Energy
Courts expose Ottawa’s green overreach

From the Fraser Institute
It has been a rough autumn for the Trudeau government. First, the Supreme Court of Canada struck down significant parts of the federal Impact Assessment Act (also known as Bill C-69), ruling the act to be broadly unconstitutional and finding that the government had made the review process ambiguous and overly broad while intruding on provincial authority. Then last week, Canada’s Federal Court struck down the Trudeau government’s ban on single-use plastics finding the government’s classification of “plastic manufactured items” (PMI) as toxic materials under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA) to be unsound.
And yet, the Trudeau government has already signalled the next stage in its crusade against plastics. Having banned a limited set of plastics-of-convenience (straws, cutlery, etc.), it plans to ban plastic films and containers used up and down the food chain to keep foods isolated from contamination, protected from pests and destructive oxidation, and cold, which is critical to preventing microbial contamination and spoilage.
One can hope that this second court strike will lead the government to reconsider and preferably scrap its entire “Zero Plastic Waste by 2030” plan, which is deeply flawed. As I showed in a 2022 study published by the Fraser Institute, Canada does not have a significant plastic waste problem. Less than 1 per cent of plastics used in Canada end up as waste in the environment while 99 per cent is safely buried in landfills, recycled or incinerated. Canada is not a measurable part of the world’s plastic pollution problem.
Moreover, the government’s own analysis suggests that pursuing this war on plastics will ultimately lead to greater waste of alternative materials, raising concerns among environmentalists. Even if the Trudeau government’s “Zero Plastic” plan were to work, it would produce an undetectable reduction in the growth of global plastic pollution of three thousandths of one per cent. Remember, this is by the government’s own admission.
And even that small reduction in environmental harm will likely be offset by increased environmental harms due to replacements for the plastic products banned by the government. Again, per the government’s own analysis, “Zero Plastic” regulations are expected to increase the waste generated from substitutes by almost 300,000 tonnes in 2024 and by around 2.9 million tonnes over the full life of the plan (2023 to 2032), mainly driven by paper substitutes.
Bottom line—the Trudeau government’s anti-plastic regulations would keep about 1.5 million tonnes of plastics from entering the waste stream over the course of the program, but would add about 2.9 million tonnes of other materials to the waste stream from the use of substitutes. And increase the costs of waste management in Canada.
The government should take a hint from the two recent court rulings—which found two of its signature environmental initiatives unconstitutional, unreasonable and ill-founded—and take both the Impact Assessment Act and the “Zero Plastic Waste by 2030” plan back to the drawing board. Of course, given federal Environment Minister Steven Guilbeault’s reaction to the Supreme Court ruling—basically, the government doesn’t think it’s doing anything wrong and does not intend to change course—this government is unlikely to make serious efforts at compliance with the new court ruling on plastics. Serious reform will likely have to wait for a change in government.
Author:
Business
US Energy Secretary says price of energy determined by politicians and policies


