International
New U.S. Intelligence: ‘Endemic’ CCP Corruption, Organized Crime, and Graft Tied to Xi’s Network

WASHINGTON — An explosive new disclosure by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence has pulled back the curtain on endemic corruption in the Chinese Communist Party—reaching the top echelons of power, including President Xi Jinping. Released as an unclassified document and drafted by ODNI’s National Intelligence Council, the report explains how graft, bribery, and political favoritism are an essential feature of CCP power structures, festering for decades, involving organized crime and factional struggles—even under Xi’s trademark anti-corruption campaign.
By publicly releasing these findings, U.S. officials are signaling a readiness to reveal what intelligence agencies have long documented but kept classified. Sources with knowledge of the matter indicate Washington appears increasingly willing to trace corruption and international money laundering directly to the Politburo, citing explosive cases such as a Western intelligence investigation that allegedly linked Xi Jinping’s cousin, Ming Chai, to a casino money-laundering junket in Australia.
In an era of sharply escalating tensions—spanning trade, technology, and territorial disputes—Washington’s move seems aimed at exposing internal vulnerabilities in Xi’s regime while also undermining the offshore money laundering and strategic corruption Beijing is believed to use for influence-building across the Western Hemisphere and the South Pacific. It offers American citizens a transparent glimpse into what the U.S. government views as key fault lines within China’s ruling party, as the world’s two most powerful states appear set on a collision course—driven in no small part by Xi’s urgent push to subsume Taiwan.
In a striking detail, the ODNI cites journalistic research, initially blocked by Bloomberg before eventually being reported by The New York Times in 2012, that tied immense family wealth to both then-Premier Wen Jiabao and the incoming President Xi. The Times reported that Wen’s immediate family controlled at least $2.7 billion in assets, while Xi’s siblings, nieces, and nephews collectively held more than $1 billion in business and real-estate holdings. Beijing promptly tightened its censorship apparatus in the report’s aftermath, curtailing foreign news outlets that delved into elite wealth.
“Xi may have urged family members to divest holdings as he came into power. However, industry research provides evidence that, as of 2024, Xi’s family retains millions in business interests and financial investments,” the ODNI report says. It adds that corruption cases reaching the highest levels—relying on open-source rather than classified U.S. intelligence—“shows corruption cases within the CCP Central Committee span leading officials overseeing a range of portfolios and projects.”
Among the examples cited is Zhang Wei, a Chinese businessman arrested in 2020 for “organizing, leading, and participating in organized crime; illegal detention; and illegal possession of firearms and ammunition,” before being found guilty the following year of illegally absorbing public deposits.
Another high-profile instance is Chen Gang, who was accused in 2019 of accepting over $18 million in bribes—some tied to his oversight of 2008 Beijing Olympics construction projects. More recently, in April 2024, Yao Qian, Director of the China Securities Regulatory Commission was investigated for “serious violations of discipline and law,” possibly connected to China’s Central Bank Digital Currency initiative.
The fact that Xi—who carefully cultivates an image of austere probity—has family members reportedly retaining millions of dollars in investments remains a deeply sensitive topic for Beijing. In highlighting these details, U.S. intelligence appears to be drawing attention to a broader governance model that incentivizes graft, even as Xi’s “tigers and flies” campaign claims to have taken down nearly five million officials since 2012.
The ODNI’s document underscores how Xi’s crackdown is not merely a legal imperative but also a party-directed instrument for punishing “political indiscipline and ideological impurity.”
“Although Xi has not used the campaign primarily to target his political rivals, a drive to eliminate competing power centers factored significantly into decisions made in the initial phases of the campaign. Early in Xi’s tenure, senior officials with ties to his predecessors were targeted with investigations and arrests,” the report says. “More significantly, political connections to high-ranking officials have not protected officials from prosecution, including those with close personal ties to Xi himself; the anti-corruption campaign has purged top officials considered loyal to Xi and who had risen under his patronage.”
Significantly, the ODNI highlights persistent corruption in the People’s Liberation Army—and a surge of high-level purges driven by Xi’s effort to consolidate control before the PLA’s target of full combat readiness by 2027, with Taiwan looming as the central focus. “In 2024, Xi stressed during a speech to military commanders that ‘the barrels of guns must always be in the hands of those who are loyal and dependable to the Party,’” the report states, adding that Xi’s emphasis on PLA loyalty “may also reflect concerns that corrupt practices will prevent the military from acquiring the capabilities and readiness he has directed it to achieve by 2027, in preparation for a potential conflict over Taiwan.”
