Economy
Abandoned Greenland ice base calls co2 concerns into question
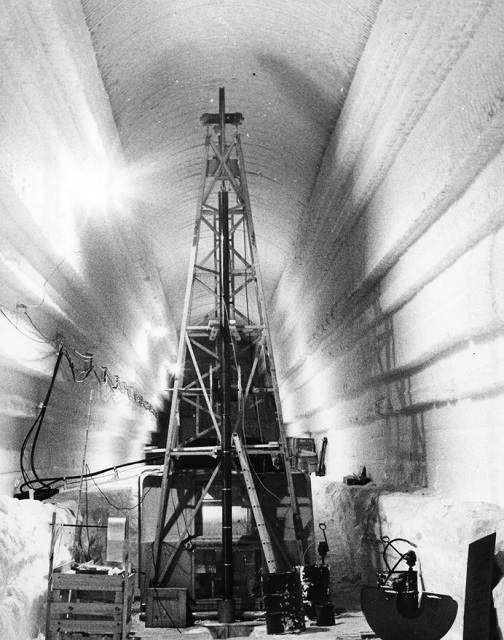

Wired.com had another story with a climate change hook on July 20 called, “An Abandoned Arctic Military Base Just Spilled a Scientific Secret.” It began “During the Cold War, the US built a network of tunnels in the Greenland ice sheet. Sixty years later, the base has provided a critical clue about the climate crisis.”
From 1959 to 1966, Project Iceworm in Greenland was meant to establish military bases in caverns carved out of glacial ice, with Camp Century being the trial run. The plan was to locate as many as 600 intercontinental ballistic missiles in under-ice caverns, invisible to the Soviets, and within striking range of the USSR.
However, the project never did work out and it was terminated in 1966.
The climate angle comes out of what was discovered in remarkable ice core the military drilled through the glacier.
The Wired article said that researchers drilled a 4,550-foot-deep core through the ice sheet, and when they hit earth, they drilled another 12 feet, bringing up a plug of frozen sand, dirty ice, cobbles, and mud.
It continued, “Nobody cared much about the sediment, though, until 2018, when it was rediscovered in … a University of Copenhagen freezer.” Now, an international team of researchers has analyzed that sediment, and made a major scientific discovery.
“In that frozen sediment are leaf fossils and little bits of bugs and twigs and mosses that tell us in the past there was a tundra ecosystem living where today there’s almost a mile of ice,” says University of Vermont geoscientist Paul Bierman, coauthor of a new paper describing the finding in the journal Science. “The ice sheet is fragile. It can disappear, and it has disappeared. Now we have a date for that.”
Wired wrote, “Previously, scientists reckoned that Greenland iced over some 2.5 million years ago, and has been that way since. In 2021, Bierman and his colleagues determined that it was actually ice-free sometime in the past million years. Now, they’ve dated the tundra ecosystem captured in the Camp Century core to a mere 416,000 years ago—so northwestern Greenland couldn’t have been locked in ice then.”
And here’s where the mental gymnastics take place: Scientists also know that at that time, global temperatures were similar or slightly warmer than what they are today. However, back then, atmospheric concentrations of planet-warming carbon dioxide were about 280 parts per million, compared to today’s 422 parts per million—a number that continues to skyrocket.”
The article continued, “Because humans have so dramatically and rapidly warmed the climate, we’re exceeding the conditions that had previously led to the wide-scale melting of Greenland’s ice sheet and gave rise to the tundra ecosystem. “It’s a forewarning,” says Utah State University geoscientist Tammy Rittenour, a coauthor of the new paper. “This can happen under much lower CO2 conditions than our current state.”
Whoa, there, Nelly! You’re telling me that carbon dioxide levels were a full third less than they are today, and yet the northernmost portions of Greenland (the most likely to freeze) was tundra? Greenland did not have the better part of a mile of ice covering it when CO2 was well below the supposedly crucial threshold of 350 parts per million?
Indeed, the article goes on to say, “That melting [of all the Greenland ice] could be incredibly perilous. The new study finds that the Greenland ice melt 400,000 years ago caused at least 5 feet of sea level rise, but perhaps as much as 20 feet. “These findings raise additional concern that we could be coming perilously close to the threshold for collapse of the Greenland ice sheet and massive additional sea level rise of a meter or more,” says University of Pennsylvania climate scientist Michael Mann, who wasn’t involved in the research. Today, less than a foot of global sea level rise is already causing serious flooding and storm surge problems for coastal cities—and that’s without the potential for an additional 20 feet.”
Again, look at the claim: carbon dioxide levels were much lower, sea levels were much higher, and the Greenland ice sheet was much smaller.
This new evidence makes reasonable people wonder if there truly is a link between carbon dioxide levels, global warming, and disappearance of ice sheets. How could so much ice be gone, melted into the ocean, with such a low CO2 level?
Surely something here doesn’t jive. And yet the world is in a tizzy over rising carbon dioxide levels.
Maybe someone should go back to Greenland, and drill a few more core samples to test this theory before we destroy our economy and our lives.
Perhaps the science of climate change isn’t settled after all.
Brian Zinchuk is editor and owner of Pipeline Online, and occasional contributor to the Frontier Centre for Public Policy. He can be reached at [email protected]. First published here.
Business
Fuelled by federalism—America’s economically freest states come out on top

