Fraser Institute
U.S. election should focus or what works and what doesn’t work

From the Fraser Institute
As Republicans and Democrats make their final pitch to voters, they’ve converged on some common themes. Kamala Harris wants to regulate the price of food. Donald Trump wants to regulate the price of credit. Harris wants the tax code to favour the 2.5 per cent of workers who earn tips. So does Trump. Harris wants the government to steer more labour and capital into manufacturing. And so does Trump.
With each of these proposals, the candidates think the United States would be better off if the government made more economic decisions and—by implication—if individual citizens made fewer economic decisions. Both should pay closer attention to Zimbabwe. Yes, Zimbabwe.
Why does a country with abundant natural resources, rich culture and unparalleled beauty have one-sixth the average income of neighbouring Botswana? While we’re at it, why do twice as many children die in infancy in Azerbaijan as across the border in Georgia? Why do Hungarians work 20 per cent longer than their Austrian neighbours but earn 45 per cent less? Why is extreme poverty 200 times more common in Laos than across the Mekong River in Thailand?
Or how about this one: Why were more than one-quarter of Estonians formerly exposed to dangerous levels of air pollution when the country was socialist while today nearly every Estonian breathes clean air in what is ranked the cleanest country in the world.
These are anecdotes. However, the plural of anecdote is data, and through careful and systematic study of the data, we can learn what works and what doesn’t. Unfortunately, the populist economic policies in vogue among Democrats and Republicans do not work.
What does work is economic freedom.
Economic freedoms are a subset of human freedoms. When people have more economic freedom, they are allowed to make more of their own economic choices—choices about work, about buying and selling goods and services, about acquiring and using property, and about forming contracts with others.
For nearly 30 years, the Fraser Institute has been measuring economic freedom across countries. On one hand, governments can stop people from making their own economic choices through taxes, regulations, barriers to trade and manipulation of the value of money (see the proposals of Harris and Trump above). On the other hand, governments can enable individual economic choice by protecting people and their property.
The index published in Fraser’s annual Economic Freedom of the World report incorporates 45 indicators to measure how governments either prevent or enable individual economic choice. The result reveals the degree of economic freedom in 165 countries and territories worldwide, with data going back to 1970.
According to the latest report, comparatively wealthy Botswanans rank 84 places ahead of Zimbabweans in terms of the economic freedom their government permits them. Georgians rank 107 places ahead of Azerbaijanis, Thais rank 60 places ahead of Laotians, and Austrians are 32 places ahead of Hungarians.
The benefits of economic freedom go far beyond anecdotes and rankings. As Estonia—once one of the least economically free places in the world and now among the freest—dramatically shows, freer countries tend not only to be more prosperous but greener and healthier.
In fact, economists and other social scientists have conducted nearly 1,000 studies using the index to assess the effect of economic freedom on different aspects of human wellbeing. Their statistical comparisons include hundreds and sometimes thousands of data points and carefully control for other factors like geography, natural resources and disease environment.
Their results overwhelmingly support the idea that when people are permitted more economic freedom, they prosper. Those who live in freer places enjoy higher and faster-growing incomes, better health, longer life, cleaner environments, more tolerance, less violence, lower infant mortality and less poverty.
Economic freedom isn’t the only thing that matters for prosperity. Research suggests that culture and geography matter as well. While policymakers can’t always change people’s attitudes or move mountains, they can permit their citizens more economic freedom. If more did so, more people would enjoy the living standards of Botswana or Estonia and fewer people would be stuck in poverty.
As for the U.S., it remains relatively free and prosperous. Whatever its problems, decades of research cast doubt on the notion that America would be better off with policies that chip away at the ability of Americans to make their own economic choices.
Author:
Business
Brutal economic numbers need more course corrections from Ottawa

