Agriculture
What the USMCA Might Mean for Agriculture and Biotechnology?

We welcome guest writers to all of our Todayville platforms. Here’s a submission from Emily Folk. Emily is passionate about agricultural sustainability and more of her work can be found on her site, Conservation Folks. In this story, Emily Folk explains the USMCA Impact on Agriculture.
What Could USMCA Mean for Agriculture and Biotechnology?
The United States Mexico Canada Agreement (USMCA) has been in the news a lot lately. The leaders of the respective nations signed the trade agreement on November 30, 2019, and ratification is pending. You can think of the USMCA as an updated version of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
U.S. President Donald Trump vowed to renegotiate NAFTA after publicly speaking unfavourably about it. The USMCA is the result of that vow. The agreement spans several areas, such as the origin of automobile parts and new labor laws in Mexico that make it easier for workers to unionize. The USMCA also has a “sunset clause” that makes its terms expire after 16 years. Plus, every six years, the leaders of the countries involved must agree on whether to extend the deal.
Some agriculture-specific stipulations also exist within the USMCA. Additionally, the agreement notably mentions biotechnology. Here’s a closer look at how the USMCA might change these two industries.
More Exporting Opportunities for Farmers
One of the key points often mentioned about the USMCA is that parties expect the agreement to cause a $2 billion increase in U.S. agriculture exports, triggering a $65 billion rise in U.S. gross domestic product (GDP). Canada and Mexico are currently the top two exporting markets for American farmers, supporting more than 325,000 American jobs. In 2018, the food and agricultural exports destined for Canada and Mexico totaled more than $39.7 billion.
The USMCA also opens exporting opportunities that did not exist before. Now, U.S. dairy farmers will have expanded access to send products such as fluid and powdered milk, cheese and cream to Canadian parties. There will also no longer be U.S. tariffs on whey and margarine. This change is notable, considering the Canadian dairy market produced roughly 17% of the United States’ annual output over the past three years.
In exchange, Canada will give the United States new access to chicken and eggs, plus increased access to turkey. Plus, all other agriculture products traded between the U.S. and Mexico will be under a zero-tariff model.
Moving Forward With Agricultural Biotechnology
Another improvement associated with the USMCA is that it looks at agricultural technology more broadly than other trade agreements have.
For example, the Trans-Pacific Partnership — a proposed trade agreement between 12 nations — only addressed biotechnology regarding recombinant DNA (rDNA). That process involves joining the molecules from two different species, then inserting the product into a host to create new genetic combinations. Instead, the USMCA opens possibilities for all kinds of agricultural technology, including gene editing. Moving ahead with biotechnology could be crucial for addressing pressing matters that affect agriculture, such as water scarcity.
Approximately 700 million people suffer from water scarcity, and that number could double by 2025. Also, the agriculture industry is the greatest user of water. Things must change — both to address the growing water scarcity problem and to give farmers more options for growing things without using so much water.
Biotechnology has already helped, and it seems highly likely to continue spurring progress. In one example, scientists altered the expression of one gene common to all plants. This change led to a 25% increase in the plants’ water-use efficiency without adversely impacting yield or photosynthesis.
As part of the USMCA, Mexico, Canada and the United States agreed to improve information sharing and cooperation about biotechnology matters related to trade. That change could speed new developments, resulting in positive outcomes for all involved groups and the world at large.
Fairer Agricultural Grading Standards
A grading system for agricultural products defines trading procedures. For example, commercial buyers of a product grown in another country refer to the grading standards to set expectations about a product’s quality. The USMCA specifies that Canada will evaluate U.S. imported wheat and assign it a grade no less favourable than it would give Canadian-grown wheat.
Canada will also no longer require country of origin statements associated with inspection certificates or quality grades. The United States and Canada will discuss issues related to seed regulations under the USMCA, too.
Concerning Mexico and the United States, the two countries agreed to non-discriminatory grading standards and services. Moreover, a dialogue will begin between the two countries to flesh out the details for quality standards and grading regarding trade.
A Promising Future
It’s too early to say what the real-life effects will be of the changes outlined here. But, the commitments laid out within the USMCA seem like they’ll represent clear improvements for agriculture professionals, as well as everyone who benefits from their goods.

I’m Emily Folk, and I grew up in a small town in Pennsylvania. Growing up I had a love of animals, and after countless marathons of watching Animal Planet documentaries, I developed a passion for ecology and conservation. You can read more of my work by clicking this link: Conservation Folks.
Extreme Weather Patterns Causing State of Agricultural Emergency in Canada
Agriculture
Bill C-282, now in the Senate, risks holding back other economic sectors and further burdening consumers

