COVID-19
The Rouleau Commission’s recommendations: Laundering the government’s agenda for censorship and expanded emergency powers

From the MacDonald Laurier Institute
By Ryan Alford
In this commentary, Ryan Alford examines how the Rouleau Commission’s personnel, agenda, and fundamental assumptions were all determined by Cabinet, the very body whose actions it was charged with assessing.
On August 31, Minister of Public Safety Dominic LeBlanc issued a six month progress report on implementing the recommendations of the Public Order Emergency Commission (POEC), also known as the Rouleau Inquiry. It is notable for what it explicitly notes as being implemented, and for what remains to be implemented without significant comment. That said, it would be an error to begin with a comparison between what the Final Report of the Rouleau Inquiry recommended and what the federal government is now implementing. Rather, the critical point of comparison is between the Order-in-Council establishing the Commission – that is, Commissioner Rouleau’s marching orders from the Government – and the legislative agenda that is now being pursued.
The Emergencies Act itself calls for a mandatory public inquiry into “the circumstances that led to the declaration [of an emergency] being issued and the measures taken for dealing with the emergency.” Before the POEC, civil libertarians had understood this to mean that the mandate of any inquiry would be to examine whether the government had a reasonable basis to conclude threats existed to national security that could not be dealt with under any other Canadian law, and whether the emergency measures taken by the cabinet conformed to the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. In short, it was always assumed the Inquiry would have a tight focus on whether a national emergency, as defined by law, existed and whether the declaration (and every action taken under it) had been constitutional.
That reassuring assumption proved unfounded. In the Order of April 25, 2022, the Governor General in Council, on the recommendation of the Prime Minister, redefined the meaning of the “circumstances that led to the emergency”, which now included “the impact, role and sources of misinformation and disinformation, including the use of social media”. It also directed the Commissioner to “make recommendations, as pertains to the matters examined in the Public Inquiry, on the use or any necessary modernization of [the Emergencies] Act”.
Thus, cabinet dictated the fundamental assumptions that guided the Rouleau Commission. Two of these assumptions stand out from the others. First, that misinformation and disinformation on social media had a significant impact on the organizers and participants of the Freedom Convoy. Second, that the Emergencies Act might need “modernization”. Both of these premises are highly problematic and should not have been granted at the outset of the hearings (i.e.: prior to the admission of any evidence).
The hearings phase provided ample demonstration of the spuriousness of these assumptions. Witness testimony reiterated that the concerns of Freedom Convoy protestors were practical and political in nature. Many had been directly affected by vaccine mandates that curtailed their ability to work and travel. Others expressed the view that these mandates had expanded the powers of government beyond what was acceptable. While these might not have constituted an indisputable justification for a sustained and disruptive protest, there was no evidence presented in the hearings that the Freedom Convoy protests were predicated chiefly, or even substantially, on social media-borne misinformation or disinformation.
Second, the only testimony from witnesses that supported the notion that the Emergencies Act needs to be modernized came from those closest to the heart of the federal government, namely the National Security and Intelligence Advisor to the Prime Minister and the Clerk and Deputy Clerk of the Privy Council Office (PCO). The documents, chiefly emails, expressing their concerns about the purportedly antiquated requirements for declaring a public order emergency seemed to follow shortly after the Director of CSIS had circulated a memorandum conveying his opinion that these requirements had not been met.
Essentially, when the request to conclude that a public order emergency existed had been rebuffed by CSIS, the RCMP, and, most critically, the Intelligence Bureau of the Ontario Provincial Police, which was at the time coordinating on the ground intelligence collection, senior government bureaucrats started to express concern that the Emergencies Act and the CSIS Act were out of date.
Many observers found this claim unconvincing; not least because, unlike many pieces of public safety-related legislation – for instance, the Criminal Code – neither the Emergencies Act or the CSIS Act had been previously flagged as in need of updating as both are relatively modern pieces of legislation, enacted in 1988 and 1984, respectively. Notably, these laws themselves had been passed in response to the serious abuse of the War Measures Act during the October Crisis of 1970 and, in the decade that followed, the unlawful activities of the National Security Division of the RCMP, as detailed in the final report of the McDonald Commission (1981).
Accordingly, it was not surprising that, in the three decades since the enactment of these two laws, there had been no amendments that would have loosened the legislated restrictions on federal government’s ability to expand its own powers at the expense of Parliament and the provinces. The Order-in-Council nevertheless mandated that the Inquiry consider the issue of the “necessary modernization” of the Emergencies Act, and the Commission continued to take this directive seriously – even after it had become apparent that the argument that modernization was needed had originated in an internal dispute over whether a declaration of a public order emergency during the Freedom Convoy would be unlawful. (All of the police and intelligence agencies consulted by the government had concluded that the statutory and constitutional requirements for the use of the Emergencies Act had not been met).
What is even more problematic is the possibility that Cabinet had made the call to invoke the Emergencies Act on the premise that it was appropriate to measure the facts on the ground in Ottawa against the standard of an “evolved” interpretation of the Act (likely at the urging of senior bureaucrats). This may well have been the same logic employed by Minister of Justice David Lametti. We’ll likely never know for sure, owing to the Prime Minister’s assertion of solicitor-client privilege over a secret memo outlining the Justice Department’s legal argument for invoking the Act, which convinced the Cabinet to come to the opposite conclusion from the one stated in the Director of CSIS’ memorandum of the previous day.
