Business
Immersive technologies are the future, so how do they benefit industry?

These are exciting times. For those who may be unaware of the advancement of this incredible immersive technology over recent years, you may be surprised by the abundance of benefits virtual reality(VR) and augmented reality(AR) can offer to a wide range of industries. In addition to entertainment and gaming, immersive technologies offer the opportunity to benefit industries such as oil and gas, cleantech, education, manufacturing, agriculture, retail, real estate and many more.
Consider this, when learning new processes or training for a specific position, creating an immersive learning program could advance cognition, engagement and retention of vital information over what could be learned through traditional programs. While we may be still some time away from this being the norm, it is hard to ignore the forward-thinking work going on in this industry.

Vizworx is a Calgary based tech company specializing in multiple advanced technologies. While they are one of the great teams at the forefront of this imaginative world of immersive technology, their core mission for all of their clients is simple – they solve problems.
Focusing on key areas, the Vizworx team is well versed in VR, AR, mixed reality(MR), artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IoT), geospatial data mapping, biometric evaluation, and custom visualization solutions to name a few. Thankful for the opportunity to discuss this topic with Jeff LaFrenz, CEO of Vizworx and of their subsidiary Panoptica.
Proud winner of multiple awards over recent years such as the Cross Sectoral Company Success Award from ConvergX in 2020, Outstanding Achievement in Applied Technology by ASTech and The Innovation Award by PTAC in 2019, to name a few. Recently, Jeff was a recipient of the University of Calgary 2020 Alumni Service Award.
– “What is physical and virtual becomes a blurry line at some point in the future” –
Challenging as it is to condense, the incredible applications this immersive technology can have for industrial processes. While this topic could be extrapolated into each individual sector, the overall benefits are still being uncovered as this technology continues to evolve. However, it is important to explore the narrative of what it can offer today.
Infrastructure planning
This can be construed in two ways.
The first. Real estate may integrate immersive technologies at a higher capacity than other industries in the near future. We are aware of 360-degree walking tours, however, imagine having the ability to use a VR headset to be fully immersed in what could be your new home, where you interact with space on a true scale. Moving forward, the experience may prove to be the key to innovating the buying or renting process.
As noted in Engineering.com back in 2016, we now have the ability to walk through a home virtually before any construction begins. If we consider the long term financial risk we all face with building a new home, mitigating any misconstrued requests and ensuring the model is true to the physical, benefits both the future homeowner and project managers. The same can be said for all parties involved in the construction of condo units, including pre-sale to consumers.
The second, industrial facility production.
While it can be difficult to summarize the process included in planning, pre-production, regulations and geo-mapping that goes into the production of infrastructure. With the use of this technology, a large scale project could be first explored through a VR model to engage with what could be the post-production facility, mitigating the risks of inefficient mapping, overhead and problematic regulations.
In theory, creating a virtual tour and geospatial map of an upcoming project could allow for tours, audits and restructuring before production. Mitigating the risk of inefficient planning, saving time and ensuring that the final production model will be cost-effective. With the level of cognition that is possible, we could see a re-evaluation of the process of industrial construction pursued as this technology continues to enhance the user experience.
This type of solution is catered to by the subsidiary of Vizworx called Panoptica. This arm of the company specializes in creating immersive engineering review models. If we consider the complexity of certain infrastructure requirements for facilities such as power generation or waste management, the ability to review models, assess ventilation and inform engineers who may have concerns regarding certain functionalities, can allow for a far more streamlined process.
With the amount of capital required for certain industrial facilities, Jeff offers his insight into how Panoptica, or similar review model technology could offer a major advantage when visiting the pre-production stage of an infrastructure review or build.
“One of the challenges every industrial space is running into is data overload. Typically from a human perspective, a lot of what we do is to come from a human perspective of how you present the data to dramatically impact how people understand what it is as well as how they are going to make decisions.” – Jeff LaFrenz, CEO