From the Fraser Institute
Do economic rivalries between Texas and California or New York and Florida feel like yet another sign that America has become hopelessly divided? There’s a bright side to their disagreements, and a new ranking of economic freedom across the states helps explain why.
As a popular bumper sticker among economists proclaims: “I heart federalism (for the natural experiments).” In a federal system, states have wide latitude to set priorities and to choose their own strategies to achieve them. It’s messy, but informative.
New York and California, along with other states like New Mexico, have long pursued a government-centric approach to economic policy. They tax a lot. They spend a lot. Their governments employ a large fraction of the workforce and set a high minimum wage.
They aren’t socialist by any means; most property is still in private hands. Consumers, workers and businesses still make most of their own decisions. But these states control more resources than other states do through taxes and regulation, so their governments play a larger role in economic life.
At the other end of the spectrum, New Hampshire, Tennessee, Florida and South Dakota allow citizens to make more of their own economic choices, keep more of their own money, and set more of their own terms of trade and work.
They aren’t free-market utopias; they impose plenty of regulatory burdens. But they are economically freer than other states.
These two groups have, in other words, been experimenting with different approaches to economic policy. Does one approach lead to higher incomes or faster growth? Greater economic equality or more upward mobility? What about other aspects of a good society like tolerance, generosity, or life satisfaction?
For two decades now, we’ve had a handy tool to assess these questions: The Fraser Institute’s annual “Economic Freedom of North America” index uses 10 variables in three broad areas—government spending, taxation, and labor regulation—to assess the degree of economic freedom in each of the 50 states and the territory of Puerto Rico, as well as in Canadian provinces and Mexican states.
It’s an objective measurement that allows economists to take stock of federalism’s natural experiments. Independent scholars have done just that, having now conducted over 250 studies using the index. With careful statistical analyses that control for the important differences among states—possibly confounding factors such as geography, climate, and historical development—the vast majority of these studies associate greater economic freedom with greater prosperity.
In fact, freedom’s payoffs are astounding.
States with high and increasing levels of economic freedom tend to see higher incomes, more entrepreneurial activity and more net in-migration. Their people tend to experience greater income mobility, and more income growth at both the top and bottom of the income distribution. They have less poverty, less homelessness and lower levels of food insecurity. People there even seem to be more philanthropic, more tolerant and more satisfied with their lives.
New Hampshire, Tennessee, and South Dakota topped the latest edition of the report while Puerto Rico, New Mexico, and New York rounded out the bottom. New Mexico displaced New York as the least economically free state in the union for the first time in 20 years, but it had always been near the bottom.
The bigger stories are the major movers. The last 10 years’ worth of available data show South Carolina, Ohio, Wisconsin, Idaho, Iowa and Utah moving up at least 10 places. Arizona, Virginia, Nebraska, and Maryland have all slid down 10 spots.
Over that same decade, those states that were among the freest 25 per cent on average saw their populations grow nearly 18 times faster than those in the bottom 25 per cent. Statewide personal income grew nine times as fast.
Economic freedom isn’t a panacea. Nor is it the only thing that matters. Geography, culture, and even luck can influence a state’s prosperity. But while policymakers can’t move mountains or rewrite cultures, they can look at the data, heed the lessons of our federalist experiment, and permit their citizens more economic freedom.
Business
The world is no longer buying a transition to “something else” without defining what that is