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Bill C-282 currently sits in the Canadian Senate and stands on the precipice of becoming law in a matter of weeks. Essentially, this bill seeks to bestow immunity upon supply management from any potential future trade negotiations without offering increased market access to potential trade partners.
In simpler terms, it risks holding all other economic sectors hostage solely to safeguard the interests of a small, privileged group of farmers. This is far from an optimal scenario, and the implications of this bill spell bad news for Canadians.
Supply management, which governs poultry, egg, and dairy production in Canada, has traditionally enabled us to fulfill our domestic needs. Under this system, farmers are allocated government-sanctioned quotas to produce food for the nation. At the same time, high tariffs are imposed on imports of items such as chicken, butter, yogurt, cheese, milk, and eggs. This model has been in place for over five decades, ostensibly to shield family farms from economic volatility.
However, despite the implementation of supply management, Canada has witnessed a comparable decline in the number of farms as the United States, where a national supply management scheme does not exist. Supply management has failed to preserve much of anything beyond enriching select agricultural sectors.
For instance, dairy farmers now possess quotas valued at over $25 billion while concurrently burdening dairy processors with the highest-priced industrial milk in the Western world. Recent data indicates a significant surge in prices at the grocery store, with yogurt prices alone soaring by over 30 percent since December 2023. This escalation is increasingly straining the budgets of many consumers.
It’s evident to those knowledgeable about the situation that the emergence of Bill C-282 should come as no surprise. Proponents of supply management exert considerable influence over politicians across party lines, compelling them to support this bill to safeguard the interests of less than one percent of our economy, much to the ignorance of most Canadians. In the last federal budget, the dairy industry alone received over $300 million in research funds, funds that arguably exceed their actual needs.
While Canada’s agricultural sector accounts for approximately seven percent of our GDP, supply-managed industries represent only a small fraction of that figure. Supply-managed farms represent about five percent of all farms in Canada. Forging trade agreements with key partners such as India, China, and the United Kingdom is imperative not only for sectors like automotive, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology but for the vast majority of farms in livestock and grains to thrive and contribute to global welfare and prosperity. It is essential to recognize that Canada has much more to offer than merely self-sufficiency in food production.
Over time, the marketing boards overseeing quotas for farmers have amassed significant power and have proven themselves politically aggressive. They vehemently oppose any challenges to the existing system, targeting politicians, academics, and groups advocating for reform or abolition. Despite occasional resistance from MPs and Senators, no major political party has dared to question the disproportionate protection afforded to one sector over others. Strengthening our supply-managed sectors necessitates embracing competition, which can only serve to enhance their resilience and competitiveness.
A recent example of the consequences of protectionism is the United Kingdom’s decision to walk away from trade negotiations with Canada due to disagreements over access to our dairy market. Not only do many Canadians appreciate the quality of British cheese, but increased competition in the dairy section would also help drive prices down, a welcome relief given current economic challenges.
In the past decade, Canada has ratified trade agreements such as CUSMA, CETA, and CPTPP, all of which entailed breaches in our supply management regime. Despite initial concerns from farmers, particularly regarding the impact on poultry, eggs, and dairy, these sectors have fared well. A dairy farm in Ontario recently sold for a staggering $21.5 million in Oxford County. Claims of losses resulting from increased market access are often unfounded, as farmer boards simply adjust quotas when producers exit the industry.
In essence, Bill C-282 represents a misguided initiative driven by farmer boards capitalizing on the ignorance of urban residents and politicians regarding rural realities. Embracing further protectionism will not only harm consumers yearning for more competition at the grocery store but also impede the growth opportunities of various agricultural sectors striving to compete globally and stifle the expansion prospects of non-agricultural sectors seeking increased market access.
Dr. Sylvain Charlebois is senior director of the agri-food analytics lab and a professor in food distribution and policy at Dalhousie University.
Agriculture
Degrowth: How to Make the World Poorer, Polluted and Miserable

From StosselTV
Activists have a new goal: “DEgrowth.”
They say “growth is killing us.” They couldn’t be MORE wrong.
“Growth is not killing us. It’s saving us!” says author Johan Norberg. He explains why growth is essential to human progress, especially for poor people. “In poor countries, if you manage to grow by 4% annually over 20 years,” he points out, “that reduces poverty in that country on average by 80%.
But DEgrowth activists insist that growth means “climate chaos.” They say a smaller economy would be “sweeter.” They say “We must urgently dismantle capitalism!” It’s destructive nonsense. This video explains why.
————
To get our new weekly video from Stossel TV, sign up here: https://www.johnstossel.com/#subscribe
————
After 40+ years of reporting, I now understand the importance of limited government and personal freedom.
——————————————
Libertarian journalist John Stossel created Stossel TV to explain liberty and free markets to young people.
Prior to Stossel TV he hosted a show on Fox Business and co-anchored ABC’s primetime newsmagazine show, 20/20. Stossel’s economic programs have been adapted into teaching kits by a non-profit organization, “Stossel in the Classroom.” High school teachers in American public schools now use the videos to help educate their students on economics and economic freedom. They are seen by more than 12 million students every year.
Stossel has received 19 Emmy Awards and has been honored five times for excellence in consumer reporting by the National Press Club.
Other honors include the George Polk Award for Outstanding Local Reporting and the George Foster Peabody Award.
-

 COVID-1910 hours ago
COVID-1910 hours agoCDC Quietly Admits to Covid Policy Failures
-
 COVID-1913 hours ago
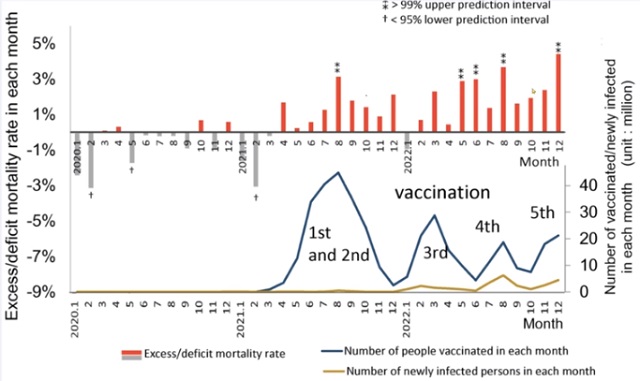
COVID-1913 hours agoJapanese study shows disturbing increase in cancer related deaths during the Covid pandemic
-

 Great Reset8 hours ago
Great Reset8 hours agoClimate expert warns against extreme ‘weather porn’ from alarmists pushing ‘draconian’ policies
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoWhy Are Canadian Mayors So Far Left And Out Of Touch?
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoDanielle Smith warns arsonists who start wildfires in Alberta that they will be held accountable
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoCanada’s Governor General slammed for hosting partisan event promoting Trudeau’s ‘hate speech’ bill
-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoExtreme Weather and Climate Change
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTelegram founder tells Tucker Carlson that US intel agents tried to spy on user messages