Foreign Investment / Remote Tours
Evidently, this pandemic continues to confuse and re-calibrate plans to interact with others around the world. As flight schedules continue to be disrupted and to be monitored during a fortnight quarantine post-arrival in a foreign country. Now more than ever, the opportunity to create a virtual demonstration of an early-stage start-up mitigates confusion in regards to travel plans but also lowers overhead for foreign investors to travel to that location for an in-person demonstration.
“Humans by law have a biological spatial understanding, these technologies leverage that ability to present information that is spatially oriented. I could present you with a rendering of a building, and that would be hard for you to understand, or I could drop you into that building in virtual or augmented reality where you can walk around it and you would get it right away” – Jeff LaFrenz, CEO
One bright light in the ecosystem of innovative technology in the energy space is Eavor Technologies, a closed loop geothermal technology company that has been continuously disrupting the space. With a major push around the world for clean baseload energy that is both dispatchable and scalable, Eavor is a global front runner. Recently featured in Rolling Stone for their new “Harmony” video and insight from their team.
Due to the major disruption in flight schedules, Eavor Technologies created a virtual walking tour of their “Eavor Lite” facility, which is their proof of concept stage site located in Rocky Mountain House, Alberta. To think of the pandemic no longer allowing any convenience for international travel let alone group tours. This solution created an intuitive immersive experience where you as the visitor can walk around and access panels throughout, where their team offers deeper insight into their technology. It can be toured through the Oculus Quest and also through a desktop or smartphone, found here.


(Source: Eavor Technologies Eavor Lite facility, Virtual Reality Tour Announced By Cutting Edge Canadian Energy Tech Company, September 15th 2020)
Operational Training
Cognition and retention of information vary both on the human and technical level. Traditional methods of training employees consist of the use of company assets, written or video material and in some cases exams. While these methods are still widely used today, there is the argument for a declining level of engagement with this type of information and the increase of online activity, thus leading to a lower level of retention.
The solution could very well lie in this immersive technology. There is little data available on the segmented levels of cognition and retention in traditional vs immersive training, however, it is important to note that a high majority of us learn by doing, exactly what an immersive experience offers without the use of expensive equipment that could be better served.
Panoptica contains a suite of tools that leverage mixed reality technologies. Teams can collaborate digitally from anywhere individually as they view models in a true 1:1 scale. By creating a 3D model that can be evaluated, allows for any inefficiencies to become apparent in the design process, thus mitigating time and overhead.

(Source: Medium, “Model Reviews in a Post-COVID Era”, Vizworx review model, Carter Yont, published July 28th)
Safety and Emergency Training
One example is training for airline pilots, where they are subject to an immersive training course that will uncover all circumstances where an emergency may arise. Being a passenger on countless flights, I am even glad this technology exists.
Immersive training is not new. Cited from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health in Pittsburgh back in 2006, countries such as Germany, Australia and the US came together to explore the benefits to the mining industry. 14 different countries came together to discuss how VR can be employed in the future or research, development and safety training.

(Source: CDC, “Virtual Reality in Mine Training”, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, 2006)
While this was years ago, it is a reminder that this technology has been around for some time. As time and education move forward, the quality of the image rendering, functionality and reduction of cost continues to benefit the end-user.
As mentioned, Panoptica can create a 1:1 ratio 3D review model. In addition to playing a major role in planning, safety training programs are an essential part of any industrial process. When you consider the assets and time allocated from senior employees, the cost increases in such a way where those assets and staff could be put to more cost-effective work. The cost of producing an immersive training program that can be utilized from anywhere is minuscule in comparison.
“If you look at the future of where these immersive technologies are going, price points are coming down significantly, and the capabilities are going up significantly. We are going to have this blended environment where employees could walk around an industrial facility and look at a boiler, overlaid on that physical world is all the data and digital information required. What is physical and virtual becomes kind of a blurry line at some point in the future. That is where we want to be, seamless engagement with our environment between physical and virtual worlds.” Jeff LaFrenz, CEO
We are only scratching the surface here, there is still much to uncover in the world of immersive technology in this tech revolution. We can look forward to things such as retail shopping from the comfort of your living room where you can try items on virtually, or even where engineering students will avail of an immersive learning program that could advance cognition and retention to a point where innovation reaches far beyond our wildest aspirations.
I recommend visiting the Vizworx and Panoptica websites. Check out their blog on Medium and be sure to give them a follow on Twitter to stay up to date on any developments in the future.
For more stories, please visit Todayville Calgary
Business
Canada’s economy has stagnated despite Ottawa’s spin

