Business
Canadian Energy Companies Look South For Growth

From EnergyNow.ca
By Heather Exner-Pirot
Enbridge’s announcement in September that it was acquiring three U.S.-based utilities for USD$14 billion saw Canada’s largest energy company also become North America’s largest gas utility. The deal is significant not only on its own merits, but as part of a bigger trend: Canadian energy companies that are looking for growth prospects are finding them south of the border.
The trend is not new. In 2016, Canadian utilities went on an American shopping spree. Fortis acquired ITC for USD$11.3 billion; Ontario-based Algonquin Power & Utilities Corp acquired Missouri-based Empire District Electric Company for USD$2.4 billion; and Nova Scotia-based Emera acquired Florida-based TECO in a USD$10.4 billion deal.
Pipelines were in the mix too, with TC Energy acquiring Columbia Pipeline Group, a gas transmission network, that year for USD$13 billion.
In 2017, Hydro One purchased U.S. power supplier Avista for USD $3.4 billion, and AltaGas took over WGL Holdings (which supplies natural gas to the White House) for USD $4.6 billion. More recently, TriSummit acquired the Alaska gas distribution, transmission, and storage assets of SEMCO Energy for US$800 million in March.
As such, the Enbridge utility megadeal can be seen less as a harbinger and more of a culmination.
What is behind this Canadian appetite for American utilities and pipelines? At one level, it is a response to the inherent limitations of the Canadian utilities sector, which is heavily regulated and often provincially owned. Add in Ottawa’s torrent of climate policies aiming to cut growth in Canadian oil and gas, and pastures look greener elsewhere.
But it also speaks to the confidence the sector’s biggest players have in the long term prospects for natural gas. The Dominion deal adjusts Enbridge’s earnings from a 60-40 mix between crude oil & liquids, and natural gas & renewable energy respectively, to something closer to a 50-50 split. Enbridge, like many energy companies, is betting on natural gas being a bridge fuel in the energy transition rather than being phased out. And whatever fuel mix we use in the future, it will require pipelines and distribution, whether in the form of natural gas, renewable natural gas (RNG), hydrogen or otherwise.
“…it also speaks to the confidence the sector’s biggest players have in the long term prospects for natural gas.”
Two phenomena are worth emphasizing here. The first is that the United States is seen as a jurisdiction for growth; Canada, not so much. Our biggest energy companies are expanding to the south, but the reverse is not true. Enbridge and TC Energy are leading the way, but Cenovus, Cameco, Hydro-Québec and others are also making moves, on top of the long list of utilities above.
This is not just anecdotal. According to the U.S. State Department,1 Canadian foreign direct investment (FDI) in the United States was about 26% higher than their reciprocal FDI in 2022, or USD$528 billion compared to their USD$406 billion. This is part of a broader trend that has been worsening since 2014. In that year, Canadian investment abroad was only about CAD$100 billion more than foreign investment in Canada. By 2022 the imbalance had grown to a whopping CAD$725 billion.2 Canadian companies are generating wealth; they are just generating a smaller proportion of it at home.
The second is that the Canadian and American energy markets are highly interdependent, and growing more so. In fact, 2022 saw record energy trade between our two countries, reaching USD$190 billion, almost triple what it was in the throes of the COVID-19 pandemic, and beating the last high water mark of USD$178 billion in 2008. From natural gas and liquids pipelines to refineries and electricity grids, fundamentally we have a single North American energy system.
As such, we should be developing and coordinating energy and climate policy much more closely. It is inefficient, not to mention painful for the energy sector, when Canada and the United States – and many provinces and states on top of that – propose substantially different standards, goals, and regulations. Energy is an area that needs closer policy collaboration and alignment between our two nations in order to achieve sustainability, reliability and affordability of supply.
This need is manifesting itself in a growing Canadian presence in the US capital. In the past year or so, TC Energy has established a policy team in Washington DC, and Cenovus and the Business Council of Canada have opened up offices there (as has my own think tank, the Macdonald-Laurier Institute). As entreaties to Ottawa fall on deaf ears, businesses are looking for reception elsewhere.
The Canadian energy sector is betting big on natural gas, be it through retail, pipeline transportation or LNG exports. Where possible, it’s betting on Canada too. But the United States and other markets are where growth is on offer.
We should all celebrate the success of Canadian companies abroad. But we should be creating a policy and business environment that allows them to grow in our own back yard too.
Heather Exner-Pirot is the Director of Energy, Natural Resources and Environment at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute.
Business
Carney’s Honeymoon Phase Enters a ‘Make-or-Break’ Week

