Environment
Ottawa’s plastic ban may actually hurt the environment

From the Fraser Institute
” a market research firm, found that in New Jersey… “non-woven polypropylene… consumes over 15 times more plastic and generates more than five times the amount of GHG emissions during production per bag than polyethylene plastic bags.” In other words, the ban helped increase pollution. “
Despite a court ruling late last year, which deemed the Trudeau government ban on single-use plastic (cutlery, straws, grocery bags, etc.) “unreasonable and unconstitutional,” the ban essentially remains in place pending appeal or further regulatory action. But according to the government’s own data and analysis, plastic waste is a virtual non-issue in Canada, as 99 per cent of all plastic waste is disposed of safely in landfills or is incinerated. And less than 1 per cent of Canada’s plastic waste finds its way into the environment.
Moreover, there’s great potential for people to replace banned plastic items, including plastic grocery bags, with other plastic bags not included in the ban such as heavy gauge “reusable” shopping totes and other types of plastic trash bags made of heavier-gauge plastics than the filmy bags banned from grocery stores.
In New Jersey, for example, while plastic grocery bag use did decline following a statewide ban in 2022, plastic substitute materials skyrocketed, plastic consumption rose threefold for heavier reusable bags and sixfold for woven and non-woven polypropylene bags, which are not produced domestically, not recycled nor do they contain recycled content. Freedonia, a market research firm, found that in New Jersey “increased consumption of polypropylene bags” contributed to a “500% increase in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions compared to non-woven polypropylene bag production” and that “non-woven polypropylene… consumes over 15 times more plastic and generates more than five times the amount of GHG emissions during production per bag than polyethylene plastic bags.” In other words, the ban helped increase pollution.
In California, an environmental interest group called CALPIRG recently issued a report generally favouring plastic bag bans, observing that they do indeed reduce the use of banned bags. However, the report notes that “loopholes,” which allow consumers to use heavier plastic bag alternatives, results in more plastic consumption and waste—not less. According to CALPIRG, plastic bag disposal rates increased in one jurisdiction (Alameda) from 157,000 tons in the year before the ban on single-use grocery bags to 231,000 tons in 2021. On a per-person basis, it rose from 4.1 tons disposed of per 100,000 people to 5.9 tons disposed of per 100,000 over that same span.
In both New Jersey and California, efforts are underway to “fix” the loopholes that have allowed proliferation of plastic consumption and waste in the wake of plastic bag bans. However, these actions are unlikely to work unless they can somehow stop consumers from simply switching to plastic garbage bags or buying online heavier-gauge plastic shopping totes (and trashing them after a few shopping trips). Consumers have already shown they’re prepared to do these things.
Here at home, there’s no reason to believe that Canadian consumers will react any differently to a ban on single-use plastics. Canadians are just as likely to reach for the convenient substitute, whether that’s heavier paper products or heavier plastic products not covered under existing bans.
If sanity reigned, Canada would get ahead of the perverse consequences likely to flow from plastic bans by scrapping the entire idea and allowing consumers to consume what they believe best suits their lives and pocketbooks. Canada already has an admirable waste management system that keeps 99 per cent of disposed plastics safely locked away in environmentally protective landfills or eliminates them completely through incineration.
There’s no need for plastic bans or a governmental takeover of the plastics sector via regulation. Government should throw these bans in the bin.
Author:
Agriculture
Canada’s air quality among the best in the world

From the Fraser Institute
By Annika Segelhorst and Elmira Aliakbari
Canadians care about the environment and breathing clean air. In 2023, the share of Canadians concerned about the state of outdoor air quality was 7 in 10, according to survey results from Abacus Data. Yet Canada outperforms most comparable high-income countries on air quality, suggesting a gap between public perception and empirical reality. Overall, Canada ranks 8th for air quality among 31 high-income countries, according to our recent study published by the Fraser Institute.
A key determinant of air quality is the presence of tiny solid particles and liquid droplets floating in the air, known as particulates. The smallest of these particles, known as fine particulate matter, are especially hazardous, as they can penetrate deep into a person’s lungs, enter the blood stream and harm our health.
Exposure to fine particulate matter stems from both natural and human sources. Natural events such as wildfires, dust storms and volcanic eruptions can release particles into the air that can travel thousands of kilometres. Other sources of particulate pollution originate from human activities such as the combustion of fossil fuels in automobiles and during industrial processes.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) publish air quality guidelines related to health, which we used to measure and rank 31 high-income countries on air quality.
Using data from 2022 (the latest year of consistently available data), our study assessed air quality based on three measures related to particulate pollution: (1) average exposure, (2) share of the population at risk, and (3) estimated health impacts.
The first measure, average exposure, reflects the average level of outdoor particle pollution people are exposed to over a year. Among 31 high-income countries, Canadians had the 5th-lowest average exposure to particulate pollution.
Next, the study considered the proportion of each country’s population that experienced an annual average level of fine particle pollution greater than the WHO’s air quality guideline. Only 2 per cent of Canadians were exposed to fine particle pollution levels exceeding the WHO guideline for annual exposure, ranking 9th of 31 countries. In other words, 98 per cent of Canadians were not exposed to fine particulate pollution levels exceeding health guidelines.
Finally, the study reviewed estimates of illness and mortality associated with fine particle pollution in each country. Canada had the fifth-lowest estimated death and illness burden due to fine particle pollution.
Taken together, the results show that Canada stands out as a global leader on clean air, ranking 8th overall for air quality among high-income countries.
Canada’s record underscores both the progress made in achieving cleaner air and the quality of life our clean air supports.
Alberta
Net Zero goal is a fundamental flaw in the Ottawa-Alberta MOU