The ODNI’s broader assessment emphasizes that corruption is not merely an occasional lapse but a systemic challenge to China’s governance, facilitated by centralized CCP power, a Party-centric concept of law, and minimal transparency. Studies suggest that corruption has persisted in China since its founding, intensified by rapid economic growth in the 1980s and 1990s, and has been so pervasive since 2000 that it threatens the very legitimacy of the regime.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Health
Why the January 2026 Vaccine Policy Reset Was Necessary, Not Radical
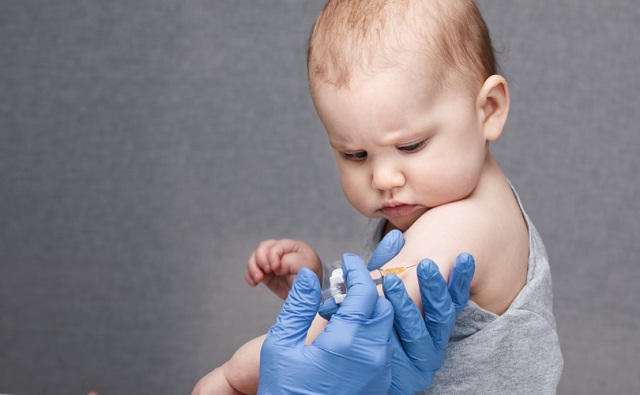
CDC Cuts Total Doses in Alignment with the rest of most of Western Civilization. I suspect we found evidence within CDC supporting.
The CDC’s January 2026 childhood vaccine schedule realignment is not a retreat from science—it is its restoration. By aligning the U.S. with international norms, reclassifying low-benefit vaccines, and preserving universal access, the policy reasserts informed consent, parsimony, and scientific integrity as central to public health. This editorial evaluates the evidence, clarifies common misinterpretations, and outlines the stakes of institutional credibility in the era of collapsing trust.
Ending the Era of Maximalism
In January 2026, the CDC issued a long-overdue correction to the American childhood vaccine schedule. Despite headlines framing this move as a rollback or retreat, not a single vaccine was removed from access or coverage. The change was not reductive—it was clarifying. It replaced one-size-fits-all mandates with a proportional, transparent structure based on international norms, current evidence, and a sobering admission of what science does not yet know. This was not a political maneuver. It was a governance correction, rooted in the principles of informed consent and institutional legitimacy.
The real story is not what was removed, but what was realigned—and why. The revised architecture reflects a basic truth: trust cannot be coerced. It must be earned. That is the starting point of science. And the endpoint of policy.
The CDC Recognizes Its Schedule as a Coercive Instrument
For decades, the CDC’s “routine recommendation” has operated less as guidance and more as soft mandate. Once a vaccine was recommended for all children, it cascaded through state school-entry requirements, insurance policies, quality metric scoring, and pediatrician compliance programs. Families who opted out often faced dismissal from care. Physicians faced insurer incentives tied to vaccination quotas. In this ecosystem, choice was technically permitted—but penalized.
The CDC’s own assessment acknowledges this explicitly: “Instead of implementing vaccination mandates, most peer nations maintain high childhood vaccination rates through public trust and education” (CDC, 2026, p.3). The updated policy aims to dismantle this coercive scaffolding—not by withdrawing vaccines, but by restoring clarity to what is essential, what is conditional, and what is contextual.
Comparative Overreach: America as an Outlier
The United States was not just a global leader in pediatric vaccination. It was a statistical outlier. According to the CDC’s comparative review (2026, Table 2), the U.S. schedule in 2024 recommended vaccines against 17 diseases, requiring 84 to 88 total doses delivered across 57 to 71 injections. By contrast:
- Denmark covers 10 diseases with 30 doses and only 11 injections.
- UK uses fewer doses but retains near-universal MMR uptake.
- Canada varies by province but aligns closely with European practice.
Importantly, many peer nations refrain from recommending routine use of hepatitis A, influenza, meningococcal B, and rotavirus for all children. These are not poor or negligent countries. They are scientifically robust, and they achieve high uptake by preserving credibility, not enforcing compliance.
The report introduces the ethical principle of clinical equipoise—the acknowledgment of uncertainty in the face of professional disagreement. When peer nations with equivalent disease burdens and health infrastructures diverge in recommendations, it signals unresolved evidence gaps, not ignorance.
