Alberta
Garfield Marks; “Oil-by-Seaway” proposal still draws interest.

The proposal to by-pass Quebec in shipping oil to refineries in New Brunswick via Thunder Bay then shipping through the St. Lawrence Seaway still has legs.
Nov 9 2019, Comments by D.B. Chalcroft on the
PROPOSAL TO SHIP OIL TO EASTERN CANADA VIA ST. LAWRENCE SEAWAY by Garfield Marks
Garfield Marks published his “Oil-by-Seaway” and it has subsequently been covered in the CBC media and more recently on CHQR 770 radio.
The Garfield Marks “Oil-by-Seaway” Proposal
Concept – To replace the eastern half (about 2600 km) of the proposed Energy East Pipeline with tanker shipping from Thunder Bay via the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence Seaway to St. John, New Brunswick.
The Energy East pipeline proposed by TC Energy in 2014, would have converted about 3000 km of the existing natural gas pipeline from Hardisty, Alberta to the Ontario-Quebec border, to diluted bitumen transportation; and would have built 1600 kms of new pipeline from the Ontario-Quebec border to St. John, New Brunswick. The capacity of the pipeline was to have been 1.1 million barrels (200,000 tonnes) of crude oil per day, was estimated to cost $12 billion, and at 4600 km would have been the longest pipeline in North America. TC Energy subsequently cancelled the project in October 2017, citing regulatory rule changes. In addition the Government of Quebec has stated that there is no social license for the Energy East pipeline through Quebec.
“Oil-by-Seaway” Tanker Shipping Option
The “Oil-by-Seaway” proposal would include converting 2000 km of the existing TC Energy Natural Gas pipeline from Hardisty, Ab, to Thunder Bay to carry diluted bitumen, and creating a new oil tanker shipping system from Thunder Bay through the existing St Lawrence Seaway and by ocean to the major Irving oil refinery at St. John , NB.
The existing St. Lawrence Seaway has more available shipping capacity than is presently being utilized. During the 1970s and 1980s, cargo shipments from Thunder Bay, for example, averaged about 20,000,000 metric tonnes per year with between 850 and 1470 vessels per year leaving the port. Since 2009 cargo shipments from Thunder Bay have averaged only about 8,000,000 tonnes/year on some 400 vessels per year.
The existing locks in the St. Lawrence Seaway at the Welland Canal and near Montreal, impose length, width, and draft, size restrictions (maximums of 225.5 m long by 23.8 m wide and draft of 8 m) on the vessels that can use the Great Lakes shipping system. The maximum size of bulk cargo that can be shipped through the system is about 29,000 tonnes per Seaway-capable ship – these ships are known as “lakers”.
The St Lawrence Seaway averages about 275 days of navigation per year – the other 90 days being closed to shipping due to winter conditions.
In order for “Oil-by-Seaway” shipping to deliver the 1,100,000 BPD (200,000 tonnes per day) of oil to the St John, NB terminal as envisaged by Energy East, in a shipping season of 275 days, would require the daily shipping deliveries to be 265,000 tonnes/day during the navigation season. This would require close to 10 “laker-tankers” per day to unload at St. John, NB. Assuming the turn-around time for a “laker-tanker” from Thunder Bay to St. John to Thunder Bay is about 16 days including 2 days for loading and unloading – means that a fleet of about 160 “laker-tankers” would be required to achieve this delivery commitment, plus storage facilities at St John of about 100,000,000 barrels.
The Welland Canal currently has about 1500-1800 vessel transits each way per year, or on average 5-7 transits per day each way. However in 1960 the total number of vessel transits was as high as 4500 each way (an average of 16 /day) although vessels were smaller carrying an average of only 3,400 tonnes of cargo. The Oil-by-Seaway proposal would add 2700 passages per year bringing the total to around 4500 per year or 16 per day each way, very similar to the 1960 record rate albeit with larger average vessel sizes.
Ballpark Cost Estimate for 160 Laker-Tankers
What would it cost to create a fleet of say 160 “Laker-tankers”? As a very rough comparison, the three Newfoundland Off-shore Shuttle Tankers that pickup roughly 230,000 BPD (47,000 tonne/day) of oil production from the five producing platforms on the Grand Banks, cost a reported $375,000,000 (ie $125M/ship)in 2016, and have a deadweight of 148,000 tonnes and gross tonnage of 85,000 tonnes each, meaning each ship can carry up to about 60,000 tonnes of cargo (oil) . These three Shuttle Tankers deliver the 47,000 tonne/day of Grand Bank oil production to the trans-shipment terminal at Whiffen Head, NL with an average turn-around time of 3-5 days . A rough cost estimate for the Laker-Tankers can be obtained by taking $125M X 29,000 t/ 60,000 t = $60 million. Therefore the cost of one “Laker-tanker” with 29,000 tonne capacity is estimated to be in the order of $60 million, and a fleet of 160 Laker-tankers would be in the ballpark of $10 billion.
