Agriculture
Moisture situation in Alberta following warm and dry first half of winter
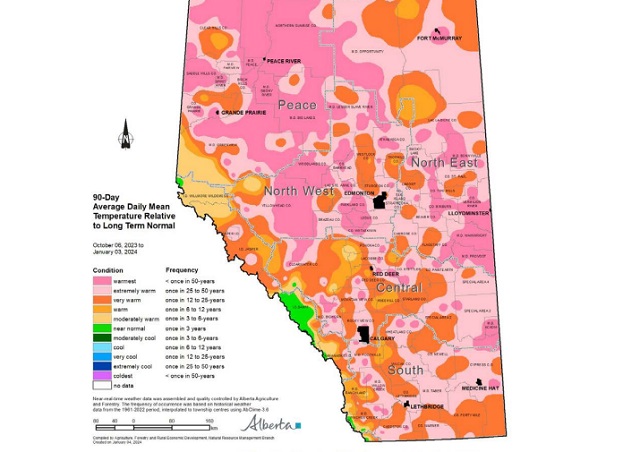
Agricultural Moisture Situation Update – January 3, 2024
Synopsis
This year’s El Niño has developed into a strong El Niño and currently has a 54% chance of developing into a “historically strong” event, according to NOAA. Current forecasts are projecting El Niño to diminish in April 2024. In the past for Alberta, not all El Niño’s have resulted in warmer and drier weather; however, this unusually warm and dry winter will forever be tied to the 2023-2024 El Niño and will serve as an important data point in the future.
In the 90-days since October 6, 2023, temperatures have remained well above average, with many parts of the northern-half of the province seeing temperatures this warm less than once in 50 years (Map 1). This coupled with low precipitation accumulations has resulted in virtually snow free
conditions across parts of all four of our agricultural regions
(Map 2).
Winter Precipitation Accumulations
November 1, 2023 to January 3, 2024
Since November 1st, the unofficial start to winter in Alberta, precipitation has been well below average across much of Alberta’s agricultural areas (Map 3).

Most of the lands south of Grande Prairie and north of Ponoka are estimated to have a winter thus far, this dry on average, less than once in 50-years. Dry conditions have also persisted across the Central and Southern Regions, ranging from a few widely scattered pockets of near normal to at least once in 25 year lows, centered around the Jenner area (approx. 200 km east of Calgary). Total accumulations currently range from less than 3 mm through parts of the North West and North East Regions up to only 20-30 mm along the foothills and through the western and northern portions of the Peace Region (Map 4).

For the dryer parts of the North West and North East Regions this translates to less than 10% of the 1991-2020 average (Map 5).

Elsewhere, most other lands have received precipitation accumulations that have generally been less
than 50% of the 1991-2020 average.
Perspective
From an annual moisture budget perspective, October through to March generally mark the dry season across the agricultural areas (Map 6), accounting for only about 20% of average annual accumulations across most of the Southern Region, to upwards of 30-35% across the Peace Region.

These significant moisture deficits thus far (50% of the way through the dry season), while discouraging to many, make up only a small portion of the annual moisture budget for an area. Winter is not over yet and if the current forecast is correct, a significant cold snap is on its way over the next few days and it is expected to persist well into next week, perhaps even longer. Along with the cold snap, there is also a forecast for moisture and the promise of at least some snow cover across many areas.
Spring is yet many weeks away and anything can happen between now and then. Furthermore, February on average, is the driest month of the year with most agricultural lands normally receiving less than 15 mm of moisture during this month (Map 6). Let’s hope, for the sake of our producers,
that we descend into at least near “normal” winter conditions and that we see one of Alberta’s famous weather reversals, with respect to moisture. Above average snow fall is very much needed now. Much of the land is extremely dry and has been held tenaciously in the grip of a long-lasting dry
cycle that needs to end soon!
Agriculture
Bill C-282, now in the Senate, risks holding back other economic sectors and further burdening consumers

