Opinion
Climate Murder? Media Picks Up Novel Legal Theory Suggesting Big Oil Is Homicidal

 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Nick Pope
A new narrative is making its way through major media outlets about major oil corporations: climate change that they purportedly caused is taking lives, and they could be held liable for homicide.
In recent weeks, numerous outlets have run stories or opinion pieces promoting or otherwise examining the novel legal theory, which is the subject of a new paper published by the Harvard Environmental Law Review, according to a Tuesday E&E News report detailing the architects’ efforts to market their idea to prosecutors. The Boston Globe, The Guardian, Newsweek, Inside Climate News and other outlets have all recently published pieces promoting the idea that leading oil companies could or should be charged with murder for their role in climate change, which the theory’s architects claim has caused thousands of deaths in the U.S.
David Arkush, who runs Public Citizen’s climate program, and Donald Braman, a professor at George Washington University’s law school, articulated the theory in a March paper. Public Citizen is a left-of-center organization founded by failed Green Party presidential candidate Ralph Nader that, among other things, pressures American International Group (AIG) to stop providing insurance coverage for fossil fuel companies, according to its website and Influence Watch.
“Activists and journalists have called executives of major oil companies ‘mass murderers,’ lamenting that ‘millions of human beings will die so that they can have private planes and huge mansions,’ and a growing chorus of communities devastated by [fossil fuel companies’] lethal conduct have begun to demand accountability,” the authors state in their paper. “But as of this writing, no prosecutor in any jurisdiction has charged [fossil fuel companies] with any form of homicide over climate-related deaths. They should.”
The paper also suggests that the American Petroleum Institute (API), a leading trade association for the oil and gas industry, was involved in the industry’s purported attempts to obscure the effects of emissions.
“The record of the past two decades demonstrates that the industry has achieved its goal of providing affordable, reliable American energy to U.S. consumers while substantially reducing emissions and our environmental footprint,” a spokesperson for API told the Daily Caller News Foundation. “Any suggestion to the contrary is false.”
The two authors contend that energy corporations were aware of the warming that emissions from their products and operations would cause for decades, and that those companies decided to mislead the public and obscure what effects those emissions may have. A similar narrative lies at the heart of climate lawsuits that have been filed against energy companies in numerous jurisdictions across the U.S. in recent years.
Arkush wrote a Wednesday piece for Newsweek laying out his theory and referencing these climate lawsuits, opining that the fossil fuel industry’s purported “crimes may be among the, if not the, most consequential in human history.” The Boston Globe ran a similar opinion piece authored by Arkush and another official for Public Citizen on March 17.
The Guardian ran its own piece about the climate homicide theory on March 21, using the headline “Fossil fuel firms could be tried in US for homicide over climate-related deaths, experts say.” Clean Technica, a site that promotes green energy, ran a March 16 piece on the new legal theory with the headline “Climate Criminals — Prosecuting Big Oil For Environmental Crimes.”
Inside Climate News published an April 4 story on the subject, using the headline “Should Big Oil Be Tried for Homicide?” and including excerpts from interviews with the two architects of the climate homicide theory. The pair suggested that the aim is not to punish individuals or seek vengeance, but instead achieve results that would prompt companies to shift their investments away from fossil fuels, according to Inside Climate News’ story.
