Environment
Talks adopt ‘rulebook’ to put Paris climate deal into action

KATOWICE, Poland — Almost 200 nations, including the world’s top greenhouse gas producers, China and the United States, have adopted a set of rules meant to breathe life into the 2015 Paris climate accord by setting out how countries should report their emissions and efforts to reduce them.
But negotiators delayed other key decisions until next year — a move that frustrated environmentalists and countries that wanted more ambitious goals in light of scientists’ warnings that the world must shift sharply away from fossil fuels in the coming decade.
“The majority of the rulebook for the Paris agreement has been created, which is something to be thankful for,” said Mohamed Adow, a climate policy expert at Christian Aid. “But the fact countries had to be dragged kicking and screaming to the finish line shows that some nations have not woken up” to the dire consequences of global warming as outlined in a report by the U.N Panel on Climate Change, or IPCC.
Officials at the talks, which ended late Saturday in the Polish city of Katowice, agreed upon universal rules on how nations can cut emissions. Poor countries secured assurances on financial support to help them reduce emissions, adapt to changes such as rising sea levels and pay for damage that has already happened.
“Through this package, you have made a thousand little steps forward together,” said Michal Kurtyka, a senior Polish official who led the talks.
While each country would likely find some parts of the agreement it did not like, he said, efforts were made to balance the interests of all parties.
“We will all have to give in order to gain,” he said. “We will all have to be courageous to look into the future and make yet another step for the sake of humanity.”
The talks took place against a backdrop of growing concern among scientists that global warming is proceeding faster than governments are responding to it. Last month, a study found that global warming will worsen disasters such as the deadly California wildfires and the powerful hurricanes that have hit the United States this year.
The recent report by the IPCC concluded that while it’s possible to cap global warming at 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) by the end of the century compared to pre-industrial times, doing so would require a dramatic overhaul of the global economy, including a shift away from fossil fuels.
Alarmed by efforts to include that idea in the final text of the meeting, the oil-exporting nations of the U.S., Russia, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait blocked an endorsement of the IPCC report midway through this month’s talks. That prompted uproar from vulnerable countries like small island nations and environmental groups.
The final text omitted a previous reference to specific reductions in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and merely welcomed the “timely completion” of the IPCC report, not its conclusions.
Johan Rockstrom, a scientist who helps to lead the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, called the agreement “a relief.” The Paris deal, he said, “is alive and kicking, despite a rise in populism and nationalism.”
His biggest concern, he said, is that the summit “failed to align ambitions with science, in particular missing the necessity of making clear that global emissions from fossil fuels must be cut by half by 2030” to stay in line with the IPCC report.
Alden Meyer, director of strategy and policy at the Union of Concerned Scientists, said the talks created “a solid foundation for implementation and strengthening” of the Paris agreement and could help bring the U.S. back into the deal by a future presidential administration.
One major sticking point was how to create a functioning market in carbon credits. Economists believe that an international trading system could be an effective way to drive down greenhouse gas emissions and raise large amounts of money for measures to curb global warming.
But Brazil wanted to keep the piles of carbon credits it had amassed under an old system that developed countries say wasn’t credible or transparent.
Among those that pushed back hardest was the United States, despite President Donald Trump’s decision to pull out of the Paris climate accord and his promotion of coal as a source of energy.
“Overall, the U.S. role here has been somewhat schizophrenic — pushing coal and dissing science on the one hand, but also working hard in the room for strong transparency rules,” said Elliot Diringer of the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions, a Washington
The U.S. is still technically in the Paris agreement until 2020, which is why American officials participated in the Katowice talks.
When it came to closing potential loopholes that could allow countries to dodge their commitments to cut emissions, “the U.S. pushed harder than nearly anyone else for transparency rules that put all countries under the same system, and it’s largely succeeded,” Diringer said.
In the end, a decision on the mechanics of an emissions-trading system was postponed to next year’s meeting. Countries also agreed to consider the issue of raising ambitions at a U.N. summit in New York next September.
Canada’s Environment Minister Catherine McKenna suggested there was no alternative to such meetings if countries want to tackle global problems, especially as multilateral diplomacy is under pressure from nationalism.
“The world has changed. The political landscape has changed,” she told The Associated Press. “Still you’re seeing here that we’re able to make progress. We’re able to discuss the issues. We’re able to come to solutions.”
___
Read more stories on climate issues by The Associated Press at https://www.apnews.com/Climate .
Frank Jordans, The Associated Press
Business
EPA to shut down “Energy Star” program