Accordingly, by directing the Rouleau Commission to consider whether the Emergencies Act needed to be modernized, the Cabinet may have been clandestinely requesting that the Inquiry bless its novel (and secret) interpretation of legal definition of a public order emergency. This interpretation would, as such, receive a retroactive justification if the Commission were to conclude that the Minister of Justice had merely been anticipating the legislative changes needed to modernize the Act.
For obvious reasons, this request could not be made explicitly. If the Cabinet did, in fact, rely on the “evolved” definition in a closed-door meeting protected by Cabinet and solicitor-client privilege, this would be a constitutional abomination they’d rather not see come to light. The Emergencies Act specifies a narrow range of conditions that allow the Cabinet to assume the power of Parliament to pass laws – a problematic exemption from the basic principles of responsible government at best. If the Cabinet decided to surreptitiously amend the legislation that allows it to invoke these extra-parliamentary powers, it is effectively asserting the supremacy of the executive over the legislative branch. Cabinet cannot be confined within legal bounds if it reserves for itself a secret power to adjust these bounds outwards at will.
The second assumption embedded in the POEC’s mandate received more explicit treatment in LeBlanc’s progress report. It noted that the Final Report had charged the government with addressing “social media misinformation and disinformation”, and that the Commission had made specific recommendations that “the federal government work with its partners to further study the impact of social media . . . while addressing the serious challenges that misinformation, disinformation, and other online harms present to individuals and Canadian society”. Suffice it to say that Minister LeBlanc’s progress report makes it clear that this particular recommendation is being taken very seriously.
Of course, when the Cabinet directed the Rouleau Commission to provide recommendations related to social media misinformation, it had already reached firm conclusions about the need to implement far-reaching censorship of online expression. However, in purporting to merely be implementing the recommendations of a Public Inquiry, the federal government may be able to divert attention from the fact that some of the most contentious elements of this legislation have already been passed. This includes provisions that would allow the a committee established under the CRTC’s regulatory authority to assess and censor individuals’ social media posts. Additionally, it can point to the recommendations of the Rouleau Commission as a justification for the decision to funnel still more governmental funding to purportedly “neutral” civil society organizations and academic research centres that inevitably take the position that increased governmental censorship is necessary and justifiable. (See, for instance, Ontario Tech University’s Centre on Hate, Bias, and Extremism).
Indeed, this dynamic of finding purportedly neutral sources for highly contentious proposals was present within the Rouleau Commission itself. Having failed to obtain testimony that demonstrated the need for censorship and increased emergency powers in the Inquiry’s evidence phase, the Inquiry’s in-house Research Council commissioned (and paid for) submissions from a number of academics well-known for their advocacy, some of whom were affiliated with and even co-authored their submissions with notoriously politicized and ideologically biased organizations, such as the Canadian AntiHate Network.
Finally, when it came time for the culmination of the policy phase of the Inquiry, the roundtables charged with shaping the Commission’s recommendations were packed with experts with ties to the Trudeau government, notably exTrudeau Foundation CEO Morris Rosenberg. (Rosenberg was also the author of the report commissioned by the Privy Council Office that concluded that foreign interference had not affected the 2021 federal election; Rosenberg’s report concluded, contentiously, that “domestic actors” should also be a subject
of concern.)
On the question of whether the government will propose amending the Emergencies Act, LeBlanc’s progress report is considerably more evasive. This is likely because detaching the definition of a public order emergency from the definition found in the CSIS Act, as Rouleau recommended, would dramatically expand the federal government’s power to declare an emergency. If the legislative amendment tracks the Cabinet’s desires, the Emergencies Act could be triggered by any activity that threatens the “economic security” of Canada. As the more critical policy experts noted at the roundtable (and in their policy recommendations), this definition is practically limitless, as any disruptive protest (or strike, lockout, mass gathering, boycott, etc.) could have an “impact” on the national economy.
Accordingly, it seems likely that, before proposing such an amendment, the government will want to gauge the prevailing winds in Parliament. The surest indicator of unfavourable conditions would be the rigorous assessment of the Special Joint Committee on the Declaration of Emergency, which has equal status under the Emergencies Act with the Public Inquiry, and should not feel any need to defer to its findings – particularly as the Rouleau Commission’s personnel, agenda, and fundamental assumptions were all determined by Cabinet, the very body whose actions it was charged with assessing.
The Special Joint Parliamentary Committee can serve as a neutral judge, and it should exercise independent judgment when compiling its own definitive report. The Committee will be an especially important arbiter of the key issue of whether the federal government, having expanded the scope of its emergency powers in secret, should receive retroactive benediction in the form of a newly amended Emergencies Act, which would encompass responses to “economic threats” (an illusory limitation, to be clear). Such an outcome would make Cabinet, and effectively the Prime Minister, our true sovereign.
About the author
Ryan Alford is a Senior Fellow of the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, a Professor at the Bora Laskin Faculty of Law at
Lakehead University, and a Bencher of the Law Society of Ontario. He was also granted the status of a Party by the Public Order Emergency Commission and appeared in that capacity before the Rouleau Inquiry.
Bruce Dowbiggin
The Covid 19 Disaster: When Do We Get The Apologies?

