Alberta
Alberta Budget 2024 – Employment

Budget 2024: Maintaining Alberta’s economic advantage
Budget 2024 is a responsible plan that maintains Alberta’s competitive advantage so businesses and industry can continue to innovate, thrive and create jobs.
Budget 2024 puts Alberta on a path of continued economic growth through funding that supports creating jobs, attracting investment and developing a skilled and diversified workforce. Strategic investments will empower job creators and innovators to invest, grow and flourish in Alberta’s diversifying economy.
“Budget 2024 reaffirms our commitment to diversify, attract new investment and provide more jobs that keep Alberta’s engine humming. Strategic investments that support the growth of Alberta cities and promote apprenticeship programming and emission reduction technology will help create more opportunities to build an even stronger Alberta.”
Alberta remains a key driver of Canada’s economic prosperity, accounting for 22 per cent of all jobs created in the country last year, despite having just 12 per cent of the population. Compared with other provinces, Alberta has the highest weekly earnings and the lowest taxes, offering many incentives to newcomers seeking a great place to call home.
To further build on these advantages, Budget 2024 introduces the Alberta is Calling attraction bonus, a $5,000 refundable tax credit aimed at attracting out-of-province workers in the skilled trades. A total of $10 million will be provided to workers.
“The Alberta is Calling attraction bonus will support our government’s commitment to build a skilled and resilient labour force that helps businesses and the economy thrive. We will continue to foster the conditions for growth to ensure Alberta remains the best place to live, work, invest, do business and raise a family.”
Budget 2024 supports the sustainable growth of Alberta’s cities and communities. In addition to $724 million in municipal infrastructure funding through the Local Government Fiscal Framework in 2024-25, Budget 2024 launches the new Local Growth and Sustainability Grant, an application-based program that provides $60 million over three years to enable municipalities to fund infrastructure that supports economic development and addresses unique and emergent needs in their communities.
“We’re pleased to see so many people choosing to move to Alberta to experience the advantages this province has to offer, thanks in part to the strong communities we are supporting through predictable, sustainable funding. We also recognize the pressure this growth can put on local communities. The Local Growth and Sustainability Grant is part of our responsible plan to support a vibrant province and help communities respond to growth opportunities and acute sustainability challenges.”
As Alberta’s economy continues to grow, so does the need to sustain a vibrant and robust workforce to meet the needs of Alberta employers. Budget 2024 addresses current and future potential labour shortages by expanding skills and knowledge in key areas.
More than $100 million in new funding for apprenticeship programs will add 3,200 seats to help meet growing demand at Alberta’s post-secondary institutions. Another $361 million from the Budget 2024 Capital Plan will build and upgrade research and learning facilities in some of the province’s world-class post-secondary institutions. Investments include $63 million to renovate and expand the W.J. Elliott agricultural mechanics building at Olds College and $55 million to increase STEM programming capacity at the University of Calgary.
“Supporting growth in Alberta’s economy means ensuring no region is left behind. Our funding commitments to STEM programming at the University of Calgary and agriculture at Olds will create new opportunities for students in our rural economy and those studying in our largest urban centre.”
The Alberta Petrochemicals Incentive Program (APIP) is helping turn the province into a top global producer of petrochemicals. The APIP provides grants to cover 12 per cent of eligible capital costs for Alberta-based petrochemicals projects. In 2023-24, three projects are expected to receive APIP grant payments totalling $116 million, helping to diversify Alberta’s economy and create jobs.
“Royalties collected from oil and gas fund the things Albertans rely on, like health, education and social services. Budget 2024 supports the government’s mission to strengthen investor confidence and support job creation in communities all while lowering emissions through the use of new technologies.”
Budget 2024 highlights
- $597 million over three years from the province’s TIER (Technology Innovation and Emissions Reduction) fund to support a suite of programs that reduce emissions, support clean technology development, enhance climate resiliency and create jobs for Albertans.
- $1.5 billion for child-care services, an increase of $200 million, enabling more Albertans with young children to participate in the workforce.
- $32 million to build three new water intakes in the Designated Industrial Zone in Alberta’s Industrial Heartland, which will support long-term private investment opportunities in the area.
- Almost $30 million over three years for the Aboriginal Business Investment Fund, an increase of nearly $8 million, to help fund business startup and expansion costs in Indigenous communities.
Budget 2024 is a responsible plan to strengthen health care and education, build safe and supportive communities, manage the province’s resources wisely and promote job creation to continue to build Alberta’s competitive advantage.
Alberta
Calgary’s new city council votes to ban foreign flags at government buildings

