Community
Three ways seniors can prevent falls

Falls are the leading cause of injury in Alberta seniors. The good news is that there are steps that seniors can take to prevent falls.
“1 in 3 Alberta seniors will fall every year,” said Dr. Kathy Belton, Associate Director of the Injury Prevention Centre. “With the support of healthcare providers and programs like Finding Balance we can show seniors that there are proven ways they can reduce their risk of falling and stay active in their communities.”
KEEP ACTIVE
Seniors should try to do 30 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity 5 days a week. Activities like tai chi, dancing and cross-country skiing are lots of fun, and great ways to strengthen arm and leg muscles!
Seniors should do activities that focus on four key areas…
• Balance: exercises in a standing position or tai chi.
• Strength: wall push-ups, stair climbing or exercises with weights or bands.
• Endurance: walking, dancing, cycling or cross-country skiing.
• Flexibility: stretching, yoga or tai chi.
CHECK YOUR VISION
Seniors may notice changes in their vision. What sort of changes should seniors be looking out for? Eyes might take longer to adjust to changes in light, it may become harder to identify objects, judging the distance between objects may become difficult, especially at night and conditions like cataracts, glaucoma or macular degenerations may develop.
What can seniors do?
• Visit the eye doctor yearly for an eye exam. Alberta Health Care covers the cost of eye exams for adults 65 and older.
• Keep rooms well lit.
• Use a nightlight with a motion sensor in the hallways and bathroom.
• Wear sunglasses, year round – winter time, too!
REVIEW YOUR MEDICATIONS
Some over-the-counter medications, vitamins and herbal supplements may increase the risk of falling. Seniors should visit their doctor or pharmacist yearly, or when medications change to reduce their risk of a fall.
Here are some important questions to ask the doctor or pharmacist:
1. What is the medication used for?
2. Will it cause dizziness or drowsiness as a side effect?
3. Will it cause blurred or double vision?
4. What should I do if I have side effect?
5. What should I do if I miss a dose?
6. Should I avoid alcohol, or other foods and beverages?
“Falls are not a normal part of aging,” said Dr. Belton, “Together we can motivate seniors to take action to prevent falls and enjoy getting older, injury-free.”
Finding Balance is a seniors’ falls prevention program is developed and programmed by the Injury Prevention Centre (IPC) in partnership with healthcare practitioners and community partners across Alberta. Finding Balance runs for the month of November. www.findingbalancealberta.ca
Community
SPARC Red Deer – Caring Adult Nominations open now!

Red Deer community let’s give a round of applause to the incredible adults shaping the future of our kids. Whether they’re a coach, neighbour, teacher, mentor, instructor, or someone special, we want to know about them!
Tell us the inspiring story of how your nominee is helping kids grow up great. We will honour the first 100 local nominees for their outstanding contributions to youth development. It’s time to highlight those who consistently go above and beyond!
To nominate, visit Events (sparcreddeer.ca)

Addictions
‘Harm Reduction’ is killing B.C.’s addicts. There’s got to be a better way

