Energy
The environmental case for Canadian LNG

From Resource Works
Canada’s new prime minister has made some encouraging pronouncements recently about making Canada an energy superpower – a pledge repeated by King Charles in Tuesday’s throne speech.
Canada’s new prime minister has made some encouraging pronouncements recently about making Canada an energy superpower — a pledge repeated by King Charles in Tuesday’s throne speech.
Mark Carney, through the King, made the clarion call to make Canada “the world’s leading energy superpower in both clean and conventional energy.”
But how can Canada increase oil and gas production and exports while adhering to its green ambitions of net zero by 2050?
Two reports out last week — one from the Fraser Institute, the other from the Pembina Institute — help make a case for the net environmental benefits of a Canadian LNG export industry.
The Fraser Institute’s Exporting Canadian LNG to the World cites three B.C.-specific GHG life cycle models of coal-to-gas switching to conclude that, if LNG exports from B.C. replaced coal power in China, greenhouse gas emissions there could be reduced 34% to 62%.
If Canada were to double its current natural gas production and export it to Asia, “global GHG emissions could be reduced by up to 630 million tonnes annually,” the report asserts.
Canada’s total GHG emissions in 2023 was 694 million tonnes, according to Environment Canada. So, according to the Fraser Institute’s math, the equivalent of Canada’s total GHG emissions could be almost entirely erased, simply by exporting LNG to China to displace coal.
There’s a couple of flies in this ointment, which I’ll get to shortly, but the argument that there would be net environmental benefits to Canadian LNG exports still holds up, I think.
Coal accounts for about 45% of global emissions from fuel combustion, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Switching from coal to natural gas in thermal power generation can result in a 50% reduction in CO2 emissions, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
But natural gas isn’t just a cleaner fuel, it’s also a critical feed stock — for which there is no real substitute — for an array of industrial and petrochemical processes, including fertilizer production. Like it or not, there will be a demand for natural gas for decades to come, and Canada is demonstrating that it can produce it with much lower emissions intensity than almost anyone else.
That natural gas can reduce emissions when it displaces coal is not theoretical — there’s proof. In the U.S., a 32% decrease in CO2 emissions between 2005 and 2019 in the power sector was attributed largely to coal-to-gas fuel switching, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
“Lower CO2 emissions have largely been a result of a shift from coal to natural gas in the electricity generation mix,” the EIA concludes.
Now for the flies in the ointment.
First, while there could indeed be sizable global emissions reductions if Canadian LNG displaced coal power in China, India and other parts of Asia, we couldn’t claim those reductions under the current Paris Agreement model.
(Nota bene: Donald Trump is once again withdrawing the U.S. from the Paris Agreement, and the U.S. — now the world’s biggest LNG exporter — has no compunction over gobbling up as much LNG market share as it can.)

Canada and China are both signatories to the Paris Agreement. Each country produces its own climate action plans — nationally determined contributions — and can only count emissions reductions within its own national borders.
We can’t claim Chinese emissions reductions for our own, even if it were the result of Canadian LNG imports.
There has been talk of Internationally Transferred Mitigation Outcomes (ITMOs) that would allow Canada to be credited for emissions reduced in China from coal displacement through LNG. I don’t know why China, having achieved emissions reductions through coal-to-gas fuel switching, would surrender those reductions to Canada.
Achieving some win-win ITMO agreement would take some fancy bargaining, and perhaps Mark Carney is up to this task. He knows a thing or two about these sorts of things, having served as the UN’s special envoy on climate action and finance.
But even if ITMOs are not possible for Canadian LNG exports, there are still compelling economic and environmental arguments for Canada to act on its strengths — abundant resources, high demand for those resources, and comparatively high environmental standards.
Anti-fossil fuel activists will, of course, continue to trot out the canard that LNG is as bad, if not worse, than coal, because of the methane associated with upstream natural gas production.
It’s true that methane is the Achilles heel of natural gas and LNG. Because of its high global warming potential, even small amounts of methane — leakage rates of 2% or more — can begin to negate natural gas’s lower CO2 intensity.
Fortunately, methane leakage can be addressed through better plumbing, best practices, regulations, and better monitoring, and as the Pembina Institute points out, B.C.’s natural gas sector has leading the way here.
According to the BC Energy Regulator, measurements completed in 2021 estimate the methane intensity of B.C. natural gas production at just 0.38% to 0.48%, which is well below the 1.1% to 1.8% ceiling set for methane intensity in oil and gas production.
The result of this work on methane abatement is that B.C. has met its methane reduction targets for oil and gas two years ahead of schedule, according to the Pembina Institute.
Between 2014 and 2023, B.C. natural gas production grew 67 per cent, while methane emissions from oil and gas production fell by 51 per cent, the Pembina Institute notes in its report, Raising the Bar.
“B.C.’s success offers yet more evidence that methane emissions can be tackled without impeding the oil and gas industry’s operations,” Amanda Bryant, senior analyst for Pembina Institute, says in a press release accompanying the report.
“If anything, given the number of countries now considering new import standards that will privilege low-emissions energy products, stringent methane regulations – backed by transparent, best-in-class measurement data – are going to be key in bolstering the global competitiveness of our oil and gas sector.”
It must be added that, in addition to lower methane intensities, natural gas and LNG produced in B.C. also has lower CO2 intensities, thanks to electrification of the upstream and of some of the planned LNG plants. China, India, Japan, South Korea and other Asia Pacific nations will continue to buy natural gas and LNG from someone for years to come.
Shouldn’t that someone be Canada?
Economy
If the Liberal government has a plan for the future of conventional energy, now would be a good time to tell us what it is.