From LifeSiteNews
It is not yet clear if the flag motion applies to other flags, such as LGBT ones.
Western Canada’s largest city has put in place what amounts to a ban on politically charged flags from flying at city-owned buildings.
“Calgary’s Flag Policy means any country recognized by Canada may have their flag flown at City Hall on their national day,” said Calgary’s new mayor Jeromy Farkas on X last month.
“But national flag-raisings are now creating division. Next week, we’ll move to end national flag-raisings at City Hall to keep this a safe, welcoming space for all.”
The motion to ban foreign flags from flying at government buildings was introduced on December 15 by Calgary councilor Dan McLean and passed by a vote of 8 to 7. He had said the previous policy to allow non-Canadian flags to fly, under former woke mayor Jyoti Gondek, was “source of division within our community.”
“In recent months, this practice has been in use in ways that I’ve seen have inflamed tensions, including instances where flag raisings have been associated with anti-Semitic behavior and messaging,” McLean said during a recent council meeting.
The ban on flag raising came after the Palestinian flag was allowed to be raised at City Hall for the first time.
Farkas, shortly after being elected mayor in the fall of 2025, had promised that he wanted a new flag policy introduced in the city.
It is not yet clear if the flag motion applies to other flags, such as LGBT ones.
Despite Farkas putting forth the motion, as reported by LifeSiteNews he is very much in the pro-LGBT camp. However, he has promised to focus only on non-ideological issues during his term.
McLean urged that City Hall must be a place of “neutrality, unity, and respect” for everyone.
“When City Hall becomes a venue for geopolitical expressions, it places the city in the middle of conflicts that are well beyond our municipal mandates,” he said.
As reported by LifeSiteNews, other jurisdictions in Canada are considering banning non-Canadian flags from flying over public buildings.
Recently a political party in British Columbia, OneBC, introduced legislation to ban non-domestic government flags at public buildings in British Columbia.
Across Canada there has also been an ongoing issue with so-called “Pride” flags being raised at schools and city buildings.
Alberta
What are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest
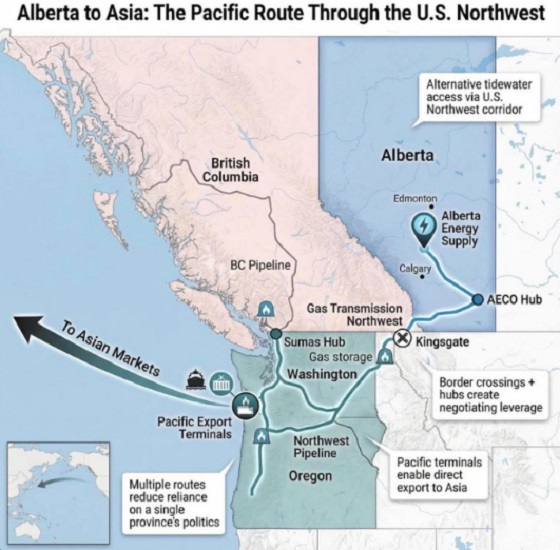
From Resource Works
Can we please just get on with building one through British Columbia instead?
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith is signalling she will look south if Canada cannot move quickly on a new pipeline, saying she is open to shipping oil to the Pacific via the U.S. Pacific Northwest. In a year-end interview, Smith said her “first preference” is still a new West Coast pipeline through northern British Columbia, but she is willing to look across the border if progress stalls.
“Anytime you can get to the West Coast it opens up markets to get to Asia,” she said. Smith also said her focus is building along “existing rights of way,” pointing to the shelved Northern Gateway corridor, and she said she would like a proposal submitted by May 2026.
Deadlines and strings attached
The timing matters because Ottawa and Edmonton have already signed a memorandum of understanding that backs a privately financed bitumen pipeline to a British Columbia port and sends it to the new Major Projects Office. The agreement envisages at least one million barrels a day and sets out a plan for Alberta to file an application by July 1, 2026, while governments aim to finish approvals within two years.
