Canadian Energy Centre
Analyst says LNG Canada likely to start exports before year-end

Welders with JGC-Fluor following completion of the final weld on the first production train at the LNG Canada project, in Kitimat, B.C. in July 2024. Since construction began in 2018, upwards of 380 pipe welders have worked on the LNG Canada project. Photo courtesy JGC-Fluor
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Canada’s first liquefied natural gas export terminal ‘on the cusp’ of its testing phase
Momentum is building for the long-awaited start-up of Canada’s first liquefied natural gas (LNG) export project.
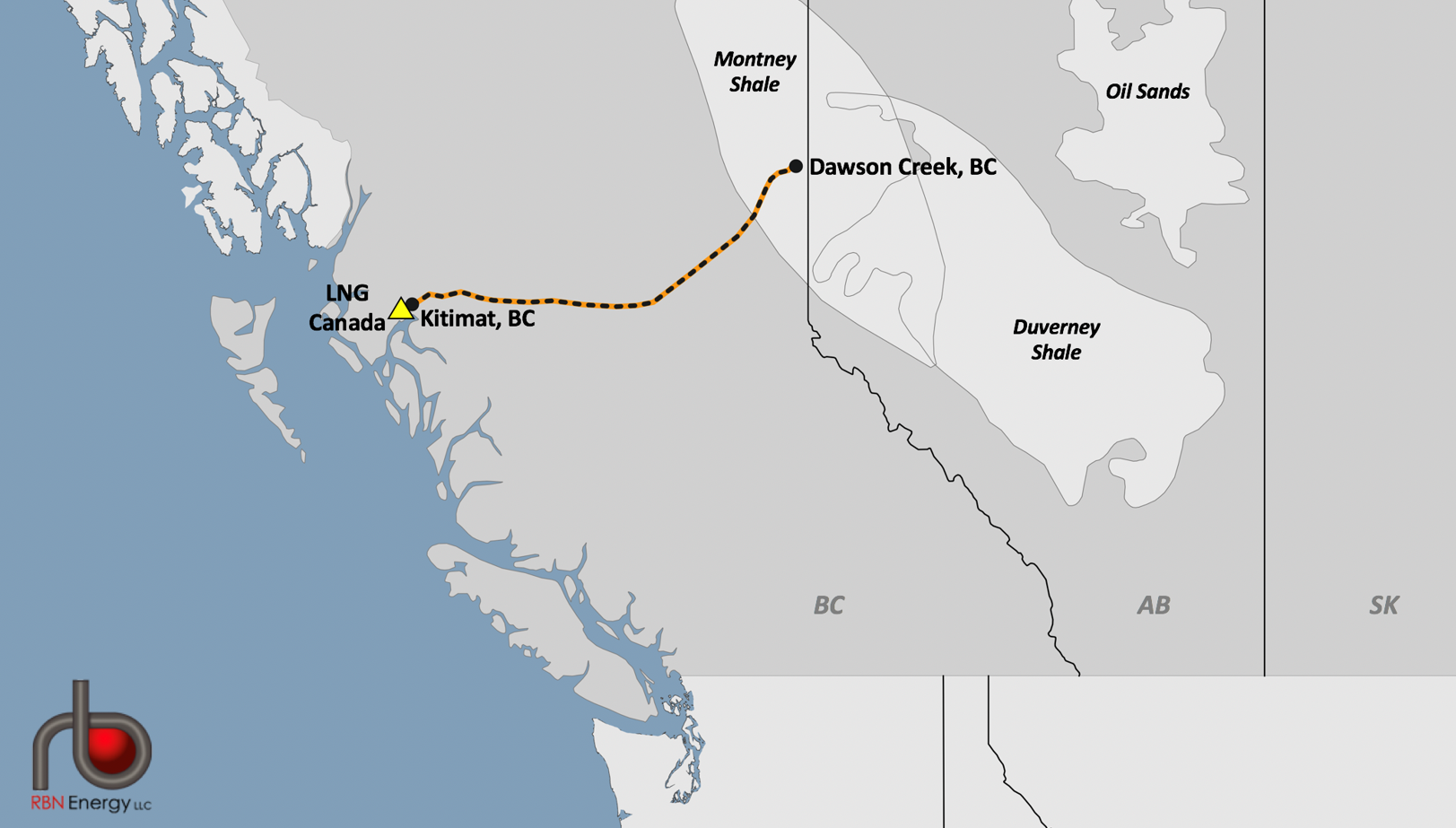
Shipments from the LNG Canada terminal at Kitimat, B.C. may now start earlier than expected, later this year rather than mid-2025, according to Martin King, Canadian energy specialist with Houston-based RBN Energy.
“LNG Canada appears to be on the cusp of its testing phase and is likely to be exporting some cargoes of LNG before the end of this year,” King wrote recently.
He made the prediction after a senior executive with Shell, the project’s lead owner, said it could deliver its first cargo earlier than previously planned, in the wake of two key milestones.
Fluor reported in July it had completed the final weld on the first production train while Petronas, which holds a 25 per cent stake in LNG Canada, announced it would add three LNG vessels to its North American fleet, doubling its size.
A longtime industry insider sees the $18 billion LNG Canada terminal as a game changer.
“This is decades in the making. Canada has been trying to get its LNG business up and running since the 1970s but it has been sidetracked for one reason or another,” says Calgary-based consultant Racim Gribaa, who has worked in the industry for more than 25 years.
“This project is perfectly placed to take advantage of an awesome opportunity given the demand for LNG worldwide is growing exponentially.”
The project, which will use the Coastal GasLink pipeline, completed in November 2023, to bring gas from northeastern British Columbia to the Kitimat terminal for processing and shipping, will have capacity to produce up to 14 million tonnes per year in its first phase.
While that’s a fraction of the 404 million tonnes of global demand in 2023, Gribaa says Asian buyers view LNG Canada as secure supplier in part due to its geography.
“The closest point to Asia is Canada’s west coast, so you have the shortest shipping route, which makes for optimal transportation costs. The traders and LNG industry see it as valuable for that reason,” says Gribaa, who previously worked in LNG trade in Qatar, one of the world’s largest exporters.
And the project is coming online at a time when worldwide demand is surging.
“The worldwide demand has effectively doubled every decade since 1990, when it was 50 MPTA. We are now closing in on 500 MPTA and that is accelerating,” Gribaa says.
“The world will need 10 LNG Canadas in 10 years and 100 more LNG Canadas in the next 30 years.”
The project has plans for a second phase that would double production to 28 million tonnes per year. Based on demand, Gribaa says “the question isn’t if it will go forward, it’s when the consortium will announce the expansion.”
World LNG demand growth will be particularly strong in Asia, where Shell’s four LNG Canada partners – Petronas (25 per cent), PetroChina (15 per cent), Mitsubishi (15 per cent) and Korea Gas Corporation (five per cent) – are headquartered.
“Each of these markets has historical demand for LNG and that demand will continue to grow in the coming decades,” he says, adding that LNG in Asia can be used for power generation and heavy industry, and to reduce air pollution from coal-fired power.
Overall, generating electricity in China with LNG from Canada rather than coal could reduce emissions by up to 62 per cent, according to a 2020 study published in the Journal for Cleaner Production.
A 2022 study by Wood Mackenzie found that growing Canada’s LNG industry could reduce net emissions in Asia by 188 million tonnes per year through 2050.
Alberta
The Canadian Energy Centre’s biggest stories of 2025