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
During the latest marathon cabinet meeting on Dec. 2, Energy Secretary Chris Wright made news when he told President Donald Trump that “The biggest determinant of the price of energy is politicians, political leaders, and polices — that’s what drives energy prices.”
He’s right about that, and it is why the back-and-forth struggle over federal energy and climate policy plays such a key role in America’s economy and society. Just 10 months into this second Trump presidency, the administration’s policies are already having a profound impact, both at home and abroad.
While the rapid expansion of AI datacenters over the past year is currently being blamed by many for driving up electric costs, power bills were skyrocketing long before that big tech boom began, driven in large part by the policies of the Obama and Biden administration designed to regulate and subsidize an energy transition into reality. As I’ve pointed out here in the past, driving up the costs of all forms of energy to encourage conservation is a central objective of the climate alarm-driven transition, and that part of the green agenda has been highly effective.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here.
Thank you!
President Trump, Wright, and other key appointees like Interior Secretary Doug Burgum and EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin have moved aggressively throughout 2025 to repeal much of that onerous regulatory agenda. The GOP congressional majorities succeeded in phasing out Biden’s costly green energy subsidies as part of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, which Trump signed into law on July 4. As the federal regulatory structure eases and subsidy costs diminish, it is reasonable to expect a gradual easing of electricity and other energy prices.
This year’s fading out of public fear over climate change and its attendant fright narrative spells bad news for the climate alarm movement. The resulting cracks in the green facade have manifested rapidly in recent weeks.
Climate-focused conflict groups that rely on public fears to drive donations have fallen on hard times. According to a report in the New York Times, the Sierra Club has lost 60 percent of the membership it reported in 2019 and the group’s management team has fallen into infighting over elements of the group’s agenda. Greenpeace is struggling just to stay afloat after losing a huge court judgment for defaming pipeline company Energy Transfer during its efforts to stop the building of the Dakota Access Pipeline.
350.org, an advocacy group founded by Bill McKibben, shut down its U.S. operations in November amid funding woes that had forced planned 25 percent budget cuts for 2025 and 2026. Employees at EDF voted to form their own union after the group went through several rounds of budget cuts and layoffs in recent months.
The fading of climate fears in turn caused the ESG management and investing fad to also fall out of favor, leading to a flood of companies backtracking on green investments and climate commitments. The Net Zero Banking Alliance disbanded after most of America’s big banks – Goldman Sachs, J.P. Morgan Chase, Citigroup, Wells Fargo and others – chose to drop out of its membership.
The EV industry is also struggling. As the Trump White House moves to repeal Biden-era auto mileage requirements, Ford Motor Company is preparing to shut down production of its vaunted F-150 Lightning electric pickup, and Stellantis cancelled plans to roll out a full-size EV truck of its own. Overall EV sales in the U.S. collapsed in October and November following the repeal of the $7,500 per car IRA subsidy effective Sept 30.
The administration’s policy actions have already ended any new leasing for costly and unneeded offshore wind projects in federal waters and have forced the suspension or abandonment of several projects that were already moving ahead. Capital has continued to flow into the solar industry, but even that industry’s ability to expand seems likely to fade once the federal subsidies are fully repealed at the end of 2027.
Truly, public policy matters where energy is concerned. It drives corporate strategies, capital investments, resource development and movement, and ultimately influences the cost of energy in all its forms and products. The speed at which Trump and his key appointees have driven this principle home since Jan. 20 has been truly stunning.
David Blackmon is an energy writer and consultant based in Texas. He spent 40 years in the oil and gas business, where he specialized in public policy and communications.
Energy
A look inside the ‘floatel’ housing B.C.’s LNG workforce
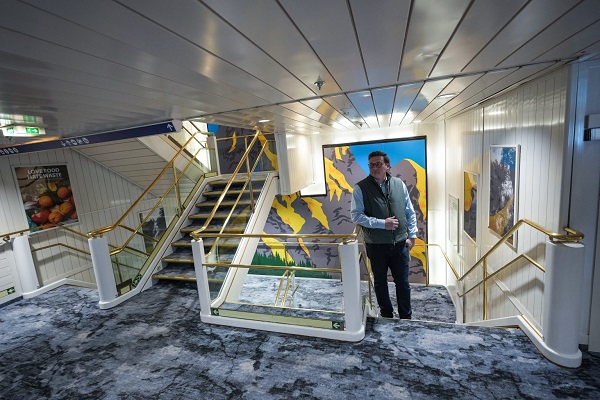

From Resource Works
Innovative housing solution minimizes community impact while supporting the massive labour force needed for the Woodfibre LNG project.
The Woodfibre LNG project — a national leader in Indigenous partnerships and a cornerstone of global energy security — relies on a large construction workforce that drives economic prosperity across the region. For many of these workers, “home” is a ship.
Refitted from a cruise liner into a dedicated accommodation vessel, or “floatel,” this innovative solution houses up to 600 workers near Squamish, B.C., while keeping pressure off local housing and minimizing the project’s community footprint.
These exclusive images, captured a year ago, offer a rare retrospective look inside the original floatel. MV Isabelle X. With a second accommodation ship, the MV Saga X, recently arrived, this photo essay gives a timely, ground-level view of life aboard: individual cabins, a full-service dining hall, recreation spaces and custom laundry facilities. It’s a glimpse into the offshore dormitory that anchors daily life for the crew bringing this vital energy project to completion.

An arcade room is seen on a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, during a media tour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

A dining area is seen on a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, during a media tour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

A cabin is seen on a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, during a media tour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

Bridgemans Services Group president Brian Grange stands at the stern on a renovated cruise ship known as a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, during a media tour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

A custom built heat pump unit that allows the ship to avoid using diesel while docked and at anchor is seen on a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, during a media tour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

The main entry and exit area for workers is seen on a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, during a media tour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

A renovated cruise ship known as a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, is seen at anchor in the harbour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.

A tugboat and water taxi are seen docked at a renovated cruise ship known as a “floatel” that Woodfibre LNG plans to use to house 600 construction workers at a liquefied natural gas export facility being built near Squamish, at anchor in the harbour in Vancouver, on Thursday, May 9, 2024. The ship arrived in B.C. waters in January after a 40-day journey from Estonia, where it had sheltered Ukrainian refugees, but the District of Squamish council voted three to four against a one-year permit for its use last week.
All photos credited to THE CANADIAN PRESS/Darryl Dyck
Resource Works News
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada’s climate agenda hit business hard but barely cut emissions
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoFrom Exception to Routine. Why Canada’s State-Assisted Suicide Regime Demands a Human-Rights Review
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Sports Hall of Fame Announces Class of 2026 Inductees
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCarney government should privatize airports—then open airline industry to competition
-

 Business21 hours ago
Business21 hours agoCarney’s Toronto cabinet meetings cost $530,000
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoIs Carney Falling Into The Same Fiscal Traps As Trudeau?
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCarney’s pipeline deal hits a wall in B.C.
-
 Health1 day ago
Health1 day ago23,000+ Canadians died waiting for health care in one year as Liberals pushed euthanasia