Discussion
The St. Lawrence Seaway is currently handling 20-25 million tonnes of cargo per year through the Welland Canal in the Downbound direction, ie towards the east, with total transits of 1400 – 1900 per year. Oil-by-Seaway to equal the Energy East proposal of 200,000 tonnes per day would add 73,000,000 tonnes/yr. to the Downbound traffic. This is a significant increase to nearly 100,000,000 tonnes/year and 16 vessel transits per day each way, through the Seaway System. It would appear that the present Seaway infrastructure may be able to accommodate this magnitude of increase without major upgrades, because it doesn’t exceed the historical highs in vessel transits which occurred in the 1960s. This would need to be confirmed with the St. Lawrence Seaway Management Corporation.
The Oil-by-Seaway proposal would require a fleet of 160 or so “Laker-Tankers” which most likely don’t currently exist, and which would cost in the order of $10 billion . This concept would also require the creation of about 100,000,000 bbl. of incremental oil storage capacity at St. John, NB, that probably wasn’t part of the Energy East proposal, to cover the 90 days each year when the Seaway is closed.
Utilizing the existing Seaway Infrastructure to transport oil by tanker would reverse a long trend of declining commodity traffic through the Seaway system. This scheme could create the impetus to update and modernize Seaway facilities, and could also reinvigorate the communities along the Seaway, with substantially more economic activity in their midst.
Fabricating 160 Laker-Tankers could provide a significant workload for Canada’s ship-building industry, perhaps including the Davie Shipyard in Quebec, and the Irving shipyard in Halifax.
There are undoubtedly many other technical, social, environmental, and regulatory issues to be identified and considered, as well as whether this concept is commercially viable.
Preliminary Conclusion
On the surface, the Garfield Marks “Oil-by-Seaway” proposal seems to have sufficient merit to warrant a more thorough analysis than presented herein.
Comments by: David B. Chalcroft, P. Eng.
Previously published;
We have not been able to run our bitumen through a pipeline to a refinery in New Brunswick. There has been resistance in parts of Ontario and in Quebec. What if we came up with another plan. Would we consider it? There will be road blocks, but not insurmountable, would we consider it?
Yes how about Thunder Bay?
Thunder Bay, Ontario, the largest Canadian port of the St. Lawrence Seaway located on the west end of Lake Superior, 1850 kms. from Hardisty, Alberta. A forgotten jewel.
So what, you may ask.
They used to ship grain from Thunder Bay in huge tankers to ports all over the world. Why not oil?
The Saint Lawrence Seaway ships fuel, gasoline and diesel tankers, to this day.
We could run oil tankers to the Irving refinery in New Brunswick, bypassing the controversial pipeline running through eastern Ontario and Quebec.
The pipeline, if that was the transport model chosen, would only need to run through parts of Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba and Ontario. Like, previously stated the pipeline would only be 1850 kms. long.
The other great thing about Thunder Bay is the abundance of rail lines. Transportation for such things as grain and forestry products from western Canada. If you can’t run pipeline from Hardisty, through to Thunder Bay, use the railroad.
Why Hardisty, you may ask.
Hardisty, according to Wikipedia, is mainly known as a pivotal petroleum industry hub where petroleum products such as Western Canada Select blended crude oil and Hardisty heavy oil are produced, stored and traded.
The Town of Hardisty owes its very existence to the Canadian Pacific Railway. About 1904 the surveyors began to survey the railroad from the east and decided to locate a divisional point at Hardisty because of the good water supply from the river.
Hardisty, Alberta has the railroad and has the product, the storage capacity, and the former Alberta government planned on investing $3.7 billion in rail cars for hauling oil while Thunder Bay has the railroad and an under utilised port at the head of the St. Lawrence Seaway.
Economics are there along with opportunity, employment would be created and the east coast could end its’ dependency on imported oil.
Do we have the vision or willingness to consider another option. I am just asking for all avenues to be considered.
In my interviews in Ontario there is a willingness to discuss this idea.
