraded, these costs will grow even larger.
To maintain a good credit rating, the government must prevent the deterioration of its finances. To do this, governments establish and follow “fiscal anchors,” which are fiscal guardrails meant to guide decisions regarding spending, taxes and borrowing.
Effective fiscal anchors ensure governments manage their finances so the debt burden remains sustainable for future generations. Anchors should be easily understood and broadly applied so that government cannot get creative with its accounting to only technically abide by the rule, but still give the government the flexibility to respond to changing circumstances. For example, a commonly-used rule by many countries (including Canada in the past) is a ceiling/target for debt as a share of the economy.
The Carney government’s budget establishes two new fiscal anchors: balancing the federal operating budget (which includes spending on day-to-day operations such as government employee compensation) by 2028/29, and maintaining a declining deficit-to-GDP ratio over the years to come, which means gradually reducing the size of the deficit relative to the economy. Unfortunately, these anchors will fail to keep federal finances from deteriorating.
For instance, the government’s plan to balance the “operating budget” is an example of creative accounting that won’t stop the government from borrowing money each year. Simply put, the government plans to split spending into two categories: “operating spending” and “capital investment” —which includes any spending or tax expenditures (e.g. credits and deductions) that relates to the production of an asset (e.g. machinery and equipment)—and will only balance operating spending against revenues. As a result, when the government balances its operating budget in 2028/29, it will still incur a projected deficit of $57.9 billion when spending on capital is included.
Similarly, the government’s plan to reduce the size of the annual deficit relative to the economy each year does little to prevent debt accumulation. This year’s deficit is expected to equal 2.5 per cent of the overall economy—which, since 2000, is the largest deficit (as a share of the economy) outside of those run during the 2008/09 financial crisis and the pandemic. By measuring its progress off of this inflated baseline, the government will technically abide by its anchor even as it runs relatively large deficits each and every year.
Moreover, according to the budget, total federal debt will grow faster than the economy, rising from a projected 73.9 per cent of GDP in 2025/26 to 79.0 per cent by 2029/30, reaching a staggering $2.9 trillion that year. Simply put, even the government’s own fiscal plan shows that its fiscal anchors are unable to prevent an unsustainable rise in government debt. And that’s assuming the government can even stick to these anchors—which, according to a new report by the Parliamentary Budget Officer, is highly unlikely.
Unfortunately, a federal government that can’t stick to its own fiscal anchors is nothing new. The Trudeau government made a habit of abandoning its fiscal anchors whenever the going got tough. Indeed, Fitch Ratings highlighted this poor track record as yet another reason to expect federal finances to continue deteriorating, and why a credit downgrade may be on the horizon. Again, should that happen, Canadian taxpayers will pay the price.
Much is riding on the Carney government’s ability to restore Canada’s credibility as a responsible fiscal manager. To do this, it must implement stronger fiscal rules than those presented in the budget, and remain accountable to those rules even when it’s challenging.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days agoRichmond Mayor Warns Property Owners That The Cowichan Case Puts Their Titles At Risk
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoSluggish homebuilding will have far-reaching effects on Canada’s economy
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMark Carney Seeks to Replace Fiscal Watchdog with Loyal Lapdog
-
 Business2 days ago
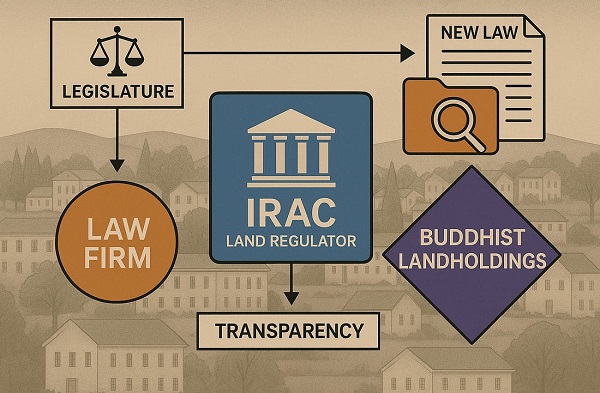
Business2 days agoP.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
-
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoMajor new studies link COVID shots to kidney disease, respiratory problems
-

 Addictions15 hours ago
Addictions15 hours agoCanadian gov’t not stopping drug injection sites from being set up near schools, daycares
-

 Business15 hours ago
Business15 hours agoParliamentary Budget Officer begs Carney to cut back on spending
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoBondi and Patel deliver explosive “Clinton Corruption Files” to Congress










