Frontier Centre for Public Policy
ECO Extremism under reported in Canada
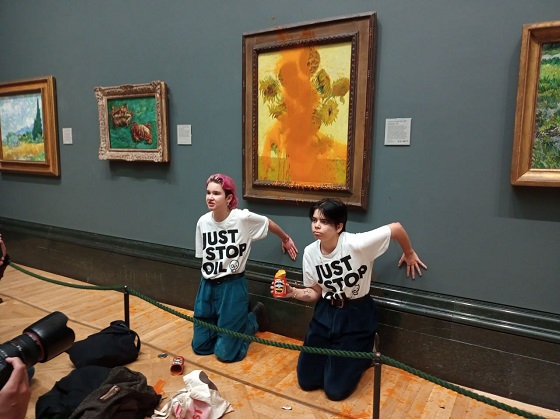
From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
How many remember that shortly after the federal government introduced emergency legislation against convoy protesters there was a real terrorist attack on a Coastal GasLink pipeline worksite in British Columbia?
Ottawa and Canadian security agencies are ignoring a threat posed by eco-extremists motivated by self-righteous climate change alarmism.
How many remember that shortly after the federal government introduced emergency legislation against convoy protesters there was a real terrorist attack on a Coastal GasLink pipeline worksite in British Columbia?
About 20 masked assailants wielding axes entered a pipeline worksite and intimidated Coastal GasLink workers and caused millions of dollars of damage to equipment and vehicles.
While politicians and mainstream media were fixated on bouncy castles and hot tubs, armed fanatics were intimidating human beings with weapons and destroying energy infrastructure.
There was bare mention of it in the media. Politicians made cursory mention of it on social media. Unlike the convoy protests, there were no in-depth investigative pieces immediately after the eco-terrorist attacks against Costal GasLink.
Eventually some media picked up on this terror attack, but then downplayed it.
CBC’s Fifth Estate months later aired a program that attempted to disparage an RCMP unit meant to investigate extremist attacks on energy sector infrastructure. In a piece of over 40 minutes, less than a minute was devoted to exploring the February 2022 terror attack.
The CBC wrote more about the attack and did identify the culprits as anarchists but did not explore their ideological motivations. It was almost like they were just anarchists bent on destruction without a coherent ideology.
Perhaps if they would do a deep dive, they would discover that the anarchists believing they are helping an Indigenous resurgence have been raised on a diet of unscientific climate change alarmism.
I recently compiled research for a Frontier Centre study that looked at this looming eco-extremist threat.
Besides the Coastal GasLink attack, there are extremist groups like Just Stop Oil and Extinction Rebellion (in Canada). Traffic disruptions caused by Just Stop Oil have already led to bodily harm and unnecessary deaths in the UK where traffic mayhem ensued over a stunt on a bridge.
Canada has a serious blind spot when it comes to extremism associated with the far left. CSIS and Public Safety Canada are endlessly fixated on extremism associated loosely with the right, like Incels or anyone concerned about forced injections via vaccine mandates.
In Canada, the threat comes from various “Indigeno-anarchists” who believe they are supporting Indigenous people even as they attack energy projects that help First Nation communities. I discovered these extremists teach and recruit at our universities. Many professors are activists who normalize terrorism against the energy sector. Many were involved in the 2019-2020 Wet’suwet’en rail blockades that opposed Coastal GasLink.
Winnipeg activists were certainly involved. During the Wet’suwet’en blockades, they engaged in five major actions in Manitoba, from a demonstration outside an RCMP station to an action where “Indigenous warriors” blocked CN and CP rail tracks for several hours.
Calling themselves anarchists, they engaged in acts that could cause bodily harm and affect people’s ability to travel on passenger trains. Here is a document confirming they intended to commit “railroad sabotage.” Anarchists also make open mention of acts of sabotage and damage to drill sites associated with Coastal GasLink.
Central to the problem is problematic and torqued up climate change rhetoric that is causing unnecessary fear and anxiety within the public and is radicalizing people. If you believe the “earth is on fire” – which is a false belief held by many activists – some become radicalized to commit damage property and threaten lives.
Manitobans and Canadians must address the looming eco-terrorist threat before it’s too late.
Joseph Quesnel is a Senior Research Fellow with the Frontier Centre for Public Policy.
Censorship Industrial Complex
Ottawa’s New Hate Law Goes Too Far