The St. Lawrence Seaway Management Corporation is still reviewing the idea of shipping crude oil from western Canada through its system, and it’s a long way from happening, according to Bruce Hodgson, the Seaway’s director of market development.
“Obviously, there needs to be an ongoing commitment on the part of a producer, and so that’s going to be required for any project of this nature,” he said.
We could consider it, could we not?
CBC NEWS did a story about this idea on March 7 2019;
A retired oil field worker in Alberta has “floated” a novel solution to Alberta’s oil transportation woes: pipe the bitumen to Thunder Bay, Ont., then ship it up the St. Lawrence Seaway to the Irving oil refinery in New Brunswick.
Marks’ proposal might be more than a pipe dream, according to the director of the Queen’s Institute for Energy and Environmental Policy.
‘I don’t think that it’s a totally nuts idea’
“I don’t think that it’s a totally nuts idea,” Warren Mabee said. “I think that there’s some flaws to it … but this is an idea that could work in certain circumstances and at certain times of year. … It’s not the craziest thing I’ve ever heard.”
The chief executive officer of the Port of Thunder Bay said shipping oil from the port “could easily be done.”
“We ship refined gasoline and diesel up from Sarnia. We’ve done that for many many years,” Tim Heney told CBC. “So it’s not something that’s that far-fetched.”
There are, however, plenty of potential drawbacks to shipping crude through the Seaway, Mabee explained, not least of which is the fact that it isn’t open year-round.
The need to store oil or redirect it during the winter months could be costly, he said.
Potential roadblocks
Another potential pitfall is capacity, he added; there may not be enough of the right-sized tankers available to carry the oil through the Seaway.
Finally, he said, the journey by sea from Lake Superior to the Irving refinery in New Brunswick is a long one, so it might make more sense to transport the product to a closer facility such as the one in Sarnia, Ont.
The St. Lawrence Seaway Management Corporation is still reviewing the idea of shipping crude oil from western Canada through its system, and it’s a long way from happening, according to Bruce Hodgson, the Seaway’s director of market development.
“Obviously, there needs to be an ongoing commitment on the part of a producer, and so that’s going to be required for any project of this nature,” he said.
So far, no producer has come forward seeking to ship crude through Thunder Bay, he said.
Asked about the possible environmental risks of shipping oil on Lake Superior, both Hodgson and Heney said shipping by tanker is relatively safe; Hodgson noted that any tankers carrying the product would have to be double-hulled, and crews are heavily vetted.
Time to rethink pipelines?
There hasn’t been a spill in the Seaway system for more than 20 years he said.
Nonetheless, Mabee said, the potential for an oil spill on the Great Lakes could be a huge issue.
“The St. Lawrence and the Great Lakes have a lot of people living in close proximity, a lot of people who rely on it for drinking water,” he said. “There’s a delicate ecosystem there. I think a lot of people would push back against this proposal simply from that perspective.”

In fact, one of the reasons Mabee appreciates Marks’ proposal, he said, is because it invites people to weigh the pros and cons of different methods of transporting oil.
“If we’re not going to build pipelines, but we’re going to continue to use oil, it means that people are going to be looking at some of these alternative transport options,” he said.
“And if we don’t want oil on those alternative transport options, we need to give the pipelines another thought.
Time to consider all options, I dare say.
Alberta
Maxime Bernier says it’s ‘astounding’ Alberta is ‘pushing’ COVID boosters, tells Danielle Smith to stop it

From LifeSiteNews
The People’s Party of Canada leader tells the Alberta government: ‘It’s over! Get over it!’
People’s Party of Canada (PPC) leader Maxime Bernier said Alberta Premier Danielle Smith should tell provincial health bureaucrats to “back off” and stop “pushing” the mRNA COVID boosters on “anyone,” considering a recent announcement from health officials recommending yet more COVID shots.
“I find it astounding that Alberta public health bureaucrats are still pushing the mRNA boosters on anyone, and especially on children who have never been at risk, almost two years after almost all other pandemic measures have been ended,” Bernier told LifeSiteNews.
“Danielle Smith’s government should tell its bureaucrats to back off and stop stupidly feeding a needless sense of fear surrounding the virus that lingers among certain groups of society. It’s over! Get over it!”
Earlier this week, officials from Alberta Health Services (AHS), whose chief medical officer throughout the COVID crisis, Dr. Deena Hinshaw, was fired by Smith in 2022, updated its COVID booster recommendations to every “three months” starting at babies only six months old.
“Starting April 15, 2024, select groups of Albertans at high risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19 will be eligible for an additional dose,” the AHS noted on its website.