However, Inside Climate News did quote legal experts who expressed skepticism about the theory’s merits.
“I do not believe that a criminal prosecution on homicide charges against the major oil companies is appropriate or can be sustained,” John Coffee Jr., a professor at Columbia Law School who specializes in corporate law, told the outlet.
Nick Pope is a contributor at The Daily Caller.
Business
Municipal government per-person spending in Canada hit near record levels
From the Fraser Institute
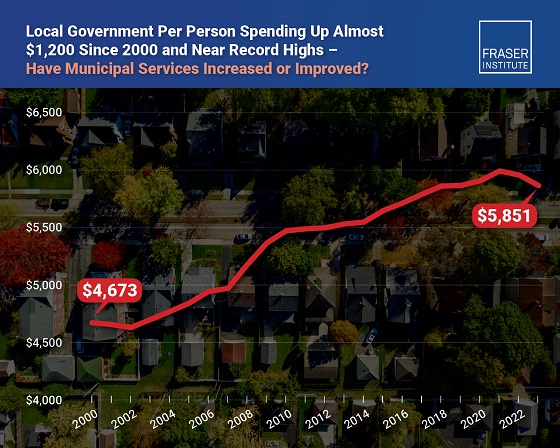
Municipal government spending in Canada hit near record levels in recent years, finds a new study by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“In light of record-high spending in municipalities across Canada, residents should consider whether or not crime, homelessness, public transit and other services have actually improved,” said Austin Thompson, senior policy analyst at the Fraser Institute and author of The Expanding Finances of Local Governments in Canada.
From 2000 to 2023, per-person spending (inflation-adjusted) increased by 25.2 per cent, reaching a record-high $5,974 per person in 2021 before declining slightly to $5,851 in 2023, the latest year of available data.
During that same period, municipal government revenue—generated from property taxes and transfers from other levels of government—increased by 33.7 per cent per person (inflation-adjusted).
And yet, among all three levels of government including federal and provincial, municipal government spending (adjusted for inflation) has actually experienced the slowest rate of growth over the last 10 years, underscoring the large spikes in spending at all government levels across Canada.
“Despite claims from municipal policymakers about their dire financial positions, Canadians should understand the true state of finances at city hall so they can decide whether they’re getting good value for their money,” said Jake Fuss, director of fiscal studies at the Fraser Institute.
The Expanding Finances of Local Governments in Canada, 1990–2023
- Canada’s local governments have experienced substantial fiscal growth in recent decades.
- Revenue and expenditure by local governments—including municipal governments, school boards, and Indigenous governments—have increased faster than population growth and inflation combined. From 1990 to 2023, real per-capita revenue rose by 32.7%, and expenditure by 30.0%.
- Local governments represent a significant component of Canada’s broader public sector. In 2023, net of inter-governmental transfers, municipal governments and school boards accounted for 18.6% of total government expenditure and 11.1% of revenue.
- Despite this growth, local governments’ share of overall government revenue and expenditure has declined over time—especially since the COVID-19 pandemic—as federal and provincial budgets have expanded even more rapidly.
- Nevertheless, between 2008 and 2023 the inflation-adjusted per-capita revenue of municipal governments in-creased by 10.1% and their expenditure by 12.4% , on average across the provinces.
- Over the same period, municipal governments recorded above-inflation increases in their combined annual operating surpluses, which contributed to an 88.1% inflation-adjusted rise in their net worth—raising important questions about the allocation of accumulated resources.
- In 2023, Ontario recorded the highest per-capita municipal revenue among the provinces ($4,156), while Alberta had the highest per-capita expenditure ($3,750). Prince Edward Island reported the lowest per-capita municipal revenue ($1,635) and expenditure ($1,186).
- Wide variation in per-capita municipal revenue and expenditure across the provinces reflects differences in the responsibilities provinces assign to municipalities, as well as possible disparities in the efficiency of service delivery—issues that warrant further scrutiny.
Click Here To Read The Full Study
armed forces
It’s not enough to just make military commitments—we must also execute them