Trust Collapse and Its Operational Consequences
Trust in U.S. health authorities fell precipitously between 2020 and 2024—from 71.5% to 40.1% (CDC, p.3). This collapse had measurable consequences. Uptake of the MMR vaccine, one of the most effective vaccines in the consensus schedule, dropped from 95.2% to 92.7% nationally. Sixteen states fell below the 90% threshold, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
Indeed, in 2025, the U.S. experienced 49 measles outbreaks—88% of the 2,065 reported cases were outbreak-associated (CDC, 2026). This wasn’t due to vaccine rejection. It was due to trust rejection. The report directly links trust erosion to coercive COVID-era policies, including mask mandates, school closures, disregard for natural immunity, and overstated claims about sterilizing immunity. The CDC writes, “The distrust of public health agencies during the pandemic has spilled over to other recommendations, including those with respect to vaccines” (p.3).
This trust decay wasn’t isolated. Countries like Denmark explicitly warned against adding low-benefit vaccines to their schedules, citing risks of degrading public confidence. Their prediction came true here. The U.S. attempted to do more—and got less.
Schedule-Level Science: Gaps Finally Acknowledged
The most important admission in the report may be this: “The effects of the overall schedule have never been fully evaluated” (CDC, p.12). That sentence should haunt anyone who defends the status quo. Despite decades of schedule expansion, there has been no comprehensive evaluation of the long-term safety, synergy, or cumulative immunologic impact of the entire pediatric vaccine regimen.
While individual vaccines like MMR, Hib, and IPV have robust pre-licensure data, many others were approved without large-scale placebo-controlled trials. Post-marketing systems such as VAERS, VSD, and BEST have identified acute risks—e.g., intussusception with rotavirus, febrile seizures with MMRV, myocarditis with mRNA vaccines—but are underpowered for delayed or systemic effects.
A 2023 VSD study found a dose-dependent association between cumulative aluminum exposure from vaccines and persistent asthma (HR = 2.0) (Daley et al., Academic Pediatrics, 2023). This is not conclusive proof of harm—but it is definitive proof of the need to study schedule-level interactions.
The CDC now calls for exactly that: randomized timing trials, long-term cohort studies comparing health outcomes across exposure strata, and formal evaluation of interaction effects, adjuvant loads, and timing differentials.
A New Ethical Architecture
The revised schedule distinguishes three recommendation types:
1. Recommended for all children — reserved for vaccines with demonstrated benefit across the population and international consensus.
2. High-risk group recommendations — for children with defined medical or exposure risks.
3. Shared clinical decision-making — for vaccines where the population-level benefit is uncertain, or where individual risk–benefit may vary.
This framework already exists in CDC language, but it had been underutilized and obscured by the dominance of routine recommendations. The new policy makes it operational.
Crucially, no vaccines are removed from coverage. The document reiterates: “All immunizations recommended by the CDC at the end of 2025—and covered by insurance at that time—should remain covered without cost sharing” (CDC, p.3). Denmark, the UK, and Switzerland use similar stratified systems. The U.S. has now caught up—not by doing less, but by doing what works.
HPV One-Dose: An Evidence-Based Pivot
The decision to shift from two doses of HPV vaccine to one is a model for evidence-responsive policy. The CDC cites multiple studies demonstrating non-inferiority of a single dose:
– Kreimer et al., NEJM 2025
– Watson-Jones et al., Lancet Global Health 2025
– Basu et al., Lancet Oncology 2021
Peer nations including the UK, Ireland, Australia, and Canada had already adopted this strategy. One dose achieves near-identical protection against vaccine-targeted HPVs with lower burden and fewer adverse events. The CDC’s alignment here is not a retreat—it’s a data-driven upgrade.
Refined “Recommended for All” List
The CDC now limits routine universal recommendations to vaccines with:
– Strong international consensus
– High demonstrated public health value
– Well-characterized safety and efficacy profiles.
These are:
– Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
– Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP/Tdap)
– Polio (IPV) – Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib)
– Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV)
– Human papillomavirus (HPV), now reduced to a single-dose schedule
– Varicella (chickenpox), retained due to U.S.-specific epidemiology
Many parents have questions about the efficacy of the measles and mumps portions of the MMR given that asymptomatic transmission of measles is an established but little-discussed fact, and before COVID-19, mumps outbreaks in fully vaccinated schools in the US was well-documented.