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Lee Harding
Ottawa says Bill C-9 fights hate. Critics say it turns ordinary disagreement into a potential crime.
Discriminatory hate is not a good thing. Neither, however, is the latest bill by the federal Liberal government meant to fight it. Civil liberties organizations and conservative commentators warn that Bill C-9 could do more to chill legitimate speech than curb actual hate.
Bill C-9 creates a new offence allowing up to life imprisonment for acts motivated by hatred against identifiable groups. It also creates new crimes for intimidation or obstruction near places of worship or community buildings used by identifiable groups. The bill adds a new hate propaganda offence for displaying terrorism or hate symbols.
The Canadian Civil Liberties Association (CCLA) warns the legislation “risks criminalizing some forms of protected speech and peaceful protest—two cornerstones of a free and democratic society—around tens of thousands of community gathering spaces in Canada.” The CCLA sees no need to add to existing hate laws.
Bill C-9 also removes the requirement that the Attorney General consent to lay charges for existing hate propaganda offences. The Canadian Constitution Foundation (CCF) calls this a major flaw, noting it removes “an important safeguard for freedom of expression that has been part of Canada’s law for decades.” Without that safeguard, decisions to prosecute may depend more on local political pressures and less on consistent national standards.
Strange as it sounds, hatred just will not be what it used to be if this legislation passes. The core problem begins with how the bill redefines the term itself.
Previously, the Supreme Court of Canada said hatred requires “extreme manifestations” of detestation or vilification that involve destruction, abhorrence or portraying groups as subhuman or innately evil. Instead, Bill C-9 defines hatred as “detestation or vilification,” stronger than “disdain or dislike.” That is a notably lower threshold. This shift means that ordinary political disagreement or sharp criticism could now be treated as criminal hatred, putting a wide range of protected expression at real risk.
The bill also punishes a hateful motivation more than the underlying crime. For example, if a criminal conviction prompted a sentence of two years to less than five years, a hateful motivation would add as much as an additional five years of jail time.
On paper, most Canadians may assume they will never be affected by these offences. In practice, the definition of “hate” is already stretched far beyond genuine threats or violence.
Two years ago, the 1 Million March for Children took place across Canada to protest the teaching of transgender concepts to schoolchildren, especially the very young. Although such opposition is a valid position, unions, LGBT advocates and even Newfoundland and Labrador Conservatives adopted the “No Space For Hate” slogan in response to the march. That label now gets applied far beyond real extremism.
Public pressure also shapes how police respond to protests. If citizens with traditional values protest a drag queen story hour near a public library, attendees may demand that police lay charges and accuse officers of implicit hatred if they refuse. The practical result is clear: officers may feel institutional pressure to lay charges to avoid being accused of bias, regardless of whether any genuine threat or harm occurred.
Police, some of whom take part in Pride week or work in stations decorated with rainbow colours in June, may be wary of appearing insensitive or intolerant. There have also been cases where residents involved in home invasion incidents were charged, and courts later determined whether excessive force was used. In a similar way, officers may lay charges first and allow the courts to sort out whether a protest crossed a line. Identity-related considerations are included in many workplace “sensitivity training” programs, and these broader cultural trends may influence how such situations are viewed. In practice, this could mean that protests viewed as ideologically unfashionable face a higher risk of criminal sanction than those aligned with current political priorities.
If a demonstrator is charged and convicted for hate, the Liberal government could present the prosecution as a matter for the justice system rather than political discretion. It may say, “It was never our choice to charge or convict these people. The system is doing its job. We must fight hate everywhere.”
Provincial governments that support prosecution will be shielded by the inability to show discretion, while those that would prefer to let matters drop will be unable to intervene. Either way, the bill could increase tensions between Ottawa and the provinces. This could effectively centralize political authority over hate-related prosecutions in Ottawa, regardless of regional differences in values or enforcement priorities.
The bill also raises concerns about how symbols are interpreted. While most Canadians would associate the term “hate symbol” with a swastika, some have linked Canada’s former flag to extremism. The Canadian Anti-Hate Network did so in 2022 in an educational resource entitled “Confronting and preventing hate in Canadian schools.”
The flag, last used nationally in 1965, was listed under “hate-promoting symbols” for its alleged use by the “alt-right/Canada First movement” to recall when Canada was predominantly white. “Its usage in modern times is an indicator of hate-promoting beliefs,” the resource insisted. If a historic Canadian symbol can be reclassified this easily, it shows how subjective and unstable the definition of a “hate symbol” could become under this bill.
These trends suggest the legislation jeopardizes not only symbols associated with Canada’s past, but also the values that supported open debate and free expression. Taken together, these changes do not merely target hateful behaviour. They create a legal framework that can be stretched to police dissent and suppress unpopular viewpoints. Rest in peace, free speech.
Lee Harding is a research fellow for the Frontier Centre for Public Policy.
Business
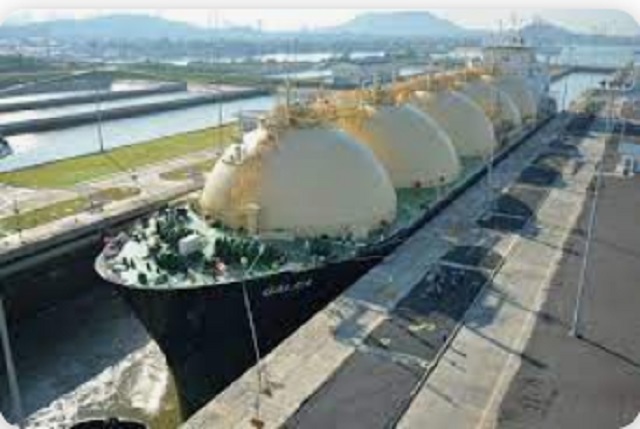
Canada Can Finally Profit From LNG If Ottawa Stops Dragging Its Feet