From Energy Now
By Jim Warren
During the Cold War, Western journalists and political analysts were typically unable to penetrate the secrecy surrounding the machinations of upper level Soviet politics. They would struggle to discern who the top contenders were in the contest to replace the current party leader and what a new leader might mean for geopolitics.
The lack of trustworthy official information prompted Kremlin watchers to adopt some rather desperate and sometimes absurd methods for divining the twists and turns of internal Communist Party intrigues.
For instance, they would look at photos of the party leadership on the reviewing stand for the annual May Day military parade. They would identify how close or far each member of the official party on the dais was sitting from the party leader. The proximity rankings were then compared with where people were positioned in relation to the leader at last year’s parade. Those who stood or sat closer to the leader than they did the previous year were presumed to be on their way up. Those who stood further away might be on their way to Siberia.
After one month in office it looks like the Carney government will require observers to go to similarly ridiculous lengths to figure out what cabinet ministers really mean when making public statements. Last week, a column by Calgary Sun’s Rick Bell discussed Danielle Smith’s demand that the Liberals quit talking in riddles. Bell suggested the Liberals would rather “stick handle” their way through questions about their policy positions than clearly indicate what those positions are.
Supporters of the oil, gas and pipeline sectors in the West remain uncertain and unconvinced when it comes to the Liberal government’s commitment to getting new pipelines built. This week’s Speech from the Throne certainly didn’t clarify the government’s plans for conventional energy production and exports.
The prime minister’s flip flopping has been particularly unhelpful. He has distanced himself from the comments he made at Kelowna early in the election campaign. While speaking there, Carney temporarily impressed supporters of new export pipelines by indicating he would use the emergency powers of the federal government to ensure oil pipelines are built to connect the prairies with the East and West coasts. Several days later he indicated he wouldn’t use those powers to override the objections of Quebec.
Currently, the prime minister says he is taking a wait and see approach. Last week he said a new pipeline extending from the prairies to a Canadian coastline is one of many possibilities depending on what sort of consensus develops around energy policy. When fumbling to explain his consensus approach, he produced the sort of word salad Danielle Smith could justifiably refer to as “talking in riddles.”
During the new government’s first Question Period on May 28, Andrew Scheer asked Carney what he intended to do about Bill C-69, the infamous No More Pipelines Bill. True to form Carney avoided providing a clear answer to the question. He responded with irrelevant canned talking points that failed to mention either the noxious Bill or increasing oil export opportunities.
Last week, Tim Hodgson, Canada’s new Energy Minister told people at a Calgary Chamber of Commerce event some of the of things they hoped to hear. According to a National Post report on the event Hodgson said he “promised to deliver new infrastructure to get Canadian energy to the coast and ultimately ‘to trusted allies’ outside the U.S.”
Hodgson also had comforting words for those concerned that Canada’s cumbersome project approval process could stymie new pipeline approval and construction. He said “Canada will no longer be defined by delay. We will be defined by delivery.”
Talk is cheap. It is difficult to imagine how costly pipeline construction delays and cancellations can be prevented without first getting rid of Bill C-69. If Hodgson was truly being sincere you’d think he would have announced plans are in the works to overturn C-69 or to at least make serious revisions to it. Since he never went that far in his remarks, the presentation fell far short of announcing that a credible plan is currently being considered.
The week prior to Hodgson’s Calgary speech, his cabinet colleague Steven Guilbeault announced that Canada did not need any new pipelines because the Trans Mountain was not operating at full capacity. Guilbeault also said that by the time a new pipeline could be built the global demand for oil and gas will have declined so much it wouldn’t be needed. Unfortunately, if a new pipeline project isn’t approved and completed within the next 15 years, Gulibeault’s second point will be on its way to becoming a self-fulfilled Liberal prophecy.
So who really speaks for the government on conventional energy policy? We’ve been presented with three different versions from three of the people who sit around the cabinet table, one of whom is supposed to be the boss. Apparently it is no longer the case that ministers are duty bound to refrain from criticizing or deviating from government policy. Yet, as far as we know, nobody has been reprimanded for announcing an incorrect version of the Liberals’ conventional energy policy.
We have been left to guess at the answers to critical questions. Has the government initiated a plan for making policy changes that deal with the concerns of the conventional energy sector and the governments of Alberta and Saskatchewan? If so, could someone please tell us what it is?
Transparency and clarity on the conventional energy file seem especially important at a time when Alberta is posed to hold a referendum on separation. Perhaps the Liberals don’t appreciate how much the lack of a coherent position in favour of building one or more new pipelines threatens national unity. Maybe their standard election winning formula of “screw the West, we’ll take the rest,” reflects what they have adopted as their long-term approach to the legitimate demands of alienated Westerners.
Barring the appearance of a clearly articulated official policy statement we might need to adopt a Canadian version of Kremlinology. That’s about the only means we would have to determine who, if anyone, is running the government—more specifically its conventional energy policy. Knowing which ministers speak for official government policy and which don’t could be useful.
We might need to ask questions like the following:
- Which cabinet ministers get to sit at the cool kids’ table at the parliamentary cafeteria?
- Which minister’s favourite companies and environmental groups have received the biggest grants and contracts since Carney became prime minister?
- Which minister enjoys the most taxpayer funded flights and luxury hotel room stays to attend international gabfests like The World Economic Forum, in Davos, Switzerland or this year’s COP 30 conference in Brazil, etc.?
- According to Parliament Hill gossip, who is most likely bound for Siberia—Steven Guilbeault or Tim Hodgson? And, when, if ever, will Jonathan Wilkinson be released from the backbench gulag and allowed back into cabinet? And why was he sent there in the first place—not green enough, or too green?
Energy
Ending energy poverty among Indigenous communities is essential