Breaking: Drs. Bonnie Henry and Theresa Tam have been appointed to the Order of Canada in recognition of their role in the country’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
And so the game of covid liar’s poker has more winners. It’s like awarding the captain of the Titanic the Nobel Prize for his work on floatation. As we now know these two— and the other WHO finger puppets in Canada— made the Covid 19 episode worse, not better, with their prescription for panic, positives and punishment. Even as they knew the truth about the limits of the virus and the efficacy of vaccines they continued to spew fallacious PCR data on the extent of the sickness and who was at risk.
Put simply, to protect vulnerable seniors they said kids were also at great risk. Which was unconscionable.
In this they encouraged Justin Trudeau in his worst instincts, combining his father’s insouciant disregard for civil rights (sending in the police) with his mother’s mental stability. Propped up by Team Tam and its U.S. allies such as Anthony Fauci, this hysteria peaked with a sequestered PM crushing the Truckers Convoy’s vaccine protest with emergency measures and destruction of civil liberties.
Lest you wonder, this overreach was recognized at the time. Justice Maclean wrote at the trial of Convoy organizers, “Defendants & other persons remain at liberty to engage in a peaceful, lawful & safe protest”. On Feb. 16, he continued a no-honking order, again writing: “Defendants & other persons remain at liberty to engage in a peaceful, lawful & safe protest.”
The leaders of the Convoy, lynched by Canadian media’s phoney claims of right-wing American interference, are still fighting jail time on charges of nuisance. While violent criminals are routinely released on bail or absolved.
Justice Richard Mosley later concluded that while the convoy was a disruption of public order, it didn’t constitute a national emergency and invoking the act “does not bear the hallmarks of reasonableness — justification, transparency and intelligibility.” But in real time Team Tam made no attempts to correct the wilder misgivings about Covid (lockdowns, mandatory vaccines). Trudeau was given a hall pass. Needless to say the purchased media made things infinitely worse regurgitating these mistakes.
In short, they knew better but hid the truth. But why pick on Henry and Tam? Under Trudeau and his wingman Jagmeet Singh this was the golden age of lies and prevarications in Canada and the U.S. No apologies were ever offered when the truth emerged.
As we’ve noted before, Trudeau cried with a teddy bear carefully positioned over 751 alleged unmarked graves in a known Catholic cemetery that the local Cowessess band abandoned. The Liberal government knew the claim of 215 “children’s graves” was false, and still ran with it to get Trudeau his photo-op. Naturally the CBC Media Party played (and still plays) accomplice in this farce as the Canadian flag was lowered to half-mast for six months and Trudeau ratted out Canada at the UN as a genocidal state.
There were more, plenty more Trudeau scandals that media endorsed and then stood by even as the truth was revealed. SNC Lavalin. We Charity. Arrive Can app. Firing indigenous justice minister. Chinese drug infiltration/ money laundering. Nazi Celebrated in Parliament. Welcome To Canada immigration. Nova Scotia massacre. McKinsey Consultation. Blackface. And so on.
And were there apologies when it came time to make the Trudeau Liberals accountable? No, they staged a media circus over Donald Trump’s assertion of 51st state. All the fake news and deliberate lies went poof, allowing Mark Carney to seamlessly assume the PM job.