From the National Citizens Coalition
The National Citizens Coalition (NCC) is sounding the alarm on a critical week for the Carney government, which, despite enjoying an unearned honeymoon in the polls, has delivered zero results for everyday Canadians. As the G7 summit looms large and the House of Commons prepares to adjourn, this is a make-or-break moment for Prime Minister Mark Carney to prove his government is more than empty promises. Canadians are watching, and the NCC is calling out the glaring failures that threaten a grim summer of economic decline, and continued crime, chaos, and rising unemployment.
Housing Minister Gregor Robertson Caught in $10.85 Million Scandal
Recent revelations from Blacklock’s Reporter expose Housing Minister Gregor Robertson’s attempt to conceal $10.85 million in personal property investments during Commons questioning. This shocking lack of transparency from the minister tasked with addressing Canada’s housing crisis raises serious questions about his integrity and ability to prioritize Canadians struggling with skyrocketing costs. While Robertson dodges accountability, and Carney apparently scoffs at providing housing relief to millions suffering under a Liberal-made crisis, young professionals and young families are wondering if they’ll ever have a chance to own a home bigger than Canada’s much-maligned supply of ‘dog-crate condos.’
The NCC demands a full ethics investigation, the resignation of Gregor Robertson — who, as one of the architects of the Vancouver housing crisis, should have never been handed this file to begin with — and immediate action to restore trust in this critical portfolio.
Pipeline Delays and Provincial Obstruction Threaten Economic Growth
The Carney government’s inaction on pipelines is stalling Canada’s economic potential. Despite promises of “nation-building projects,” British Columbia and Quebec continue to block and veto critical energy infrastructure, with Carney failing to assert federal leadership. His vague talk of “consensus” and “decarbonized” barrels has led to zero progress, leaving Alberta’s economy in limbo and Canadians facing higher energy costs. With no clear plan to advance projects, the government is squandering opportunities to create jobs and secure energy sovereignty. The NCC urges Carney to act decisively this week to break the provincial logjam and deliver results.
Immigration Chaos: Lena Diab’s Unchecked Honour System Fails Canadians
Immigration Minister Lena Diab’s reliance on an ‘honour system’ for millions of temporary visitors with expiring visas is a recipe for disaster. As Canada grapples with unsustainable immigration levels, Diab’s apparent plan for millions of temporary workers and failed ‘diploma mill’ attendees assumes compliance without enforcement, ignoring the high-propensity for fraud, and the ongoing and urgent strain on housing, healthcare, and public services. The Liberals’ Strong Borders Act promises reform, but its loaded with unnecessary overreach and vague measures.
A lack of urgency leaves Canadians vulnerable to further crime, chaos, closed emergency rooms, high rents, and failing infrastructure. With immigration continuing to spiral out of control, the NCC calls for concrete action to drastically lower immigration targets, expedite deportations, and prioritize Canadian citizens and the record amounts of unemployed before the House adjourns.
Canadians Deserve Results, Not More Hollow “Elbows up” or “Team Canada” Rhetoric
This week’s G7 summit in Alberta and the impending House adjournment are the Carney government’s last chance to show leadership, before an undeserved summer break for a government that will be overseeing deepening economic decline, rising crime under a refusal to tackle catch-and-release bail, and growing unemployment. Canadians cannot afford another season of unfulfilled promises and unchecked crises. The NCC demands Carney use the G7 platform to secure trade stability, meaningful energy deals with our allies, and table a federal budget to address the cost-of-living crisis made worse by inflationary Liberal spending. Failure to act now will cement an early legacy of inaction and leave Canadians to endure a prolonged period of hardship.
“The Carney government’s honeymoon has been built on hype, not results,” says NCC Director Alexander Brown. “From Gregor Robertson’s hidden millions, to stalled pipelines, to an immigration system in continued disarray, Canadians — and particularly young Canadians — are being let down. This week is Carney’s chance to prove he can deliver beyond the lies that were told to placate a portion of the electorate at the polls. If he fails to act, the economic decline, the crime and chaos, will only worsen, and everyday Canadians will pay the price.
“True Canadian leaders like Alberta Premier Danielle Smith are in attendance at the G7 along with Carney. If actual acts of ‘nation-building,’ and not more net-zero de-growth, do not come naturally to the PM, he should turn to those who have never wavered in their quest to make life more affordable for the hard-working citizens they are privileged to represent, and who know when to get out of the way to allow Canadians to prosper. More of the same internal, ideological sabotage from the Liberals cannot ruin this dire moment for Canada’s rebirth and recovery.”
The NCC calls on all Canadians to hold the Carney government accountable. Join us in demanding transparency, action, and results before the House adjourns and the G7 summit concludes. Together, we can fight for a stronger, more prosperous Canada.
