COVID-19
71% of reported adverse reactions to COVID-19 vaccine from just 4.2% of vaccine batches: Danish study
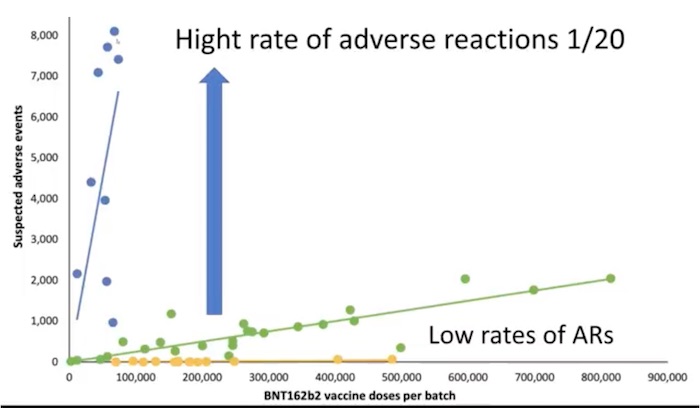
From Dr. John Campbell on YouTube
A report “Batch-dependent safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine” by Danish researchers Max Schmeling, Vibeke Manniche, Peter Riis Hansen is shedding light on the number of adverse reactions to specific batches of the Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccines.
The researchers note in their report
“Vaccine vials with individual doses are supplied in batches with stringent quality control to ensure batch and dose uniformity.2 Clinical data on individual vaccine batch levels have not been reported and batch-dependent variation in the clinical efficacy and safety of authorized vaccines would appear to be highly unlikely. However, not least in view of the emergency use market authorization and rapid implementation of large-scale vaccination programs, the possibility of batch-dependent variation appears worthy of investigation. We therefore examined rates of SAEs between different BNT162b2 vaccine batches administered in Denmark (population 5.8 million) from 27 December 2020 to 11 January 2022.”
The results of the study are astounding. In certain vaccine batches reported adverse reactions occurred in one out of every twenty shots. Other batches have yet to be associated with any adverse reactions at all. As British health researcher Dr. John Campbell explains, this study could pose very serious questions Pfizer must address.
Viral Vaccine paper
Dr. Campbell’s presentation notes:
Batch-dependent safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/1…
71% of the suspected adverse reactions occurred in 4.2% of the vaccine batches
Numbers of suspected adverse events (SAEs), after BNT612b2 mRNA vaccination in Denmark.
27 December 2020–11 January 2022, (population 5.8 million)
(According to the number of doses per vaccine batch)
Each dot represents a single vaccine batch.
By 11 November 2022 (European area) 701 million doses of Pfizer given 971,021 reports of suspected adverse effects (SAEs)
Clinical data on individual vaccine batch levels have not been reported (batch-dependent variation in the clinical efficacy and safety of authorized vaccines would appear to be highly unlikely)
We therefore examined rates of SAEs between different BNT162b2 vaccine batches administered in Denmark
Data on all SAE cases, Danish Medical Agency (DKMA) SAE seriousness was classified as non-serious, serious (hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization, life-threatening illness, permanent disability or congenital malformation) or SAE-related d****
Anonymized data SAEs were counted on a batch level by linking individual SAEs to the batch label(s) of BNT162b dose(s)
10,793,766 doses administered 4,026,575 persons 52 different BNT162b2 vaccine batches (2,340–814,320 doses per batch)
43,496 SAEs were registered in 13,635 persons 61,847 batch-identifiable SAEs, of which 14,509 (23.5%) were classified as severe, 579 (0.9%) were SAE-related d*****
Unexpectedly Rates of SAEs per 1000 doses varied considerably between vaccine batches
From 1 SAE per 20 doses given to I in many thousands to zero
Variabilities
Vaccine manufacturing
Storage
Transportation
Clinical handling and control
Administration technique
Viral vaccine paper, Dr Vibeke Manniche
COVID-19
NIH Quietly Altered Definition For Gain-Of-Function Research On Its Website, Former Fauci Aide Confirms