Lest We Forget Pt. 2 it was not exclusive to Canada. As we are now learning: Barack Obama and Joe Biden sat in an August 3, 2016 Situation Room briefing and said, yeah, let the highest officials in our administration fabricate evidence to frame the opposing party candidate Donald Trump. Obama. Biden. Comey. McCabe. Strzok. Page. Rice. Etc.
Knowingly using the faked Clinton campaign ‘Steele Dossier’ hoax, they launched a federal investigation into the Trump presidential campaign that lasted three years after Trump was sworn in as the nation’s 45th President. Arresting and jailing his partners and colleagues. Inventing fake stories for their media enablers. Let’s repeat that. Saint Obama knew there was criminal activity in the process but let his henchmen try to fix an election.

And when the ruse was uncovered no one apologized. No one in authority was fired or jailed. The Pulitzer Prizes awarded to the NT Times and Washington Post for disseminating the DEMs scandal were not rescinded. Nor were they given back by the lying newspapers.
The concerted frauds of the same U.S. DOJ, FBI and State Departments were fed by media and accepted by gullible publics in Canada and America. The fantastical 2020 election results were likewise drummed into the public irrespective of the sudden “appearance” of 27 million new votes during a pandemic.
It was all a fitting preamble to the 2020-2024 Biden senility scandal with Democrats running a man they knew was in full dementia. In the 2020 election Biden was hidden from public view, the better to let media attack Trump for spurious charges launched by partisan DNC attorneys in Georgia, New York and DC. Even then it took the suppression of Hunter Biden’s incriminating laptop just prior to the election to get his father elected.