About the National Citizens Coalition: Founded in 1967, the NCC is a non-profit organization dedicated to advocating for individual freedom, lower taxes, less government waste, and a stronger Canada. We hold governments accountable and fight for the interests of everyday Canadians.
Alberta
Alberta announces citizens will have to pay for their COVID shots
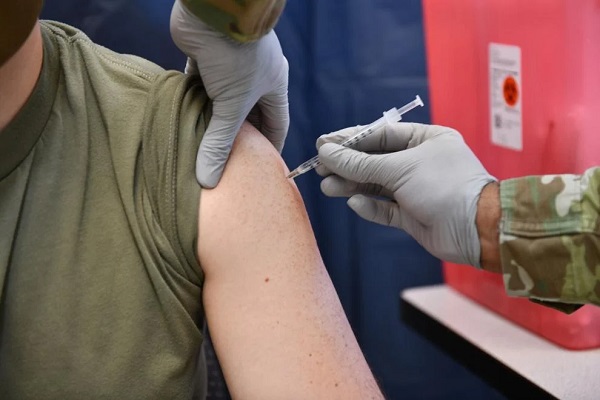
From LifeSite News
The government said that it has decided to stop ‘waste’ by not making the shots free starting this fall.
Beginning this fall, COVID shots in the province will have to be pre-ordered at the full price, about $110, to receive them. (This will roll out in four ‘phases’. In the first phases COVID shots will still be free for those with pre-existing medical conditions, people on social programs, and seniors.)
The UCP government in a press release late last week noted due to new “federal COVID-19 vaccine procurement” rules, which place provinces and territories as being responsible for purchasing the jabs for residents, it has decided to stop “waste” by not making the jab free anymore.
“Now that Alberta’s government is responsible for procuring vaccines, it’s important to better determine how many vaccines are needed to support efforts to minimize waste and control costs,” the government stated.
“This new approach will ensure Alberta’s government is able to better determine its overall COVID-19 vaccine needs in the coming years, preventing significant waste.”
The New Democratic Party (NDP) took issue with the move to stop giving out the COVID shots for free, claiming it was “cruel” and would place a “financial burden” on people wanting the shots.
NDP health critic Sarah Hoffman claimed the move by the UCP is health “privatization” and the government should promote the abortion-tainted shots instead.
The UCP said that in 2023-2024, about 54 percent of the COVID shots were wasted, with Health Minister Adriana LaGrange saying, “In previous years, we’ve seen significant vaccine wastage.”
“By shifting to a targeted approach and introducing pre-ordering, we aim to better align supply with demand – ensuring we remain fiscally responsible while continuing to protect those at highest risk,” she said.
The UCP government said that the COVID shots for the fall will be rolled out in four phases, with those deemed “high risk” getting it for free until then. However, residents who want the shots this fall “will be required to pay the full cost of the vaccine, the government says.”
The jabs will only be available through public health clinics, with pharmacies no longer giving them out.
The UCP also noted that is change in policy comes as a result of the Federal Drug Administration in the United States recommending the jabs be stopped for young children and pregnant women.
The opposite happened in Canada, with the nation’s National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) continuing to say that pregnant women should still regularly get COVID shots as part of their regular vaccine schedule.
The change in COVID jab policy is no surprise given Smith’s opposition to mandatory shots.
As reported by LifeSiteNews, early this year, Smith’s UCP government said it would consider halting COVID vaccines for healthy children.
Smith’s reasoning was in response to the Alberta COVID-19 Pandemic Data Review Task Force’s “COVID Pandemic Response” 269-page final report. The report was commissioned by Smith last year, giving the task force a sweeping mandate to investigate her predecessor’s COVID-era mandates and policies.
The task force’s final report recommended halting “the use of COVID-19 vaccines without full disclosure of their potential risks” as well as outright ending their use “for healthy children and teenagers as other jurisdictions have done,” mentioning countries like “Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, and the U.K.”
The mRNA shots have also been linked to a multitude of negative and often severe side effects in children and all have connections to cell lines derived from aborted babies.
Many Canadian doctors who spoke out against COVID mandates and the experimental mRNA injections were censured by their medical boards.
LifeSiteNews has published an extensive amount of research on the dangers of the experimental COVID mRNA jabs that include heart damage and blood clots.
-

 Health2 hours ago
Health2 hours agoLast day and last chance to win this dream home! Support the 2025 Red Deer Hospital Lottery before midnight!
-

 Business23 hours ago
Business23 hours agoCarney’s European pivot could quietly reshape Canada’s sovereignty
-

 Alberta23 hours ago
Alberta23 hours agoAlberta’s grand bargain with Canada includes a new pipeline to Prince Rupert
-

 Aristotle Foundation6 hours ago
Aristotle Foundation6 hours agoThe Canadian Medical Association’s inexplicable stance on pediatric gender medicine
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoManhunt on for suspect in shooting deaths of Minnesota House speaker, husband
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin8 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin8 hours agoWOKE NBA Stars Seems Natural For CDN Advertisers. Why Won’t They Bite?
-

 conflict9 hours ago
conflict9 hours ago“Evacuate”: Netanyahu Warns Tehran as Israel Expands Strikes on Iran’s Military Command
-

 Energy8 hours ago
Energy8 hours agoCould the G7 Summit in Alberta be a historic moment for Canadian energy?