What changed: HPV was reduced from 2–3 doses to 1. Several vaccines previously listed as universal are now reclassified. The new universal list more closely mirrors countries like Denmark, the UK, and Ireland.
Reclassification of Non-Consensus Vaccines
Vaccines such as:
– Hepatitis A
– Hepatitis B (birth dose only if mother is HBsAg-negative)
– Rotavirus
– Influenza
– COVID-19
– Meningococcal B and ACWY
– RSV monoclonal antibody (not a vaccine)
have all been moved to either:
– High-risk group recommendations (e.g., Hep A for travelers, Hep B for infants of positive/unknown mothers)
– or Shared clinical decision-making pathways
This model mirrors European governance practices, where vaccines with uncertain population-wide benefit are discussed individually between provider and parent/guardian.
What changed: These vaccines are no longer recommended for universal administration but remain fully covered and available to all families through Medicaid, CHIP, VFC, and private insurance.
Policy Emphasis on Schedule-Level Science
For the first time, the CDC acknowledges:
– The full schedule has never been rigorously studied for cumulative, synergistic, or long-term effects
– Many vaccines were approved without randomized placebo-controlled trials in children
– Post-licensure surveillance (e.g., VAERS, VSD) is underpowered to detect long-latency effects or rare but serious chronic sequelae
The CDC now explicitly calls for:
– Randomized trials using timing-based designs
– Long-term cohort studies comparing vaccinated vs unvaccinated children
– Safety studies on combined vaccine administration, adjuvants, and spacing.
This is a seachange: Scientific uncertainty is now acknowledged and embedded into the policy framework, triggering a new research mandate.
Elimination of Implicit Coercion via Schedule
While the policy does not change state-level school mandates, it removes the federal “routine” label from lower-priority vaccines, reducing pressure on providers to dismiss non-compliant families or tie insurer bonuses to rigid adherence.
In its place: a structured, choice-respecting pathway that centers parental informed consent.
What changed: The policy restores consent as a governing principle, removes schedule inflation, and distinguishes between access and recommendation.
This is a systemic reform, not a minor tweak. The policy shift restores proportionality, science-based prioritization, and institutional humility—while safeguarding coverage and access. It is a reassertion of legitimacy in the aftermath of a trust crisis.
What the Policy Rejects
This policy formally rejects several assumptions that had ossified into doctrine:
– That more vaccines necessarily equal better health.
– That mandates are required to ensure compliance.
– That high-volume schedules are scientifically complete.
– That dissent is misinformation.
– That informed consent is a formality, not a right.
The CDC explicitly names coercion as a failed tool and calls for its replacement with personalized, risk-aligned care.
What the Policy Preserves and Strengthens
This is not a deregulation agenda. It is a realignment. The policy preserves:
– Universal access to all covered vaccines.
– Full coverage under Medicaid, CHIP, and VFC.
– Trust-based compliance mechanisms.
– Ethical clarity: recommendations reflect both evidence and respect for autonomy.
– Institutional epistemic humility: public health must now justify, not presume.
The result? Less friction, more uptake—of the right vaccines, in the right populations, for the right reasons.
Anticipating and Answering the Critics
No, the liability protections were not removed. This policy does not increase vaccine risk—it increases institutional honesty.
No, measles will not surge because of this schedule. MMR remains fully recommended. The drop in uptake happened under maximalist policy.
No, international comparison is not cherry-picking. It is the standard for identifying clinical equipoise. Denmark, Germany, Ireland, and Switzerland offer leaner schedules, fewer mandates, and stronger vaccine trust.
Those who call this “anti-science” misunderstand science. This is science doing what it must: confronting uncertainty, not denying it.
The Schedule Is the Signal
The CDC’s January 2026 reform is not the dismantling of public health. It is its restoration. Trust cannot be coerced. Compliance must be earned. And scientific legitimacy must be updated to reflect both what we know—and what we still don’t.
The vaccine schedule is not just a list. It is a social contract. And for the first time in decades, it has been revised to reflect mutual respect, rather than managerial force.
The signal has changed. And for the health of children and the credibility of science, that is exactly what was needed.
Thanks for reading Popular Rationalism! This post is public so feel free to share it.