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
B.C. recently decriminalized the possession of small amounts of illicit drugs. The resulting explosion of addicts using drugs in public spaces, including parks and playgrounds, recently led the province’s NDP government to attempt to backtrack on this policy
Fuelled by the deadly manufactured opioid fentanyl, Canada’s national drug overdose rate stood at 19.3 people per 100,000 in 2022, a shockingly high number when compared to the European Union’s rate of just 1.8. But national statistics hide considerable geographic variation. British Columbia and Alberta together account for only a quarter of Canada’s population yet nearly half of all opioid deaths. B.C.’s 2022 death rate of 45.2/100,000 is more than double the national average, with Alberta close behind at 33.3/100,00.
In response to the drug crisis, Canada’s two western-most provinces have taken markedly divergent approaches, and in doing so have created a natural experiment with national implications.
B.C. has emphasized harm reduction, which seeks to eliminate the damaging effects of illicit drugs without actually removing them from the equation. The strategy focuses on creating access to clean drugs and includes such measures as “safe” injection sites, needle exchange programs, crack-pipe giveaways and even drug-dispensing vending machines. The approach goes so far as to distribute drugs like heroin and cocaine free of charge in the hope addicts will no longer be tempted by potentially tainted street drugs and may eventually seek help.
But safe-supply policies create many unexpected consequences. A National Post investigation found, for example, that government-supplied hydromorphone pills handed out to addicts in Vancouver are often re-sold on the street to other addicts. The sellers then use the money to purchase a street drug that provides a better high — namely, fentanyl.
Doubling down on safe supply, B.C. recently decriminalized the possession of small amounts of illicit drugs. The resulting explosion of addicts using drugs in public spaces, including parks and playgrounds, recently led the province’s NDP government to attempt to backtrack on this policy — though for now that effort has been stymied by the courts.
According to Vancouver city councillor Brian Montague, “The stats tell us that harm reduction isn’t working.” In an interview, he calls decriminalization “a disaster” and proposes a policy shift that recognizes the connection between mental illness and addiction. The province, he says, needs “massive numbers of beds in treatment facilities that deal with both addictions and long-term mental health problems (plus) access to free counselling and housing.”
In fact, Montague’s wish is coming true — one province east, in Alberta. Since the United Conservative Party was elected in 2019, Alberta has been transforming its drug addiction policy away from harm reduction and towards publicly-funded treatment and recovery efforts.
Instead of offering safe-injection sites and free drugs, Alberta is building a network of 10 therapeutic communities across the province where patients can stay for up to a year, receiving therapy and medical treatment and developing skills that will enable them to build a life outside the drug culture. All for free. The province’s first two new recovery centres opened last year in Lethbridge and Red Deer. There are currently over 29,000 addiction treatment spaces in the province.
This treatment-based strategy is in large part the work of Marshall Smith, current chief of staff to Alberta’s premier and a former addict himself, whose life story is a testament to the importance of treatment and recovery.
The sharply contrasting policies of B.C. and Alberta allow a comparison of what works and what doesn’t. A first, tentative report card on this natural experiment was produced last year in a study from Stanford University’s network on addiction policy (SNAP). Noting “a lack of policy innovation in B.C.,” where harm reduction has become the dominant policy approach, the report argues that in fact “Alberta is currently experiencing a reduction in key addiction-related harms.” But it concludes that “Canada overall, and B.C. in particular, is not yet showing the progress that the public and those impacted by drug addiction deserve.”
The report is admittedly an early analysis of these two contrasting approaches. Most of Alberta’s recovery homes are still under construction, and B.C.’s decriminalization policy is only a year old. And since the report was published, opioid death rates have inched higher in both provinces.
Still, the early returns do seem to favour Alberta’s approach. That should be regarded as good news. Society certainly has an obligation to try to help drug users. But that duty must involve more than offering addicts free drugs. Addicted people need treatment so they can kick their potentially deadly habit and go on to live healthy, meaningful lives. Dignity comes from a life of purpose and self-control, not a government-funded fix.
Susan Martinuk is a senior fellow at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy and author of the 2021 book Patients at Risk: Exposing Canada’s Health Care Crisis. A longer version of this article recently appeared at C2CJournal.ca.
-
 COVID-1928 mins ago
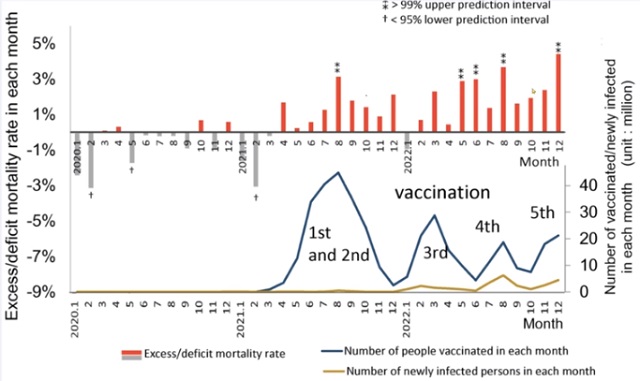
COVID-1928 mins agoJapanese study shows disturbing increase in cancer related deaths during the Covid pandemic
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoBusiness investment key to addressing Canada’s productivity crisis
-

 Jordan Peterson2 days ago
Jordan Peterson2 days agoJordan Peterson slams CBC for only interviewing pro-LGBT doctors about UK report on child ‘sex changes’
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoDanielle Smith warns arsonists who start wildfires in Alberta that they will be held accountable
-

 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoLiberal MP blasts Trudeau-backed ‘safe supply’ drug programs, linking them to ‘chaos’ in cities
-

 Freedom Convoy2 days ago
Freedom Convoy2 days agoTrudeau’s use of Emergencies Act has cost taxpayers $73 million thus far
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days agoThe Smallwood solution
-

 Agriculture2 days ago
Agriculture2 days agoBill C-282, now in the Senate, risks holding back other economic sectors and further burdening consumers