The bargain comes with strings. The MOU links the pipeline to the Pathways carbon capture network, and commits Alberta to strengthen its TIER system so the effective carbon credit price rises to at least 130 dollars a tonne, with details to be settled by April 1, 2026.
Shifting logistics
If Smith is floating an American outlet, it is partly because Pacific Northwest ports are already drawing Canadian exporters. Nutrien’s plan for a $1-billion terminal at Washington State’s Port of Longview highlighted how trade logistics can shift when proponents find receptive permitting lanes.
But the political terrain in Washington and Oregon is unforgiving for fossil fuel projects, even for natural gas. In 2023, federal regulators approved TC Energy’s GTN Xpress expansion over protests from environmental groups and senior officials in West Coast states, with opponents warning about safety and wildfire risk. The project would add about 150 million cubic feet per day of capacity.
A record of resistance
That decision sits inside a longer record of resistance. The anti-development activist website “DeSmog” eagerly estimated that more than 70 percent of proposed coal, oil, and gas projects in the Pacific Northwest since 2012 were defeated, often after sustained local organizing and legal challenges.
Even when a project clears regulators, economics can still kill it. Gas Outlook reported that GTN later said the expansion was “financially not viable” unless it could obtain rolled-in rates to spread costs onto other utilities, a request regulators rejected when they approved construction.
Policy direction is tightening too. Washington’s climate framework targets cutting climate pollution 95 percent by 2050, alongside “clean” transport, buildings, and power measures that push electrification. Recent state actions described by MRSC summaries and NRDC notes reinforce that direction, including moves to help utilities plan a transition away from gas.
Oregon is moving in the same direction. Gov. Tina Kotek issued an executive order directing agencies to move faster on clean energy permitting and grid connections, tied to targets of cutting emissions 50 percent by 2035 and 90 percent by 2050, the Capital Chronicle reported.
For Smith, the U.S. corridor talk may be leverage, but it also underscores a risk, the alternative could be tougher than the Canadian fight she is already waging. The surest way to snuff out speculation is to make it unnecessary by advancing a Canadian project now that the political deal is signed. As Resource Works argued after the MOU, the remaining uncertainty sits with private industry and whether it will finally build, rather than keep testing hypothetical routes.
Resource Works News
-

 Uncategorized2 days ago
Uncategorized2 days agoMortgaging Canada’s energy future — the hidden costs of the Carney-Smith pipeline deal
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoAustralian PM booed at Bondi vigil as crowd screams “shame!”
-

 Automotive1 day ago
Automotive1 day agoCanada’s EV gamble is starting to backfire
-

 Agriculture1 day ago
Agriculture1 day agoEnd Supply Management—For the Sake of Canadian Consumers
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta Next Panel calls to reform how Canada works
-

 Agriculture8 hours ago
Agriculture8 hours agoThe Climate Argument Against Livestock Doesn’t Add Up
-

 International3 hours ago
International3 hours agoGeorgia county admits illegally certifying 315k ballots in 2020 presidential election
-

 Environment1 day ago
Environment1 day agoCanada’s river water quality strong overall although some localized issues persist