International
Watch your a** Petro. Trump threatens Colombian President

President Trump delivered one of his bluntest warnings yet to Colombian President Gustavo Petro during a Saturday press conference, brushing aside Petro’s claim that he had no concerns about his own safety following the U.S. military operation that captured Venezuelan strongman Nicolás Maduro. Asked directly about Petro’s remarks, Trump pointed to Colombia’s role in the global cocaine trade and made clear he was not backing off earlier threats. Petro, Trump said, presides over cocaine production facilities whose product is being funneled into the United States, adding that the Colombian leader “does have to watch his a**.”
The exchange revived tensions that have been simmering since December, when Trump publicly warned Petro to shut down multiple major cocaine labs inside Colombia. At the time, Trump said U.S. authorities had precise intelligence on their locations and openly labeled Petro a “troublemaker,” cautioning him to “watch it.” Since returning to office, Trump has taken a far more confrontational posture toward leftist leaders in the hemisphere, and Petro — a self-described Marxist and former guerrilla — has repeatedly found himself in Washington’s crosshairs.
NOW – Trump says Colombian President Gustavo Petro has "to watch his ass" as he's making cocaine and sending it to the U.S. pic.twitter.com/H2ctUOmX9O
— Disclose.tv (@disclosetv) January 3, 2026
Petro’s clashes with the United States extend well beyond rhetoric. He was previously sanctioned by the Treasury Department and had his U.S. visa revoked after urging American service members to defy Trump’s orders and join what he described as a multinational force to “free Palestine.” He has also triggered diplomatic flare-ups over deportation flights, branded Trump an “obstacle to democracy,” and drew widespread condemnation last October after suggesting humanity should “get rid of Trump,” punctuating the comment with a finger snap during a televised interview.
Those remarks now hang over a far more consequential moment in U.S.–Latin American relations. Trump’s comments came in the immediate aftermath of the high-risk operation that resulted in Maduro’s capture and removal from Venezuela — a move the president hailed as a “brilliant operation.” Carried out under the banner of Operation Absolute Resolve, the joint military and law enforcement mission ended with Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores, flown to the United States without the loss of American personnel or equipment. The takedown marked the most aggressive assertion of U.S. power in the region in decades, with administration officials openly framing it as a modern enforcement of the Monroe Doctrine — rechristened by Trump as the “Donroe Doctrine.”
Maduro’s legal exposure is extensive. Indicted in 2020, the longtime socialist ruler has been accused by U.S. prosecutors of leading the Cartel de los Soles, a transnational cocaine trafficking network. According to the indictment unsealed by Attorney General Pam Bondi, Maduro’s regime worked hand-in-glove with Colombian insurgent groups including the FARC and ELN, as well as Mexican cartels such as Sinaloa and Los Zetas, to move enormous quantities of cocaine into the United States. He and Flores now face charges ranging from narco-terrorism and cocaine importation conspiracy to weapons offenses involving machine guns and destructive devices.
Petro has tried, cautiously, to put distance between himself and the fallen Venezuelan dictator. In late 2025, he referred to Maduro as a dictator for the first time, but stopped short of acknowledging the narco-trafficking allegations that have followed Caracas for years. Even after Maduro’s arrest, Petro has continued to dismiss U.S. accusations as a manufactured “narrative,” despite a trail of indictments and evidence stretching back more than half a decade.
For Trump, the message Saturday was unmistakable. The Maduro operation was not a one-off, and public defiance from regional leaders will be met with pressure, exposure, and consequences. Petro may insist he has nothing to worry about — but Trump made clear he disagrees, and he is no longer content to issue quiet warnings.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoIs Canada still worth the sacrifice for immigrants?
-

 International11 hours ago
International11 hours agoWatch your a** Petro. Trump threatens Colombian President
-

 Environment22 hours ago
Environment22 hours agoLeft-wing terrorists sabotage German power plant, causing massive power outage
-

 Alberta22 hours ago
Alberta22 hours agoTrump’s Venezuela Geopolitical Earthquake Shakes up Canada’s Plans as a “Net Zero” Energy Superpower
-

 Energy21 hours ago
Energy21 hours agoTrump’s Venezuela Move: A $17 Trillion Reset of Global Geopolitics and a Pivotal Shift in US Energy Strategy
-

 Energy21 hours ago
Energy21 hours agoThe global math: Why exporting Canadian energy is a climate win
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days ago“History in the making”: Venezuelans in Florida flood streets after Maduro’s capture
-

 Daily Caller21 hours ago
Daily Caller21 hours agoMinnesota Governor resigns from re-election campaign as massive government frauds revealed