 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By JASON COHEN
National Institutes of Health (NIH) Principal Deputy Director Lawrence Tabak confirmed on Thursday that his agency’s communications department altered NIH’s definition for gain-of-function research, with the change being “vetted” by “experts.”
The NIH until Oct. 20, 2021 defined this research as “modif[ying] a biological agent so that it confers new or enhanced activity to that agent,” while “some scientists use the term broadly to refer to any such modification,” according to the House Oversight Committee. Republican Rep. Nicole Malliotakis of New York questioned Tabak, a former aide to Dr. Anthony Fauci, about the agency changing its definition of the research on its website, asking him who authorized the alteration.
WATCH:
The current website does not define gain-of-function research, but asserts this research is usually uninvolved with enhanced potential pandemic pathogens.
“The change was made by our communications department because of the confusion that people have about the generic term of gain-of-function and the specific term gain-of-function,” Tabak testified.
Malliotakis responded by suggesting the communications department would not be qualified to make a change like this and must have had other input.
“The content was vetted,” Tabak testified. “By individuals who are subject-matter experts.”
Fauci firmly denied that the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) funded gain-of-function research on bat-based coronaviruses at the Wuhan Institute of Virology (WIV) before the COVID-19 pandemic during a Senate hearing in May 2021.
“The NIH has not ever and does not now fund gain of function research in the Wuhan Institute of Virology,” Fauci said.
Tabak testified on Thursday that the NIH did fund this research at the Wuhan Institute of Virology, but it “depends on [the] definition.”
The NIAID, which Fauci previously led, funded the nonprofit group EcoHealth Alliance to study bat-based coronaviruses in China that consisted of the transfer of $600,000 to the WIV, the Daily Caller News Foundation previously reported.
COVID-19
COVID Lab Leak: Over four later, EcoHealth Alliance funding is finally suspended

From Heartland Daily News
Thursday, May 16, 2024
Federal Funding Stripped From Nonprofit at Center of COVID Lab Leak Controversy
Today, the Biden administration suspended federal funding to the scientific nonprofit whose research is at the center of credible theories that the COVID-19 pandemic was started via a lab leak at the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
This morning, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced that it was immediately suspending three grants provided to the New York-based nonprofit EcoHealth Alliance (EHA) as it starts the process of debarring the organization from receiving any federal funds.
“The immediate suspension of [EcoHealth Alliance] is necessary to protect the public interest and due to a cause of so serious or compelling a nature that it affects EHA’s present responsibility,” wrote HHS Deputy Secretary for Acquisitions Henrietta Brisbon in a memorandum signed this morning.
For years now, EcoHealth has generated immense controversy for its use of federal grant money to support gain-of-function research on bat coronaviruses at the Wuhan lab.
In a memo justifying its funding suspension, HHS said that EcoHealth had failed to properly monitor the work it was supporting at Wuhan. It also failed to properly report on the results of experiments showing that the hybrid viruses it was creating there had an improved ability to infect human cells.
Congressional Republicans leading an investigation into EcoHealth’s research in Wuhan, and the role it may have played in starting the pandemic via a lab leak, cheered HHS’s decision.
“EcoHealth facilitated gain-of-function research in Wuhan, China without proper oversight, willingly violated multiple requirements of its multimillion-dollar National Institutes of Health [NIH] grant, and apparently made false statements to the NIH,” said Rep. Brad Wenstrup (R–Ohio), chair of the House’s Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic in a statement. “These actions are wholly abhorrent, indefensible, and must be addressed with swift action.”
Beginning in 2014, EcoHealth received a grant from NIH’s National Institute of Allergies and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to study bat coronavirus in China. Its initial scope of work involved collecting and cataloging viruses in the wild and studying them in the lab to spot which ones might be primed to “spillover” into humans and cause a pandemic.
Soon enough, EcoHealth used some of the viruses they’d collected to create “chimeric” or hybrid viruses that might be better able to infect human lung cells in genetically engineered (humanized) mice.
This so-called “gain-of-function” research has long been controversial for its potential to create deadly pandemic pathogens. In 2014, the Obama administration paused federal funding of gain-of-function research that might turn SARS, MERS, or flu viruses into more transmissible respiratory diseases in mammals.
In 2016, NIH flagged EcoHealth’s work as likely violating the 2014 pause.
EcoHealth President Peter Daszak argued to NIH at the time that the viruses his outfit was creating had not been proven to infect human cells and were genetically different enough from past pandemic viruses that they didn’t fall under the Obama administration pause.