From the Fraser Institute
By Ben Eisen, Milagros Palacios and Lawrence Schembri
Canada’s inflation-adjusted per-person annual economic growth rate (0.7 per cent) is meaningfully worse than the G7 average (1.0 per cent) over this same period. The gap with the U.S. (1.2 per cent) is even larger. Only Italy performed worse than Canada.
Growth in gross domestic product (GDP), the total value of all goods and services produced in the economy annually, is one of the most frequently cited indicators of Canada’s economic performance. Journalists, politicians and analysts often compare various measures of Canada’s total GDP growth to other countries, or to Canada’s past performance, to assess the health of the economy and living standards. However, this statistic is misleading as a measure of living standards when population growth rates vary greatly across countries or over time.
Federal Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland, for example, recently boasted that Canada had experienced the “strongest economic growth in the G7” in 2022. Although the Trudeau government often uses international comparisons on aggregate GDP growth as evidence of economic success, it’s not the first to do so. In 2015, then-prime minister Stephen Harper said Canada’s GDP growth was “head and shoulders above all our G7 partners over the long term.”
Unfortunately, such statements do more to obscure public understanding of Canada’s economic performance than enlighten it. In reality, aggregate GDP growth statistics are not driven by productivity improvements and do not reflect rising living standards. Instead, they’re primarily the result of differences in population and labour force growth. In other words, they aren’t primarily the result of Canadians becoming better at producing goods and services (i.e. productivity) and thus generating more income for their families. Instead, they primarily reflect the fact that there are simply more people working, which increases the total amount of goods and services produced but doesn’t necessarily translate into increased living standards.
Let’s look at the numbers. Canada’s annual average GDP growth (with no adjustment for population) from 2000 to 2023 was the second-highest in the G7 at 1.8 per cent, just behind the United States at 1.9 per cent. That sounds good, until you make a simple adjustment for population changes by comparing GDP per person. Then a completely different story emerges.
Canada’s inflation-adjusted per-person annual economic growth rate (0.7 per cent) is meaningfully worse than the G7 average (1.0 per cent) over this same period. The gap with the U.S. (1.2 per cent) is even larger. Only Italy performed worse than Canada.
Why the inversion of results from good to bad? Because Canada has had by far the fastest population growth rate in the G7, growing at an annualized rate of 1.1 per cent—more than twice the annual population growth rate of the G7 as a whole at 0.5 per cent. In aggregate, Canada’s population increased by 29.8 per cent during this time period compared to just 11.5 per cent in the entire G7.
Clearly, aggregate GDP growth is a poor tool for international comparisons. It’s also not a good way to assess changes in Canada’s performance over time because Canada’s rate of population growth has not been constant. Starting in 2016, sharply higher rates of immigration have led to a pronounced increase in population growth. This increase has effectively partially obscured historically weak economic growth per person over the same period.
Specifically, from 2015 to 2023, under the Trudeau government, inflation-adjusted per-person economic growth averaged just 0.3 per cent. For historical perspective, per-person economic growth was 0.8 per cent annually under Brian Mulroney, 2.4 per cent under Jean Chrétien and 2.0 per cent under Paul Martin.
Due to Canada’s sharp increase in population growth in recent years, aggregate GDP growth is a misleading indicator for comparing economic growth performance across countries or time periods. Canada is not leading the G7, or doing well in historical terms, when it comes to economic growth measures that make simple adjustments for our rapidly growing population. In reality, we’ve become a growth laggard and our living standards have largely stagnated for the better part of a decade.
Authors:
Fraser Institute
Powerful players count on corruption of ideal carbon tax