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Ian Madsen
Canada’s growing LNG exports are opening global markets and reducing dependence on U.S. prices, if Ottawa allows the pipelines and export facilities needed to reach those markets
Canada’s LNG advantage is clear, but federal bottlenecks still risk turning a rare opening into another missed opportunity
Canada is finally in a position to profit from global LNG demand. But that opportunity will slip away unless Ottawa supports the pipelines and export capacity needed to reach those markets.
Most major LNG and pipeline projects still need federal impact assessments and approvals, which means Ottawa can delay or block them even when provincial and Indigenous governments are onside. Several major projects are already moving ahead, which makes Ottawa’s role even more important.
The Ksi Lisims floating liquefaction and export facility near Prince Rupert, British Columbia, along with the LNG Canada terminal at Kitimat, B.C., Cedar LNG and a likely expansion of LNG Canada, are all increasing Canada’s export capacity. For the first time, Canada will be able to sell natural gas to overseas buyers instead of relying solely on the U.S. market and its lower prices.
These projects give the northeast B.C. and northwest Alberta Montney region a long-needed outlet for its natural gas. Horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing made it possible to tap these reserves at scale. Until 2025, producers had no choice but to sell into the saturated U.S. market at whatever price American buyers offered. Gaining access to world markets marks one of the most significant changes for an industry long tied to U.S. pricing.
According to an International Gas Union report, “Global liquefied natural gas (LNG) trade grew by 2.4 per cent in 2024 to 411.24 million tonnes, connecting 22 exporting markets with 48 importing markets.” LNG still represents a small share of global natural gas production, but it opens the door to buyers willing to pay more than U.S. markets.
LNG Canada is expected to export a meaningful share of Canada’s natural gas when fully operational. Statistics Canada reports that Canada already contributes to global LNG exports, and that contribution is poised to rise as new facilities come online.
Higher returns have encouraged more development in the Montney region, which produces more than half of Canada’s natural gas. A growing share now goes directly to LNG Canada.
Canadian LNG projects have lower estimated break-even costs than several U.S. or Mexican facilities. That gives Canada a cost advantage in Asia, where LNG demand continues to grow.
Asian LNG prices are higher because major buyers such as Japan and South Korea lack domestic natural gas and rely heavily on imports tied to global price benchmarks. In June 2025, LNG in East Asia sold well above Canadian break-even levels. This price difference, combined with Canada’s competitive costs, gives exporters strong margins compared with sales into North American markets.
The International Energy Agency expects global LNG exports to rise significantly by 2030 as Europe replaces Russian pipeline gas and Asian economies increase their LNG use. Canada is entering the global market at the right time, which strengthens the case for expanding LNG capacity.
As Canadian and U.S. LNG exports grow, North American supply will tighten and local prices will rise. Higher domestic prices will raise revenues and shrink the discount that drains billions from Canada’s economy.
Canada loses more than $20 billion a year because of an estimated $20-per-barrel discount on oil and about $2 per gigajoule on natural gas, according to the Frontier Centre for Public Policy’s energy discount tracker. Those losses appear directly in public budgets. Higher natural gas revenues help fund provincial services, health care, infrastructure and Indigenous revenue-sharing agreements that rely on resource income.
Canada is already seeing early gains from selling more natural gas into global markets. Government support for more pipelines and LNG export capacity would build on those gains and lift GDP and incomes. Ottawa’s job is straightforward. Let the industry reach the markets willing to pay.
Ian Madsen is a senior policy analyst at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy.
-

 National1 day ago
National1 day agoCanada’s free speech record is cracking under pressure
-

 Digital ID1 day ago
Digital ID1 day agoCanada considers creating national ID system using digital passports for domestic use
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoAlbertans give most on average but Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoUS Supreme Court Has Chance To End Climate Lawfare
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTaxpayers Federation calls on politicians to reject funding for new Ottawa Senators arena
-

 Fraser Institute24 hours ago
Fraser Institute24 hours agoClaims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoU.S. seizes Cuba-bound ship with illicit Iranian oil history
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoCarney Hears A Who: Here Comes The Grinch