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
The Environmental Protection Agency is planning to shut down its long-standing Energy Star program, which has certified energy-efficient appliances for over three decades. The move is part of a sweeping agency reorganization that also includes eliminating the climate change office and other environmental initiatives not mandated by law.
Key Details:
- EPA officials announced the dismantling of the Energy Star program in a staff meeting on May 6, 2025.
- The agency is eliminating its climate-related divisions, including those overseeing Energy Star and greenhouse gas reporting.
- The move is framed as part of a broader restructuring to prioritize statutory obligations and reduce government overreach.
Diving Deeper:
In a significant shift for federal environmental policy, the Environmental Protection Agency will eliminate the Energy Star program, a popular certification used to identify energy-efficient home appliances like refrigerators, dishwashers, and dryers. Internal documents and a recorded staff meeting reveal that EPA leadership is dismantling entire divisions focused on climate change and voluntary energy initiatives.
Paul Gunning, director of the EPA’s Office of Atmospheric Protection—which is also being cut—told staff the agency would “de-prioritize and eliminate” all climate-related work outside of what’s legally required. The Energy Star program, created in 1992 under President George H.W. Bush, has helped save American households and businesses over $500 billion in energy costs and prevented billions of metric tons of greenhouse gases from entering the atmosphere.
Supporters argue the program has been a bipartisan success story. Nearly 90% of U.S. consumers recognize the Energy Star label, and manufacturers have long relied on it to market efficient products. Even the U.S. Chamber of Commerce and major industries, from lighting to food-equipment makers, have urged the EPA to keep it in place. A joint letter in March from dozens of trade organizations to EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin warned that ending the program would not benefit Americans.
Critics of the move, like Paula R. Glover of the Alliance to Save Energy, say the Energy Star program costs just $32 million annually but delivers $40 billion in utility bill savings. “Eliminating the Energy Star program is counterintuitive to this administration’s pledge to reduce household costs,” she said. Glover added that with electricity demand set to rise 35–50% by 2040, energy-saving measures are more important than ever.
The Biden-era EPA heavily prioritized climate policy and environmental regulation, often blurring the lines between environmental stewardship and bureaucratic overreach. In contrast, the current administration—under 47th President Donald Trump—is refocusing the agency toward its statutory mission, aligning with the broader conservative agenda of streamlining government and cutting redundant or ideologically-driven programs.
While Trump previously attempted to defund Energy Star during his first term, the effort failed amid bipartisan concern that privatization could lead to lowered standards. The current plan appears to accomplish the same goal through internal restructuring, cutting not just Energy Star but programs related to methane emissions reduction, climate science, and policy.
Notably, the agency’s largest union has cried foul over how the reorganization was handled. Marie Owens Powell, its president, accused the agency of “union busting” after being blocked from attending reorganization meetings. Staff have been told they may be reassigned or let go as the EPA scales back to staffing levels not seen since the Reagan administration.
For an agency that has long served as the regulatory spearhead for the left’s climate agenda, this realignment could represent a return to core environmental functions—clean air and water—while removing the taxpayer burden of subsidizing climate-centric programs with questionable returns. The decision also signals a shift away from corporatist alliances that prop up select industries under the guise of energy policy.
Alberta
Energy projects occupy less than three per cent of Alberta’s oil sands region, report says

From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
‘Much of the habitat across the region is in good condition’
The footprint of energy development continues to occupy less than three per cent of Alberta’s oil sands region, according to a report by the Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Institute (ABMI).
As of 2021, energy projects impacted just 2.6 per cent of the oil sands region, which encompasses about 142,000 square kilometers of boreal forest in northern Alberta, an area nearly the size of Montana.
“There’s a mistaken perception that the oil sands region is one big strip mine and that’s simply not the case,” said David Roberts, director of the institute’s science centre.
“The energy footprint is very small in total area once you zoom out to the boreal forest surrounding this development.”

Between 2000 and 2021, the total human footprint in the oil sands region (including energy, agriculture, forestry and municipal uses) increased from 12.0 to 16.5 per cent.
At the same time, energy footprint increased from 1.4 to 2.6 per cent – all while oil sands production surged from 667,000 to 3.3 million barrels per day, according to the Alberta Energy Regulator.
The ABMI’s report is based on data from 328 monitoring sites across the Athabasca, Cold Lake and Peace River oil sands regions. Much of the region’s oil and gas development is concentrated in a 4,800-square-kilometre zone north of Fort McMurray.
“In general, the effects of energy footprint on habitat suitability at the regional scale were small…for most species because energy footprint occupies a small total area in the oil sands region,” the report says.
Researchers recorded species that were present and measured a variety of habitat characteristics.

The status and trend of human footprint and habitat were monitored using fine-resolution imagery, light detection and ranging data as well as satellite images.
This data was used to identify relationships between human land use, habitat and population of species.
The report found that as of 2021, about 95 per cent of native aquatic and wetland habitat in the region was undisturbed while about 77 per cent of terrestrial habitat was undisturbed.
Researchers measured the intactness of the region’s 719 plant, insect and animal species at 87 per cent, which the report states “means much of the habitat across the region is in good condition.”
While the overall picture is positive, Roberts said the report highlights the need for ongoing attention to vegetation regeneration on seismic lines along with the management of impacts to species such as Woodland Caribou.

The ABMI has partnered with Indigenous communities in the region to monitor species of cultural importance. This includes a project with the Lakeland Métis Nation on a study tracking moose occupancy around in situ oil sands operations in traditional hunting areas.
“This study combines traditional Métis insights from knowledge holders with western scientific methods for data collection and analysis,” Roberts said.
The institute also works with oil sands companies, a relationship that Roberts sees as having real value.
“When you are trying to look at the impacts of industrial operations and trends in industry, not having those people at the table means you are blind and don’t have all the information,” Roberts says.
The report was commissioned by Canada’s Oil Sands Innovation Alliance, the research arm of Pathways Alliance, a consortium of the six largest oil sands producers.
“We tried to look around when we were asked to put together this report to see if there was a template but there was nothing, at least nothing from a jurisdiction with significant oil and gas activity,” Roberts said.
“There’s a remarkable level of analysis because of how much data we were able to gather.”
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoOil tankers in Vancouver are loading plenty, but they can load even more
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoEnergy projects occupy less than three per cent of Alberta’s oil sands region, report says
-

 Alberta2 days ago
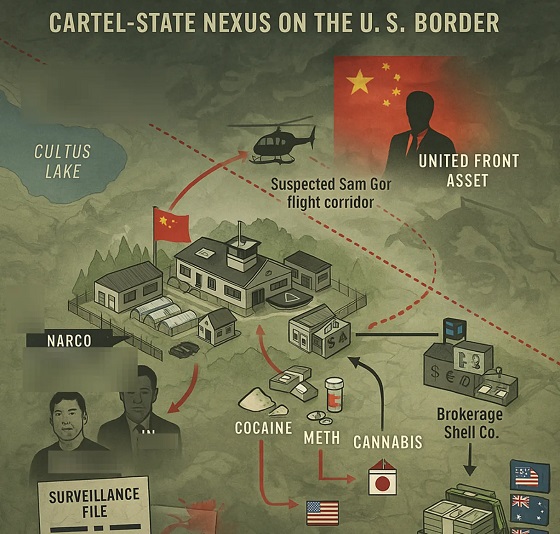
Alberta2 days agoCharges laid in record cocaine seizure
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCarney’s energy superpower rhetoric falls flat without policy certainty
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoWATCH: U.S. ending bombing campaign on Yemeni militant group
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoPam Bondi Reveals What The Holdup Is With Epstein File Release
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoInnovative Solutions Like This Plan To Provide Power For Data Centres Will Drive Natural Gas Demand For Decades
-

 Business12 hours ago
Business12 hours agoTrump announces UK will fast-track American products under new deal