Wuhan Institute of Virology and Peter Daszak of EcoHealth Alliance
NIH accepted this argument under the condition that EcoHealth immediately stop its work and notify the agency if any of its hybrid viruses did show increased viral growth in humanized mice.
But when these hybrid viruses did show increased viral growth in mice, EcoHealth did not immediately stop work or notify NIH. It instead waited until it submitted an annual progress report in 2018 to disclose the results of its experiments.
A second progress report that EcoHealth submitted in 2021, two years after its due date, also showed its hybrid viruses were demonstrating increased viral growth and enhanced lethality in humanized mice.
In testimony to the House’s coronavirus subcommittee earlier this month, Daszak claimed that EcoHealth attempted to report the results of its gain-of-function experiments on time in 2019, but was frozen out of NIH’s reporting system.
The HHS memo released today says a forensic investigation found no evidence that EcoHealth was locked out of NIH’s reporting system. The department also said that EcoHealth had failed to produce requested lab notes and other materials from the Wuhan lab detailing the work being done there and the lab’s biosafety conditions.
These all amount to violations of EcoHealth’s grant agreement and NIH grant policy, thus warranting debarment from future federal funds, reads the HHS memo.
That EcoHealth would be stripped of its federal funding shouldn’t come as too great a shock to anyone who watched Daszak’s congressional testimony from earlier this month. Even Democrats on the committee openly accused Daszak of being misleading about EcoHealth’s work and manipulating facts.
Rep. Raul Ruiz (D–Calif.), the ranking Democrat on the House’s coronavirus subcommittee, welcomed EcoHealth’s suspension, saying in a press release that the nonprofit failed its “obligation to meet the utmost standards of transparency and accountability to the American public.”
An HHS Office of the Inspector General report from last year had already found that EcoHealth had failed to submit progress reports on time or effectively monitor its subgrantee, the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
When grilling Daszak, Democrats on the Coronavirus Subcommittee went to great lengths to not criticize NIH’s oversight of EcoHealth’s work. The HHS debarment memo likewise focuses only on EcoHealth’s failures to abide by NIH policy and its grant conditions.
Nevertheless, it seems pretty obvious that NIH was failing to abide by the 2014 pause on gain-of-function funding when it allowed EcoHealth to go ahead with creating hybrid coronaviruses under the condition that they stop if the viruses did prove more virulent.
NIH compounded that oversight failure by not stopping EcoHealth’s funding when the nonprofit did, in fact, create more virulent viruses, and not following up on a never-submitted progress report detailing more gain-of-function research until two years later.
The House Subcommittee’s investigation into NIH’s role in gain-of-function research at the Wuhan lab is ongoing. Tomorrow it will interview NIH Principal Deputy Director Lawerence Tabak. In June, it will interview former NIAID Director Anthony Fauci.
Originally published by Reason Foundation. Republished with permission.
-

 Automotive2 days ago
Automotive2 days agoGovernments in Canada accelerate EV ‘investments’ as automakers reverse course
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoWhite House Reportedly Worried About Russia’s Sudden Momentum Months After Biden Declared Putin ‘Already Lost’ War
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoSouth Korean president declares low birth rate a ‘national emergency,’ plans new ministry to address it
-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoBiden signs suicidal ‘No Coal’ pact, while rest of world builds 1,000 new plants
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoSlovakian prime minister who opposed WHO Pandemic Treaty shot in assassination attempt
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoFortis et Liber: Alberta’s Future in the Canadian Federation
-

 COVID-1916 hours ago
COVID-1916 hours agoNIH Quietly Altered Definition For Gain-Of-Function Research On Its Website, Former Fauci Aide Confirms
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoUK pediatrician who led review of child ‘transitions’ says US medical groups ‘misleading the public’