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Canada’s energy landscape changed significantly in 2025, with mounting U.S. economic pressures reinforcing the central role oil and gas can play in safeguarding the country’s independence.
Here are the Canadian Energy Centre’s top five most-viewed stories of the year.
5. Alberta’s massive oil and gas reserves keep growing – here’s why

The Northern Lights, aurora borealis, make an appearance over pumpjacks near Cremona, Alta., Thursday, Oct. 10, 2024. CP Images photo
Analysis commissioned this spring by the Alberta Energy Regulator increased the province’s natural gas reserves by more than 400 per cent, bumping Canada into the global top 10.
Even with record production, Alberta’s oil reserves – already fourth in the world – also increased by seven billion barrels.
According to McDaniel & Associates, which conducted the report, these reserves are likely to become increasingly important as global demand continues to rise and there is limited production growth from other sources, including the United States.
4. Canada’s pipeline builders ready to get to work
Canada could be on the cusp of a “golden age” for building major energy projects, said Kevin O’Donnell, executive director of the Mississauga, Ont.-based Pipe Line Contractors Association of Canada.
That eagerness is shared by the Edmonton-based Progressive Contractors Association of Canada (PCA), which launched a “Let’s Get Building” advocacy campaign urging all Canadian politicians to focus on getting major projects built.
“The sooner these nation-building projects get underway, the sooner Canadians reap the rewards through new trading partnerships, good jobs and a more stable economy,” said PCA chief executive Paul de Jong.
3. New Canadian oil and gas pipelines a $38 billion missed opportunity, says Montreal Economic Institute

Steel pipe in storage for the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion in 2022. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
In March, a report by the Montreal Economic Institute (MEI) underscored the economic opportunity of Canada building new pipeline export capacity.
MEI found that if the proposed Energy East and Gazoduq/GNL Quebec projects had been built, Canada would have been able to export $38 billion worth of oil and gas to non-U.S. destinations in 2024.
“We would be able to have more prosperity for Canada, more revenue for governments because they collect royalties that go to government programs,” said MEI senior policy analyst Gabriel Giguère.
“I believe everybody’s winning with these kinds of infrastructure projects.”
2. Keyera ‘Canadianizes’ natural gas liquids with $5.15 billion acquisition