From the Fraser Institute
By Matthew Lau
Canada’s lagging productivity growth has been widely discussed, especially after Bank of Canada senior deputy governor Carolyn Rogers last year declared it “an emergency” and said “it’s time to break the glass.” The federal Liberal government, now entering its eleventh year in office, admitted in its recent budget that “productivity remains weak, limiting wage gains for workers.”
Numerous recent reports show just how weak Canada’s productivity has been. A recent study published by the Fraser Institute shows that since 2001, labour productivity has increased only 16.5 per cent in Canada vs. 54.7 per cent in the United States, with our underperformance especially notable after 2017. Weak business investment is a primary reason for Canada’s continued poor economic outcomes.
A recent McKinsey study provides worrying details about how the productivity crisis pervades almost all sectors of the economy. Relative to the U.S., our labour productivity underperforms in: mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction; construction; manufacturing; transportation and warehousing; retail trade; professional, scientific, and technical services; real estate and rental leasing; wholesale trade; finance and insurance; information and cultural industries; accommodation and food services; utilities; arts, entertainment and recreation; and administrative and support, waste management and remediation services.
Canada has relatively higher labour productivity in just one area: agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting. To make matters worse, in most areas where Canada’s labour productivity is less than American, McKinsey found we had fallen further behind from 2014 to 2023. In addition to doing poorly, Canada is trending in the wrong direction.
Broadening the comparison to include other OECD countries does not make the picture any rosier—Canada “is growing more slowly and from a lower base,” as McKinsey put it. This underperformance relative to other countries shows Canada’s economic productivity crisis is not the result of external factors but homemade.
The federal Liberals have done little to reverse our relative decline. The Carney government’s proposed increased spending on artificial intelligence (AI) may or may not help. But its first budget missed a clear opportunity to implement tax reform and cuts. As analyses from the Fraser Institute, University of Calgary, C.D. Howe Institute, TD Economics and others have argued, fixing Canada’s uncompetitive tax regime would help lift productivity.
Regulatory expansion has also driven Canada’s relative economic decline but the federal budget did not reduce the red tape burden. Instead, the Carney government empowered cabinet to decide which large natural resource and infrastructure projects are in the “national interest”—meaning that instead of predictable transparent rules, businesses must answer to the whims of politicians.
The government has also left in place many of its Trudeau-era environmental regulations, which have helped push pipeline investors away for years. It is encouraging that a new “memorandum of understanding” between Ottawa and Alberta may pave the way for a new oil pipeline. A memorandum of undertaking would have been better.
Although the government paused its phased-in ban on conventionally-powered vehicle sales in the face of heavy tariff-related headwinds to Canada’s automobile sector, it still insists that all new light-duty vehicle sales by 2035 must be electric. Liberal MPs on the House of Commons Industry Committee recently voted against a Conservative motion calling for repeal of the EV mandate. Meanwhile, Canadian consumers are voting with their wallets. In September, only 10.2 per cent of new motor vehicle sales were “zero-emission,” an ominous18.2 per cent decline from last year.
If the Carney government continues down its current path, it will only make productivity and consumer welfare worse. It should change course to reverse Canada’s economic underperformance and help give living standards a much-needed boost.
Fraser Institute
Claims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny

From the Fraser Institute
By Tom Flanagan
The new book Dead Wrong: How Canada Got the Residential School Story So Wrong is a follow-up to Grave Error, published by True North in 2023. Grave Error instantly became a best-seller. People wanted to read the book because it contained well-documented information not readily available elsewhere concerning the history of Canada’s Indian Residential Schools (IRS) and the facts surrounding recent claims about “unmarked graves.”
Why another book? Because the struggle for accurate information continues. Let me share with you a little of what’s in Dead Wrong.
Outrageously, the New York Times, one of the world’s most prestigious newspapers, has never retracted its absurd headline that “mass graves” were uncovered in Kamloops, British Columbia. Jonathan Kay, the North American editor of Quillette, exposes that scandal.
The legacy media were enthused about the so-called documentary Sugarcane, a feature-length film sponsored by National Geographic, which was nominated for an Academy Award. The only reporter to spot the dozens of factual errors in Sugarcane was independent journalist Michelle Stirling; Dead Wrong includes her analysis “The Bitter Roots of Sugarcane.”
In the spring of 2024, the small city of Quesnel, B.C., made national news when the mayor’s wife bought 10 copies of Grave Error for distribution to friends. After noisy protests held by people who had never read the book, Quesnel city council voted to censure Mayor Ron Paull and tried to force him from office. It’s all described in Dead Wrong.
Also not to be forgotten is how the Law Society of B.C. forced upon its members training materials asserting against all evidence that children’s remains have been discovered in Kamloops. As told by James Pew, B.C. MLA Dallas Brodie was expelled from the Conservative caucus for daring to point out the emperor’s lack of clothing.
Then there’s the story of Jim McMurtry, suspended by the Abbotsford District School Board shortly after the 2021 Kamloops announcement about “unmarked graves.” McMurtry’s offence was to tell students the truth that, while some Indigenous students did die in residential schools, the main cause was tuberculosis. His own book The Scarlet Lesson is excerpted here.
Historian Ian Gentles and former IRS teacher Pim Wiebel offer a richly detailed analysis of health and medical conditions in the schools. They show that these were much better than what prevailed in the Indian reserves from which most students came.
Another important contribution to understanding the medical issues is by Dr. Eric Schloss, narrating the history of the Charles Camsell Indian Hospital in Edmonton. IRS facilities usually included small clinics, but students with serious problems were often transferred to Indian Hospitals for more intensive care. Schloss, who worked in the Camsell, describes how it delivered state-of-the-art medicine, probably better than the care available to most children anywhere in Canada at the time.
Rodney Clifton’s contribution, “They would call me a ‘Denier,’” describes his experiences working in two IRS in the 1960s. Clifton does not tell stories of hunger, brutal punishment and suppression of Indigenous culture, but of games, laughter and trying to learn native languages from his Indian and Inuit charges.
Toronto lawyer and historian Greg Piasetzki explains how “Canada Wanted to Close All Residential Schools in the 1940s. Here’s why it couldn’t.” For many Indian parents, particularly single parents and/or those with large numbers of children, the IRS were the best deal available. And they offered paid employment to large numbers of Indians as cooks, janitors, farmers, health-care workers, and even teachers and principals.
Finally, Frances Widdowson analyzes the charge of residential school “denialism” used by true believers in the Kamloops narrative to shut down criticism or questions. Winnipeg Centre MP Leah Gazan in 2022 persuaded the House of Commons to give unanimous consent to a resolution on residential school genocide: “That, in the opinion of the House this government must recognize what happened in Canada’s Indian residential schools as genocide.”
In 2024, Gazan took the next step by introducing a private member’s bill to criminalize dissent about the IRS system. The bill failed to pass, but Gazan reintroduced it in 2025. Had these provisions been in force back in 2021, it might well have become a crime to point out that the Kamloops ground-penetrating radar (GPR) survey had identified soil anomalies, not buried bodies.
While the wheels of legislation and litigation grind and spin, those who wish to limit open discussion of residential schools attack truth-tellers as “denialists,” a term drawn from earlier debates about the Holocaust. As the proponents of the Kamloops narrative fail to provide convincing hard evidence for it, they hope to mobilize the authority of the state to stamp out dissent. One of the main goals of publishing Dead Wrong is to head off this drive toward authoritarianism.
Happily, Dead Wrong, like Grave Error, has already become an Amazon best-seller. The struggle for truth continues.
-

 National1 day ago
National1 day agoCanada’s free speech record is cracking under pressure
-

 Energy16 hours ago
Energy16 hours agoTanker ban politics leading to a reckoning for B.C.
-

 Energy16 hours ago
Energy16 hours agoMeet REEF — the massive new export engine Canadians have never heard of
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTaxpayers Federation calls on politicians to reject funding for new Ottawa Senators arena
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoOttawa’s New Hate Law Goes Too Far
-

 Business16 hours ago
Business16 hours agoToo nice to fight, Canada’s vulnerability in the age of authoritarian coercion
-
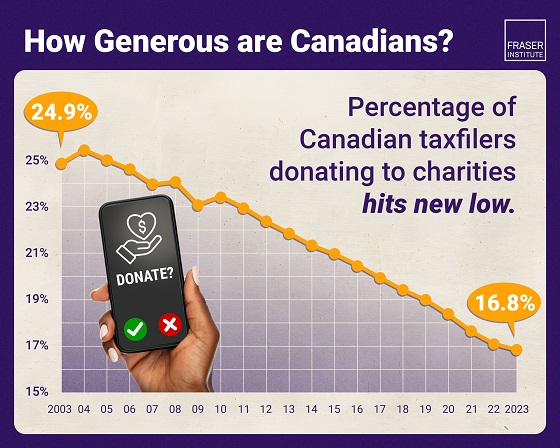
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoAlbertans give most on average but Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
-

 Fraser Institute16 hours ago
Fraser Institute16 hours agoClaims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny