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Bill C-282 currently sits in the Canadian Senate and stands on the precipice of becoming law in a matter of weeks. Essentially, this bill seeks to bestow immunity upon supply management from any potential future trade negotiations without offering increased market access to potential trade partners.
In simpler terms, it risks holding all other economic sectors hostage solely to safeguard the interests of a small, privileged group of farmers. This is far from an optimal scenario, and the implications of this bill spell bad news for Canadians.
Supply management, which governs poultry, egg, and dairy production in Canada, has traditionally enabled us to fulfill our domestic needs. Under this system, farmers are allocated government-sanctioned quotas to produce food for the nation. At the same time, high tariffs are imposed on imports of items such as chicken, butter, yogurt, cheese, milk, and eggs. This model has been in place for over five decades, ostensibly to shield family farms from economic volatility.
However, despite the implementation of supply management, Canada has witnessed a comparable decline in the number of farms as the United States, where a national supply management scheme does not exist. Supply management has failed to preserve much of anything beyond enriching select agricultural sectors.
For instance, dairy farmers now possess quotas valued at over $25 billion while concurrently burdening dairy processors with the highest-priced industrial milk in the Western world. Recent data indicates a significant surge in prices at the grocery store, with yogurt prices alone soaring by over 30 percent since December 2023. This escalation is increasingly straining the budgets of many consumers.
It’s evident to those knowledgeable about the situation that the emergence of Bill C-282 should come as no surprise. Proponents of supply management exert considerable influence over politicians across party lines, compelling them to support this bill to safeguard the interests of less than one percent of our economy, much to the ignorance of most Canadians. In the last federal budget, the dairy industry alone received over $300 million in research funds, funds that arguably exceed their actual needs.
While Canada’s agricultural sector accounts for approximately seven percent of our GDP, supply-managed industries represent only a small fraction of that figure. Supply-managed farms represent about five percent of all farms in Canada. Forging trade agreements with key partners such as India, China, and the United Kingdom is imperative not only for sectors like automotive, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology but for the vast majority of farms in livestock and grains to thrive and contribute to global welfare and prosperity. It is essential to recognize that Canada has much more to offer than merely self-sufficiency in food production.
Over time, the marketing boards overseeing quotas for farmers have amassed significant power and have proven themselves politically aggressive. They vehemently oppose any challenges to the existing system, targeting politicians, academics, and groups advocating for reform or abolition. Despite occasional resistance from MPs and Senators, no major political party has dared to question the disproportionate protection afforded to one sector over others. Strengthening our supply-managed sectors necessitates embracing competition, which can only serve to enhance their resilience and competitiveness.
A recent example of the consequences of protectionism is the United Kingdom’s decision to walk away from trade negotiations with Canada due to disagreements over access to our dairy market. Not only do many Canadians appreciate the quality of British cheese, but increased competition in the dairy section would also help drive prices down, a welcome relief given current economic challenges.
In the past decade, Canada has ratified trade agreements such as CUSMA, CETA, and CPTPP, all of which entailed breaches in our supply management regime. Despite initial concerns from farmers, particularly regarding the impact on poultry, eggs, and dairy, these sectors have fared well. A dairy farm in Ontario recently sold for a staggering $21.5 million in Oxford County. Claims of losses resulting from increased market access are often unfounded, as farmer boards simply adjust quotas when producers exit the industry.
In essence, Bill C-282 represents a misguided initiative driven by farmer boards capitalizing on the ignorance of urban residents and politicians regarding rural realities. Embracing further protectionism will not only harm consumers yearning for more competition at the grocery store but also impede the growth opportunities of various agricultural sectors striving to compete globally and stifle the expansion prospects of non-agricultural sectors seeking increased market access.
Dr. Sylvain Charlebois is senior director of the agri-food analytics lab and a professor in food distribution and policy at Dalhousie University.
Agriculture
How oil and gas support food security in Canada and around the world

General view of the ‘TD Canadian 4-H Dairy Classic Showmanship’ within the 101st edition of Royal Agricultural Winter Fair at Exhibition Place in Toronto, Ontario, on November 6, 2023. The Royal is the largest combined indoor agriculture fair and international equestrian competition in the world. Getty Images photo
From the Canadian Energy Centre
‘Agriculture requires fuel, and it requires lubricants. It requires heat and electricity. Modern agriculture can’t be done without energy’
Agriculture and oil and gas are two of Canada’s biggest businesses – and they are closely linked, industry leaders say.
From nitrogen-based fertilizer to heating and equipment fuels, oil and gas are the backbone of Canada’s farms, providing food security for Canadians and exports to nearly 200 countries around the world.
“Canada is a country that is rich in natural resources, and we are among the best, I would even characterize as the best, in terms of the production of sustainable energy and food, not only for Canadians but for the rest of the world,” said Don Smith, chief operating officer of the United Farmers of Alberta Co-operative.
“The two are very closely linked together… Agriculture requires fuel, and it requires lubricants. It requires heat and electricity. Modern agriculture can’t be done without energy, and it is a significant portion of operating expenses on a farm.”
The need for stable food sources is critical to a global economy whose population is set to reach 9.7 billion people by 2050.
The main pillars of food security are availability and affordability, said Keith Currie, president of the Canadian Federation of Agriculture (CFA).
“In Canada, availability is not so much an issue. We are a very productive country when it comes to agriculture products and food products. But food affordability has become an issue for a number of people,” said Currie, who is also on the advisory council for the advocacy group Energy for a Secure Future.
The average price of food bought in stores increased by nearly 25 per cent over the last five years, according to Statistics Canada.
Restricting access to oil and gas, or policies like carbon taxes that increase the cost for farmers to use these fuels, risk increasing food costs even more for Canadians and making Canadian food exports less attractive to global customers, CFA says.
“Canada is an exporting nation when it comes to food. In order for us to be competitive we not only have to have the right trade deals in place, but we have to be competitive price wise too,” Currie said.

Under an incredible Saskatchewan sky, a farmer walks toward his air seeder to begin the process of planting this year’s crop. Getty Images photo
Canada is the fifth-largest exporter of agri-food and seafood in the world, exporting approximately $93 billion of products in 2022, according to Agriculture Canada.
Meanwhile, Canadians spent nearly $190 billion on food, beverage, tobacco and cannabis products in 2022, representing the third-largest household expenditure category after transportation and shelter.
Currie said there are opportunities for renewable energy to help supplement oil and gas in agriculture, particularly in biofuels.
“But we’re not at a point from a production standpoint or an overall infrastructure standpoint where it’s a go-to right away,” he said.
“We need the infrastructure and we need probably a lot of incentives before we can even think about moving away from the oil and gas sector as a supplier of energy right now.”
Worldwide demand for oil and gas in the agriculture sector continues to grow, according to CEC Research.
Driven by Africa and Latin America, global oil use in agriculture increased to 118 million tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe) in 2022, up from 110 million tonnes in 1990.
Demand for natural gas also increased — from 7.5 Mtoe in 1990 to 11 Mtoe in 2022.
Sylvain Charlebois, senior director, in the Agri-Food Analytics Lab at Dalhousie University, said food security depends on three pillars – access, safety, and affordability.
“Countries are food secure on different levels. Canada’s situation I think is envious to be honest. I think we’re doing very well compared to other countries, especially when it comes to safety and access,” said Charlebois.
“If you have a food insecure population, civil unrest is more likely, tensions, and political instability in different regions become more of a possibility.”
As a country, access to affordable energy is key as well, he said.
“The food industry highly depends on energy sources and of course food is energy. More and more we’re seeing a convergence of the two worlds – food and energy… It forces the food sector to play a much larger role in the energy agenda of a country like Canada.”
-

 COVID-1919 hours ago
COVID-1919 hours agoPfizer reportedly withheld presence of cancer-linked DNA in COVID jabs from FDA, Health Canada
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoJordan Peterson, Canadian lawyer warn of ‘totalitarian’ impact of Trudeau’s ‘Online Harms’ bill
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta rejects unconstitutional cap on plastic production
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta official reveals ‘almost all’ wildfires in province this year have been started by humans
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoCome For The Graduate Studies, Stay For The Revolution
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTaxpayers criticize Trudeau and Ford for Honda deal
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDon’t be fooled by high-speed rail
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoPolitical parties will be part of municipal elections in Edmonton and Calgary pilot projects