Keyera Corp.’s natural gas liquids facilities in Fort Saskatchewan, Alta. Photo courtesy Keyera Corp.
In June, Keyera Corp. announced a $5.15 billion deal to acquire the majority of Plains American Pipelines LLP’s Canadian natural gas liquids (NGL) business, creating a cross-Canada NGL corridor that includes a storage hub in Sarnia, Ontario.
The acquisition will connect NGLs from the growing Montney and Duvernay plays in Alberta and B.C. to markets in central Canada and the eastern U.S. seaboard.
“Having a Canadian source for natural gas would be our preference,” said Sarnia mayor Mike Bradley.
“We see Keyera’s acquisition as strengthening our region as an energy hub.”
1. Explained: Why Canadian oil is so important to the United States

Enbridge’s Cheecham Terminal near Fort McMurray, Alberta is a key oil storage hub that moves light and heavy crude along the Enbridge network. Photo courtesy Enbridge
The United States has become the world’s largest oil producer, but its reliance on oil imports from Canada has never been higher.
Many refineries in the United States are specifically designed to process heavy oil, primarily in the U.S. Midwest and U.S. Gulf Coast.
According to the Alberta Petroleum Marketing Commission, the top five U.S. refineries running the most Alberta crude are:
- Marathon Petroleum, Robinson, Illinois (100% Alberta crude)
- Exxon Mobil, Joliet, Illinois (96% Alberta crude)
- CHS Inc., Laurel, Montana (95% Alberta crude)
- Phillips 66, Billings, Montana (92% Alberta crude)
- Citgo, Lemont, Illinois (78% Alberta crude)
Alberta
Alberta’s huge oil sands reserves dwarf U.S. shale

From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Oil sands could maintain current production rates for more than 140 years
Investor interest in Canadian oil producers, primarily in the Alberta oil sands, has picked up, and not only because of expanded export capacity from the Trans Mountain pipeline.
Enverus Intelligence Research says the real draw — and a major factor behind oil sands equities outperforming U.S. peers by about 40 per cent since January 2024 — is the resource Trans Mountain helps unlock.
Alberta’s oil sands contain 167 billion barrels of reserves, nearly four times the volume in the United States.
Today’s oil sands operators hold more than twice the available high-quality resources compared to U.S. shale producers, Enverus reports.
“It’s a huge number — 167 billion barrels — when Alberta only produces about three million barrels a day right now,” said Mike Verney, executive vice-president at McDaniel & Associates, which earlier this year updated the province’s oil and gas reserves on behalf of the Alberta Energy Regulator.
Already fourth in the world, the assessment found Alberta’s oil reserves increased by seven billion barrels.
Verney said the rise in reserves despite record production is in part a result of improved processes and technology.
“Oil sands companies can produce for decades at the same economic threshold as they do today. That’s a great place to be,” said Michael Berger, a senior analyst with Enverus.
BMO Capital Markets estimates that Alberta’s oil sands reserves could maintain current production rates for more than 140 years.
The long-term picture looks different south of the border.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration projects that American production will peak before 2030 and enter a long period of decline.
Having a lasting stable source of supply is important as world oil demand is expected to remain strong for decades to come.
This is particularly true in Asia, the target market for oil exports off Canada’s West Coast.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects oil demand in the Asia-Pacific region will go from 35 million barrels per day in 2024 to 41 million barrels per day in 2050.
The growing appeal of Alberta oil in Asian markets shows up not only in expanded Trans Mountain shipments, but also in Canadian crude being “re-exported” from U.S. Gulf Coast terminals.
According to RBN Energy, Asian buyers – primarily in China – are now the main non-U.S. buyers from Trans Mountain, while India dominates purchases of re-exports from the U.S. Gulf Coast. .
BMO said the oil sands offers advantages both in steady supply and lower overall environmental impacts.
“Not only is the resulting stability ideally suited to backfill anticipated declines in world oil supply, but the long-term physical footprint may also be meaningfully lower given large-scale concentrated emissions, high water recycling rates and low well declines,” BMO analysts said.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLand use will be British Columbia’s biggest issue in 2026
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoChina Stages Massive Live-Fire Encirclement Drill Around Taiwan as Washington and Japan Fortify
-

 Digital ID1 day ago
Digital ID1 day agoThe Global Push for Government Mandated Digital IDs And Why You Should Worry
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoFeds pull the plug on small business grants to Minnesota after massive fraud reports
-

 Business17 hours ago
Business17 hours agoDOOR TO DOOR: Feds descend on Minneapolis day cares tied to massive fraud
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin17 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin17 hours agoIn Contentious Canada Reality Is Still Six Degrees Of Hockey
-

 Business17 hours ago
Business17 hours agoCanada needs serious tax cuts in 2026
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoWhy Japan wants Western Canadian LNG