AHS health officials still assert that all “vaccines are safe, effective and save lives,” and that one can get a COVID shot at the same time as a flu vaccine.
On April 16, Bernier commented on the AHS’s new COVID jab guideline changes on X, in which he asked, “What’s going on in Alberta with their “conservative” government?
Bernier, who was a firm opponent of both the COVID shots and mandates, told LifeSiteNews that AHS’s recommendations are puzzling, given “more and more scientific evidence is emerging of dangerous side effects when injecting from these experimental substances.”
“Even though these are only recommendations, and nothing is mandated, this ‘guidance’ by government agencies influences people’s decisions,” Bernier said.
AHS claims that the booster shots “are anticipated to provide a good immune response against currently circulating strains.”
Those under 18 still need written or verbal consent from their parents to get the shot.
AHS is recommending booster jabs for seniors, healthcare workers as well as those with underlying medical conditions. They also recommend that First Nations people and “members of racialized and other equity-denied communities,” as well as pregnant women get the shots as well.
The COVID shots were heavily promoted by the federal government as well as all provincial governments in Canada, with the Alberta government under former Premier Jason Kenney being no exception.
The mRNA shots themselves have been linked to a multitude of negative and often severe side effects in children.
Danielle Smith took over from Kenney as leader of the United Conservative Party (UCP) on October 11, 2022, after winning the leadership. Kenney was ousted due to low approval ratings and for reneging on promises not to lock Alberta down as well as enacting a vaccine passport. Smith was opposed to COVID jab mandates.
Bernier: It’s ‘deplorable’ some provinces still mandate COVID shot for Heathcare workers
While Alberta does not mandate the COVID shots for healthcare workers anymore, British Columbia still does as well as some health regions in Ontario, a fact that Bernier called “deplorable.”
“I find it deplorable that nurses, doctors and other healthcare workers in B.C. and Ontario still have to be vaccinated to work in hospitals and that thousands of them have not been reintegrated,” Bernier told LifeSiteNews.
“The authoritarian covid measures adopted by all governments have been traumatic enough for millions of Canadians. All of them should be lifted.”
Last year, LifeSiteNews reported on how the details of the Canadian federal government’s COVID-19 vaccine contract with Pfizer for millions of doses of the mRNA-based experimental shots were recently disclosed after being hidden for over three years.
The contract with Pfizer shows the government agreed to accept the unknown long-term safety and efficacy of the shots. The details of the Pfizer contract do not disclose how much the government spent on the jabs.
A bill introduced by Conservative Party leader Pierre Poilievre that would have given Canadians back their “bodily autonomy” by banning future jab mandates was voted down last year after Trudeau’s Liberals and other parties rejected it.
Adverse effects from the first round of COVID shots have resulted in a growing number of Canadians filing for financial compensation over injuries from the jabs via the federal Vaccine Injury Program (VISP).
VISP has already paid well over $11 million to those injured by COVID injections.
Earlier this year, LifeSiteNews reported on how officials from Health Canada have admitted that there is “residual plasmid DNA” in the COVID shots after a Conservative MP asked the agency through an official information request if the DNA fragments were in the shots.
As for Bernier, earlier this month he called out Poilievre for dodging a question regarding Canada’s participation in the United Nations’ pro-abortion Paris Climate Agreement.
Throughout most of the COVID crisis, Canadians from coast to coast were faced with COVID mandates, including jab dictates, put in place by both the provincial and federal governments.
After much pushback, thanks to the Freedom Convoy, most provincial mandates were eliminated by the summer of 2022.
There are currently multiple ongoing class-action lawsuits filed by Canadians adversely affected by COVID mandates.
Alberta
Canada’s advantage as the world’s demand for plastic continues to grow

From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
‘The demand for plastics reflects how essential they are in our lives’
From the clothes on your back to the containers for household products to the pipes and insulation in your home, plastics are interwoven into the fabric of day-to-day life for most Canadians.
And that reliance is projected to grow both in Canada and around the world in the next three decades
The Global Plastics Outlook, published by the Paris-based Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), forecasts the use of plastics globally will nearly triple by 2060, driven by economic and population growth.
The use of plastics is projected to double in OECD countries like Canada, the United States and European nations, but the largest increases will take place in Asia and Africa.
“The demand for plastics reflects how essential they are in our lives, whether it is packaging, textiles, building materials or medical equipment,” says Christa Seaman, vice-president, plastics with the Chemical Industry Association of Canada (CIAC), which represents Canada’s plastics producers.