Haida Heritage Centre, Haida Gwaii, Queen Charlotte Islands
From Resource Works
Halting funding for natural gas expansion cut off many Indigenous communities from affordable energy.
Energy poverty in Canada is both an urgent and underreported crisis that is affecting Indigenous, rural, and remote communities across the country.
This is a resource-rich country, but Canada has continually failed to remedy the glaring energy affordability and accessibility gap in these communities. In particular, Indigenous families and households have to face disproportionately high energy costs due to their geographic isolation, a lack of built infrastructure, and neglect during policymaking.
In a report for the Energy for a Secure Future, authored by Heather Exner-Pirot, titled “The Other Energy Security: Addressing Energy Poverty in Canada’s Indigenous Communities,” she lays out these many problems that must be fixed.
It is a dire situation, with remote Indigenous communities being forced to spend over three times more of their household income on energy than the Canadian average. Twenty-six percent of Indigenous households fall into the category of energy poverty, as defined by the Canadian Urban Sustainability Practitioners (CUSP).
Many families spend more than six percent of their disposable income on energy, and this has worsened in recent years as energy costs rise with inflation and other present economic hardships.
Natural gas is the most plentiful and affordable source of household energy in Canada, but it cannot be accessed by many Indigenous communities that lack pipeline infrastructure. Although natural gas is cheaper and cleaner than diesel, propane, heating oil, or wood, the expansion of gas infrastructure into remote regions has hit snags in recent years.
From the 1980s to the 2000s, Ottawa supported the expansion of infrastructure to rural areas in a bid to alleviate affordability issues. However, the shift to reducing emissions and growing renewable energy has resulted in a lack of support for natural gas infrastructure.
This has had the counterproductive effect of leaving Indigenous communities with higher costs and higher emitting fuels like heating oil and diesel due to a lack of alternatives. As a source of energy, diesel is handy and reliable, but is expensive, heavily polluting, and expensive to transport into remote areas.
Renewables like solar and wind help to meet climate goals, but they are not feasible in remote northern communities because of their unreliability and high upfront costs. Phasing out fossil fuels in rural and remote Canada is a bad decision for the people affected without a fair transition strategy.
Many of the Indigenous leaders featured in Exner-Pirot’s report expressed grave concerns about the impact of energy poverty in their communities. They cited the many difficult choices that they have to make, such as having to pick between adequate heating or food.
These leaders are frustrated with the decisions made by distant authorities that prioritize ambitious sustainability goals instead of immediate, practical solutions. Many explicitly called for the expansion of natural gas, declaring it to be feasible, cost-effective, and cleaner than their current options.
One of the more striking statements is their assertion that withholding federal funding from natural gas projects actively denies Indigenous communities relief from energy poverty.
There is good evidence that reveals the benefits of expanding natural gas.
Red Lake, Ontario saw its energy costs fall by 70 percent once it was connected to natural gas infrastructure. Alberta’s Bigstone Cree Nation formerly used propane for decades, but then saw their energy security and affordability greatly improve after the province expanded the natural gas network.
The O’Chiese First Nation, also in Alberta, has been a model for energy autonomy and energy development, having harnessed its natural gas production for the benefit of the whole community.
Exner-Pirot’s report ends with several clear recommendations:
- Equal treatment of all fuels under carbon pricing to eliminate undesirable incentives
- Expanded eligibility for funding programs to include transitional fuels like natural gas
- Financial support for Indigenous-led energy security projects
- Explicit provincial targets and timelines for natural gas infrastructure expansion, using Ontario’s Natural Gas Expansion Program as a model
There is no debate that Canadian energy policy in Indigenous and remote communities has to change immediately. As they currently stand, they are exacerbating energy poverty by cutting out transitional and practical solutions.
No one-size-fits-all approach works for the countless Indigenous communities that reside in Canada, and they each need a tailored approach that respects their geographic and economic realities, as well as their right to self-determination.
-