From the Fraser Institute
Prime Minister Trudeau recently whipped out the big guns of rhetoric and said the premiers of Alberta, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Ontario, Prince Edward Island and Saskatchewan are “misleading” Canadians and “not telling the truth” about the carbon tax. Also recently, a group of economists circulated a one-sided open letter extolling the virtues of carbon pricing.
Not to be left out, a few of us at the Fraser Institute recently debated whether the carbon tax should or could be reformed. Ross McKitrick and Elmira Aliakbari argued that while the existing carbon tax regime is badly marred by numerous greenhouse gas (GHG) regulations and mandates, is incompletely revenue-neutral, lacks uniformity across the economy and society, is set at an arbitrary price and so on, it remains repairable. “Of all the options,” they write, “it is widely acknowledged that a carbon tax allows the most flexibility and cost-effectiveness in the pursuit of society’s climate goals. The federal government has an opportunity to fix the shortcomings of its carbon tax plan and mitigate some of its associated economic costs.”
I argued, by contrast, that due to various incentives, Canada’s relevant decision-makers (politicians, regulators and big business) would all resist any reforms to the carbon tax that might bring it into the “ideal form” taught in schools of economics. To these groups, corruption of the “ideal carbon tax” is not a bug, it’s a feature.
Thus, governments face the constant allure of diverting tax revenues to favour one constituency over another. In the case of the carbon tax, Quebec is the big winner here. Atlantic Canada was also recently won by having its home heating oil exempted from carbon pricing (while out in the frosty plains, those using natural gas heating will feel the tax’s pinch).
Regulators, well, they live or die by the maintenance and growth of regulation. And when it comes to climate change, as McKitrick recently observed in a separate commentary, we’re not talking about only a few regulations. Canada has “clean fuel regulations, the oil-and-gas-sector emissions cap, the electricity sector coal phase-out, strict energy efficiency rules for new and existing buildings, new performance mandates for natural gas-fired generation plants, the regulatory blockade against liquified natural gas export facilities” and many more. All of these, he noted, are “boulders” blocking the implementation of an ideal carbon tax.
Finally, big business (such as Stellantis-LG, Volkswagen, Ford, Northvolt and others), which have been the recipients of subsidies for GHG-reducing activities, don’t want to see the driver of those subsidies (GHG regulations) repealed. And that’s only in the electric vehicle space. Governments also heavily subsidize wind and solar power businesses who get a 30 per cent investment tax credit though 2034. They also don’t want to see the underlying regulatory structures that justify the tax credit go away.
Clearly, all governments that tax GHG emissions divert some or all of the revenues raised into their general budgets, and none have removed regulations (or even reduced the rate of regulation) after implementing carbon-pricing. Yet many economists cling to the idea that carbon taxes are either fine as they are or can be reformed with modest tweaks. This is the great carbon-pricing will o’ the wisp, leading Canadian climate policy into a perilous swamp.
Author:
-

 COVID-1913 hours ago
COVID-1913 hours agoCDC Quietly Admits to Covid Policy Failures
-

 Brownstone Institute3 hours ago
Brownstone Institute3 hours agoDeborah Birx Gets Her Close-Up
-
 COVID-1916 hours ago
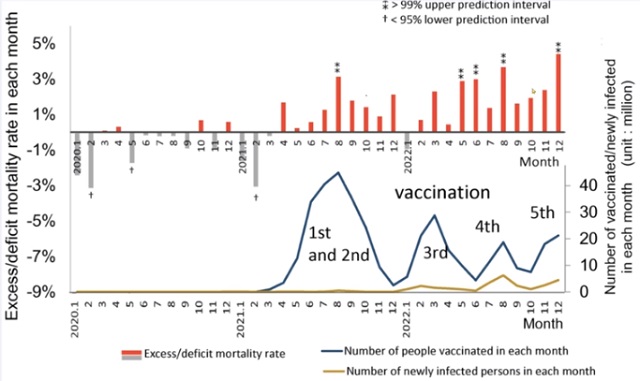
COVID-1916 hours agoJapanese study shows disturbing increase in cancer related deaths during the Covid pandemic
-

 Great Reset11 hours ago
Great Reset11 hours agoClimate expert warns against extreme ‘weather porn’ from alarmists pushing ‘draconian’ policies
-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoExtreme Weather and Climate Change
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoWhy Are Canadian Mayors So Far Left And Out Of Touch?
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTelegram founder tells Tucker Carlson that US intel agents tried to spy on user messages
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoNew capital gains hike won’t work as claimed but will harm the economy