From Resource Works
Even Bill Gates has shifted his stance, acknowledging that renewables alone can’t sustain a modern energy system — a reality still driving decisions in Canada.
You know the world has shifted when the New York Times, long a pulpit for hydrocarbon shame, starts publishing passages like this:
“Changes in policy matter, but the shift is also guided by the practical lessons that companies, governments and societies have learned about the difficulties in shifting from a world that runs on fossil fuels to something else.”
For years, the Times and much of the English-language press clung to a comfortable catechism: 100 per cent renewables were just around the corner, the end of hydrocarbons was preordained, and anyone who pointed to physics or economics was treated as some combination of backward, compromised or dangerous. But now the evidence has grown too big to ignore.
Across Europe, the retreat to energy realism is unmistakable. TotalEnergies is spending €5.1 billion on gas-fired plants in Britain, Italy, France, Ireland and the Netherlands because wind and solar can’t meet demand on their own. Shell is walking away from marquee offshore wind projects because the economics do not work. Italy and Greece are fast-tracking new gas development after years of prohibitions. Europe is rediscovering what modern economies require: firm, dispatchable power and secure domestic supply.
Meanwhile, Canada continues to tell itself a different story — and British Columbia most of all.
A new Fraser Institute study from Jock Finlayson and Karen Graham uses Statistics Canada’s own environmental goods and services and clean-tech accounts to quantify what Canada’s “clean economy” actually is, not what political speeches claim it could be.
The numbers are clear:
- The clean economy is 3.0–3.6 per cent of GDP.
- It accounts for about 2 per cent of employment.
- It has grown, but not faster than the economy overall.
- And its two largest components are hydroelectricity and waste management — mature legacy sectors, not shiny new clean-tech champions.
Despite $158 billion in federal “green” spending since 2014, Canada’s clean economy has not become the unstoppable engine of prosperity that policymakers have promised. Finlayson and Graham’s analysis casts serious doubt on the explosive-growth scenarios embraced by many politicians and commentators.
What’s striking is how mainstream this realism has become. Even Bill Gates, whose philanthropic footprint helped popularize much of the early clean-tech optimism, now says bluntly that the world had “no chance” of hitting its climate targets on the backs of renewables alone. His message is simple: the system is too big, the physics too hard, and the intermittency problem too unforgiving. Wind and solar will grow, but without firm power — nuclear, natural gas with carbon management, next-generation grid technologies — the transition collapses under its own weight. When the world’s most influential climate philanthropist says the story we’ve been sold isn’t technically possible, it should give policymakers pause.
And this is where the British Columbia story becomes astonishing.
It would be one thing if the result was dramatic reductions in emissions. The provincial government remains locked into the CleanBC architecture despite a record of consistently missed targets.
Since the staunchest defenders of CleanBC are not much bothered by the lack of meaningful GHG reductions, a reasonable person is left wondering whether there is some other motivation. Meanwhile, Victoria’s own numbers a couple of years ago projected an annual GDP hit of courtesy CleanBC of roughly $11 billion.
But here is the part that would make any objective analyst blink: when I recently flagged my interest in presenting my research to the CleanBC review panel, I discovered that the “reviewers” were, in fact, two of the key architects of the very program being reviewed. They were effectively asked to judge their own work.
You can imagine what they told us.
What I saw in that room was not an evidence-driven assessment of performance. It was a high-handed, fact-light defence of an ideological commitment. When we presented data showing that doctrinaire renewables-only thinking was failing both the economy and the environment, the reception was dismissive and incurious. It was the opposite of what a serious policy review looks like.
Meanwhile our hydro-based electricity system is facing historic challenges: long term droughts, soaring demand, unanswered questions about how growth will be powered especially in the crucial Northwest BC region, and continuing insistence that providers of reliable and relatively clean natural gas are to be frustrated at every turn.
Elsewhere, the price of change increasingly includes being able to explain how you were going to accomplish the things that you promise.
And yes — in some places it will take time for the tide of energy unreality to recede. But that doesn’t mean we shouldn’t be improving our systems, reducing emissions, and investing in technologies that genuinely work. It simply means we must stop pretending politics can overrule physics.
Europe has learned this lesson the hard way. Global energy companies are reorganizing around a 50-50 world of firm natural gas and renewables — the model many experts have been signalling for years. Even the New York Times now describes this shift with a note of astonishment.
British Columbia, meanwhile, remains committed to its own storyline even as the ground shifts beneath it. This isn’t about who wins the argument — it’s about government staying locked on its most basic duty: safeguarding the incomes and stability of the families who depend on a functioning energy system.
Resource Works News
-

 Alberta15 hours ago
Alberta15 hours agoThe Recall Trap: 21 Alberta MLA’s face recall petitions
-

 Digital ID2 days ago
Digital ID2 days agoCanada considers creating national ID system using digital passports for domestic use
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoHere’s why city hall should save ‘blanket rezoning’ in Calgary
-

 Fraser Institute2 days ago
Fraser Institute2 days agoClaims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoToo nice to fight, Canada’s vulnerability in the age of authoritarian coercion
-

 Fly Straight - John Ivison2 days ago
Fly Straight - John Ivison2 days agoMPs who cross the floor are dishonourable members
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoMeet REEF — the massive new export engine Canadians have never heard of
-
 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoTanker ban politics leading to a reckoning for B.C.