 espionage20 hours ago
espionage20 hours agoTrudeau Government Unlawfully Halted CSIS Foreign Operation, Endangering Officers and Damaging Canada’s Standing With Allies, Review Finds
-
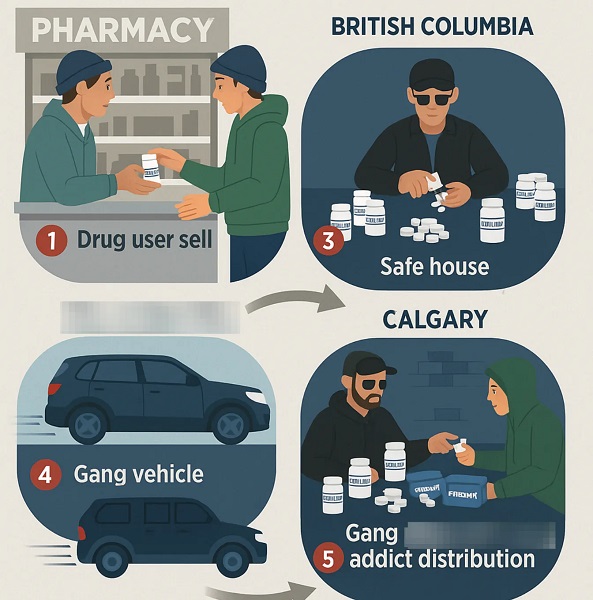
 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days ago“A Dangerous Experiment”: Doctor Says Ideological Canadian Governments Ignored Evidence as Safer Supply Exacerbated Fentanyl Death Surge
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoRFK Jr. cancels $700 million mRNA bird flu ‘vaccine’ contract with Moderna over safety concerns
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoProvincial pension plan may mean big savings for Albertans
-
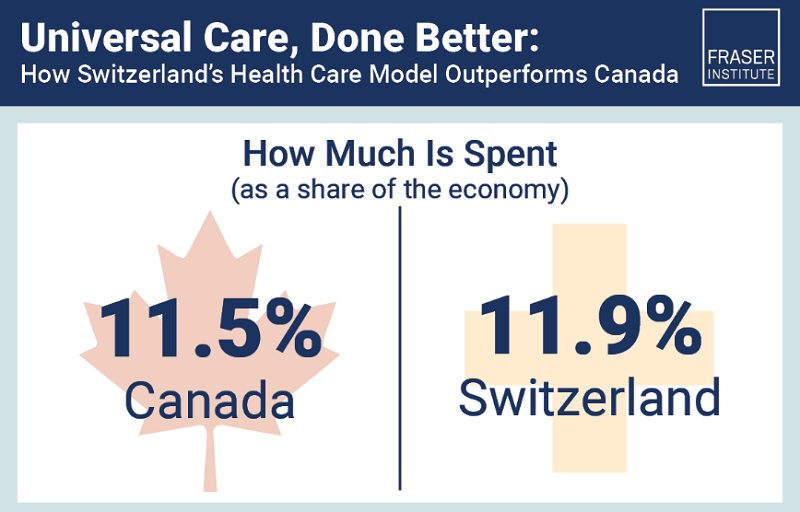
 Business20 hours ago
Business20 hours agoSwitzerland has nearly 65% more doctors and much shorter wait times than Canada, despite spending roughly same amount on health care
-

 National1 day ago
National1 day agoMajority of Canadians want feds to focus on illegal gun smuggling not gun buyback program
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoQuestion Period : Barrett vs. Carney Clash Over Offshore Investments
-

 Daily Caller8 hours ago
Daily Caller8 hours agoWatch As Tucker Carlson And Glenn Greenwald Get A Good Laugh Over CNN Pretending Biden’s Decline Is Breaking News