The dance of denial continued in Biden’s term as he physically and mentally deteriorated before the American public. But inquiries about who was running the government if not Biden were harshly suppressed. Media lackeys noted he was sharp as a tack mentally and in tip-top physical condition when he wasn’t falling down stairs.
It took the stunning 2024 debate debacle with Trump to strip away the lies about Biden’s health, now said to be advanced prostate cancer and Parkinson’s. The media, caught in their own lies about Biden’s condition, offered no apologies and tried to blame Biden’s stutter for the performance.. Right.
These were the two greatest U.S. hoaxes from people who’d cried hoax incessantly. They were hardly the only abuse of public trust. Some of the perpetrators are said to now be under investigation— even as they hand out awards to each other. The media’s credibility is shattered and yet they still blame others. Jaded voters are taking a “we’ll see” approach. But expectations of any change in DC or Ottawa are limited.
As Stephen Taylor posted on X: “Turns out for Liberals, ‘elbows up’ just means ‘noses up’ like it always has.”
Bruce Dowbiggin @dowbboy is the editor of Not The Public Broadcaster A two-time winner of the Gemini Award as Canada’s top television sports broadcaster, his new book Deal With It: The Trades That Stunned The NHL And Changed hockey is now available on Amazon. Inexact Science: The Six Most Compelling Draft Years In NHL History, his previous book with his son Evan, was voted the seventh-best professional hockey book of all time by bookauthority.org . His 2004 book Money Players was voted sixth best on the same list, and is available via brucedowbigginbooks.ca.
Freedom Convoy
Court Orders Bank Freezing Records in Freedom Convoy Case
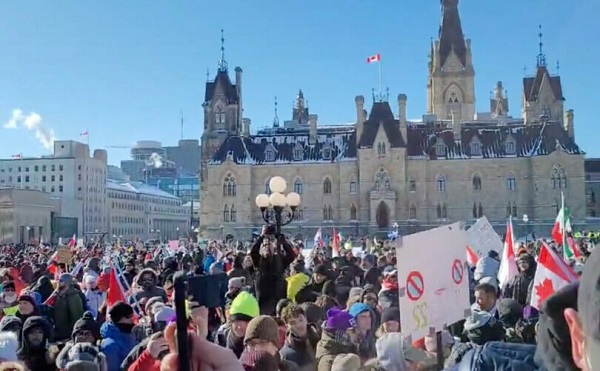
|
A Canadian court has ordered the release of documents that could shed light on how federal authorities and law enforcement worked together to freeze the bank accounts of a protester involved in the Freedom Convoy.
Both the RCMP and TD Bank are now required to provide records related to Evan Blackman, who took part in the 2022 demonstrations and had his accounts frozen despite not being convicted of any crime at the time.
The Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms (JCCF) announced the Ontario Court of Justice ruling. The organization is representing Blackman, whose legal team argues that the actions taken against him amounted to a serious abuse of power.
“The freezing of Mr. Blackman’s bank accounts was an extreme overreach on the part of the police and the federal government,” said his lawyer, Chris Fleury. “These records will hopefully reveal exactly how and why Mr. Blackman’s accounts [were] frozen.”
Blackman was arrested during the mass protests in Ottawa, which drew thousands of Canadians opposed to vaccine mandates and other pandemic-era restrictions.
Although he faced charges of mischief and obstructing police, those charges were dismissed in October due to a lack of evidence. Despite this, prosecutors have appealed, and a trial is set to begin on August 14.
At the height of the protests, TD Bank froze three of Blackman’s accounts following government orders issued under the Emergencies Act. Then-Prime Minister Justin Trudeau had invoked the act to grant his government broad powers to disrupt the protest movement, including the unprecedented use of financial institutions to penalize individuals for their support or participation.
In 2024, a Federal Court Justice ruled that Trudeau’s decision to invoke the act had not been justified.
Blackman’s legal team plans to use the newly released records to demonstrate the extent of government intrusion into personal freedoms.
According to the JCCF, this case may be the first in Canada where a criminal trial includes a Charter challenge over the freezing of personal bank accounts under emergency legislation.
|
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoThe Covid 19 Disaster: When Do We Get The Apologies?
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoSweeping Boston Indictment Points to Vast Chinese Narco-Smuggling and Illegal Alien Labor Plot via Mexican Border
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta school boards required to meet new standards for school library materials with regard to sexual content
-

 International21 hours ago
International21 hours agoSupport for the Ukraine war continues because no one elected is actually in charge.
-

 Business20 hours ago
Business20 hours agoTrump slaps Brazil with tariffs over social media censorship
-

 Environment1 day ago
Environment1 day agoEPA releases report on chemtrails, climate manipulation
-

 Business24 hours ago
Business24 hours agoCBC six-figure salaries soar
-

 Addictions23 hours ago
Addictions23 hours agoCan addiction be predicted—and prevented?