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss and Grady Munro
To reach 2 per cent of GDP this year, the federal government is committing an additional $9.3 billion towards the military budget. Moreover, to reach 3.5 per cent of GDP by 2035, it’s estimated the government will need to raise yearly spending by an additional $50 billion—effectively doubling the annual defence budget from $62.7 billion to approximately $110 billion.
As part of this year’s NATO summit, Canada and its allies committed to increase annual military spending to reach 5 per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) by 2035. While this commitment—and the government’s recent push to meet the previous spending target of 2 per cent of GDP—are important steps in fulfilling Canada’s obligations to the alliance, there are major challenges the federal government will need to overcome to execute these plans.
Since 2014, members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) have committed to spend at least 2 per cent of GDP (a measure of overall economic output) on national defence. Canada had long-failed to fulfill this commitment, to the ire of our allies, until the Carney government recently announced a $9.3 billion boost to defence spending (up to a total of $62.7 billion) that will get us to 2 per cent of GDP during the 2025/26 fiscal year.
However, just as Canada reached the old target, the goal posts have now moved. As part of the 2025 NATO summit, alliance members (including Canada) committed to reach an increased spending target of 5 per cent of GDP in 10 years. The new target is made up of two components: core military spending equivalent to 3.5 per cent of GDP, and another 1.5 per cent of GDP for other defence-related spending.
National defence is a core function of the federal government and the Carney government deserves credit for prioritizing its NATO commitments given that past governments of different political stripes have failed to do so. Moreover, the government is ensuring that Canada remains in step with its allies in an increasingly dangerous world.
However, there are major challenges that arise once you consider how the government will execute these commitments.
First, both the announcement that Canada will reach 2 per cent of GDP in military spending this fiscal year, and the future commitment to spend up to 3.5 per cent of GDP on defence by 2035, represent major fiscal commitments that Canada’s budget cannot simply absorb in its current state.
To reach 2 per cent of GDP this year, the federal government is committing an additional $9.3 billion towards the military budget. Moreover, to reach 3.5 per cent of GDP by 2035, it’s estimated the government will need to raise yearly spending by an additional $50 billion—effectively doubling the annual defence budget from $62.7 billion to approximately $110 billion. However, based on the last official federal fiscal update, the federal government already plans to run an annual deficit this year—meaning it spends more than it collects in revenue—numbering in the tens of billions, and will continue running large deficits for the foreseeable future.
Given this poor state of finances, the government is left with three main options to fund increased military spending: raise taxes, borrow the money, or cut spending in other areas.
The first two options are non-starters. Canadian families already struggle under a tax burden that sees them spend more on taxes than on food, shelter, and clothing combined. Moreover, raising taxes inhibits economic growth and the prosperity of Canadians by reducing the incentives to work, save, invest, or start a business.
Borrowing the money to fund this new defence spending will put future generations of Canadians in a precarious situation. When governments borrow money and accumulate debt (total federal debt is expected to reach $2.3 trillion in 2025-26), the burden of this debt falls squarely on the backs of Canadians—likely in the form of higher taxes in the future. Put differently, each dollar we borrow today must be paid back by more than a dollar in higher taxes tomorrow.
This leaves cutting spending elsewhere as the best option, but one that requires the government to substantially readjusts its priorities. The federal government devotes considerable spending towards areas that are not within its core responsibilities and which shouldn’t have federal involvement in the first place. For instance, the previous government launched three major initiatives to provide national dental care, national pharmacare and national daycare, despite the fact that all three areas fall squarely under provincial jurisdiction. Instead of continuing to fund federal overreach, the Carney government should divert spending back to the core function of national defence. Further savings can be found by reducing the number of bureaucrats, eliminating corporate welfare, dropping electric vehicle subsidies, and many other mechanisms.
There is a fourth option by which the government could fund increased defence spending, which is to increase the economic growth rate within Canada and enjoy higher overall revenues. The problem is Canada has long-suffered a weak economy that will remain stagnant unless the government fundamentally changes its approach to tax and regulatory policy.
Even if the Carney government is able to successfully adjust spending priorities to account for new military funding, there are further issues that may inhibit money from being spent effectively.
It is a well-documented problem that military spending in Canada is often poorly executed. A series of reports from the auditor general in recent years have highlighted issues with the readiness of Canada’s fighter force, delays in supplying the military with necessary materials (e.g. spare parts, uniforms, or rations), as well as delays in delivering combat and non-combat ships needed to fulfill domestic and international obligations. All three of these cases represent instances in which poor planning and issues with procurement and supply chains) are preventing government funding from translating into timely and effective military outcomes.
The Carney government has recently made major commitments to increase military funding to fulfill Canada’s NATO obligations. While this is a step in the right direction, it’s not enough to simply make the commitments, the government must execute them as well.
-
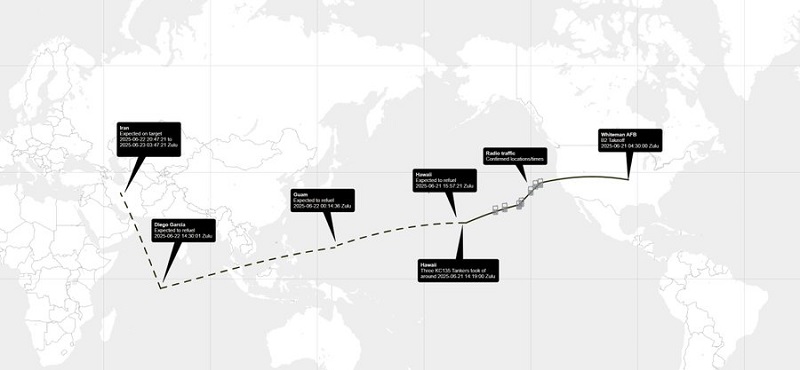
 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoSo Alberta, what’s next?
-

 Bjorn Lomborg2 days ago
Bjorn Lomborg2 days agoThe Physics Behind The Spanish Blackout
-

 COVID-1920 hours ago
COVID-1920 hours agoOntario man launches new challenge against province’s latest attempt to ban free expression on roadside billboards
-
 Health2 days ago
Health2 days ago‘Transgender’ males have 51% higher death rate than general population: study
-

 Business22 hours ago
Business22 hours agoFederal government should finally cut Trudeau-era red tape
-

 Alberta21 hours ago
Alberta21 hours agoCanadian Oil Sands Production Expected to Reach All-time Highs this Year Despite Lower Oil Prices
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTaxpayers Federation presents Teddy Waste Awards for worst government waste
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoDespite shaky start, ceasefire shows signs of holding