She says as countries look to meet climate and sustainability goals, demand for plastic will grow.
“Plastics in the market today demonstrate their value to our society. Plastics are used to make critical components for solar panels and wind turbines. But they also can play a role in reducing weight in transportation or in ensuring goods that are transported have less weight in their packaging or in their products.”
Canada produces about $35 billion worth of plastic resin and plastic products per year, or over five per cent of Canadian manufacturing sales, according to a 2019 report published by the federal government.
Seaman says Canadian plastic producers have competitive advantages that position them to grow as demand rises at home and abroad. In Alberta, a key opportunity is the abundant supply of natural gas used to make plastic resin.
“As industry and consumer expectations shift for production to reduce emissions, Canada, and particularly Alberta, are extremely well placed to meet increased demand thanks to its supply of low-carbon feedstock. Going forward, production with less emissions is going to be important for companies,” Seaman says.
“You can see that with Dow Chemical’s decision to spend $8.8 billion on a net zero facility in Alberta.”
While modern life would not be possible without plastics, the CIAC says there needs to be better post-use management of plastic products including advanced recycling, or a so-called “circular economy” where plastics are seen as a resource or feedstock for new products, not a waste.
Some companies have already started making significant investments to generate recyclable plastics.
For example, Inter Pipeline Ltd.’s $4.3 billion Heartland Petrochemical Complex near Edmonton started operating in 2023. It produces a recyclable plastic called polypropylene from propane, with 65 per cent lower emissions than the global average thanks to the facility’s integrated design.
Achieving a circular economy – where 90 per cent of post-consumer plastic waste is diverted or recycled – would benefit Canada’s economy, according to the CIAC.
A Deloitte study, commissioned by Environment & Climate Change Canada, estimated diverting or reusing 90 per cent of post-consumer plastic waste by 2030 will save $500 million annually while creating 42,000 direct and indirect jobs. It would also cut Canada’s annual CO2 emissions by 1.8 megatonnes.
Right now, about 85 per cent of plastics end up in Canada’s landfills. To reach the 90 per cent diversion rate, Seaman says Canada must improve its infrastructure to collect and process the plastic waste currently being landfilled.
But she also says the industry rather than municipalities need to take responsibility for recycling plastic waste.
“This concept is referred to as extended producer responsibility. Municipalities have the responsibility for managing recycling within a waste management system. Given the competing costs and priorities, they don’t have the incentive to invest into recycling infrastructure when landfill space was the most cost-effective solution for them,” she says.
“Putting that responsibility on the producers who put the products on the market makes the most sense…The industry is adapting, and we hope government policy will recognize this opportunity for Canada to meet our climate goals while growing our economy.”
-
 COVID-193 hours ago
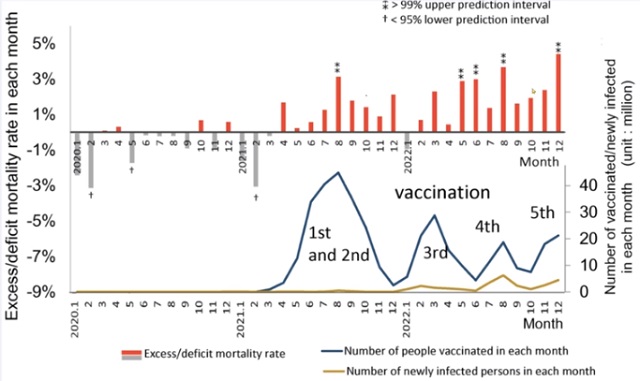
COVID-193 hours agoJapanese study shows disturbing increase in cancer related deaths during the Covid pandemic
-

 Jordan Peterson2 days ago
Jordan Peterson2 days agoJordan Peterson slams CBC for only interviewing pro-LGBT doctors about UK report on child ‘sex changes’
-

 Freedom Convoy2 days ago
Freedom Convoy2 days agoTrudeau’s use of Emergencies Act has cost taxpayers $73 million thus far
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoDanielle Smith warns arsonists who start wildfires in Alberta that they will be held accountable
-

 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoLiberal MP blasts Trudeau-backed ‘safe supply’ drug programs, linking them to ‘chaos’ in cities
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days agoThe Smallwood solution
-

 Agriculture2 days ago
Agriculture2 days agoBill C-282, now in the Senate, risks holding back other economic sectors and further burdening consumers
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoWhy Are Canadian Mayors So Far Left And Out Of Touch?