From the Fraser Institute
By Jason Clemens and Elmira Aliakbari
The challenge of GHG emissions in 2050 is not in the industrial world but rather in the developing world, where there is still significant basic energy consumption using timber and biomass.
The new Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between the federal and Alberta governments lays the groundwork for substantial energy projects and infrastructure development over the next two-and-a-half decades. It is by all accounts a step forward, though, there’s debate about how large and meaningful that step actually is. There is, however, a fundamental flaw in the foundation of the agreement: it’s commitment to net zero in Canada by 2050.
The first point of agreement in the MOU on the first page of text states: “Canada and Alberta remain committed to achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.” In practice, it’s incredibly difficult to offset emissions with tree planting or other projects that reduce “net” emissions, so the effect of committing to “net zero” by 2050 means that both governments agree that Canada should produce very close to zero actual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Consider the massive changes in energy production, home heating, transportation and agriculture that would be needed to achieve this goal.
So, what’s wrong with Canada’s net zero 2050 and the larger United Nations’ global goal for the same?
Let’s first understand the global context of GHG reductions based on a recent study by internationally-recognized scholar Vaclav Smil. Two key insights from the study. First, despite trillions being spent plus international agreements and regulatory measures starting back in 1997 with the original Kyoto agreement, global fossil fuel consumption between then and 2023 increased by 55 per cent.
Second, fossil fuels as a share of total global energy declined from 86 per cent in 1997 to 82 per cent in 2022, again, despite trillions of dollars in spending plus regulatory requirements to force a transition away from fossil fuels to zero emission energies. The idea that globally we can achieve zero emissions over the next two-and-a-half decades is pure fantasy. Even if there is an historic technological breakthrough, it will take decades to actually transition to a new energy source(s).
Let’s now understand the Canada-specific context. A recent study examined all the measures introduced over the last decade as part of the national plan to reduce emissions to achieve net zero by 2050. The study concluded that significant economic costs would be imposed on Canadians by these measures: inflation-adjusted GDP would be 7 per cent lower, income per worker would be more than $8,000 lower and approximately 250,000 jobs would be lost. Moreover, these costs would not get Canada to net zero. The study concluded that only 70 per cent of the net zero emissions goal would be achieved despite these significant costs, which means even greater costs would be imposed on Canadians to fully achieve net zero.
It’s important to return to a global picture to fully understand why net zero makes no sense for Canada within a worldwide context. Using projections from the International Energy Agency (IEA) in its latest World Energy Outlook, the current expectation is that in 2050, advanced countries including Canada and the other G7 countries will represent less than 25 per cent of global emissions. The developing world, which includes China, India, the entirety of Africa and much of South America, is estimated to represent at least 70 per cent of global emissions in 2050.
Simply put, the challenge of GHG emissions in 2050 is not in the industrial world but rather in the developing world, where there is still significant basic energy consumption using timber and biomass. A globally-coordinated effort, which is really what the U.N. should be doing rather than fantasizing about net zero, would see industrial countries like Canada that are capable of increasing their energy production exporting more to these developing countries so that high-emitting energy sources are replaced by lower-emitting energy sources. This would actually reduce global GHGs while simultaneously stimulating economic growth.
Consider a recent study that calculated the implications of doubling natural gas production in Canada and exporting it to China to replace coal-fired power. The conclusion was that there would be a massive reduction in global GHGs equivalent to almost 90 per cent of Canada’s total annual emissions. In these types of substitution arrangements, the GHGs would increase in energy-producing countries like Canada but global GHGs would be reduced, which is the ultimate goal of not only the U.N. but also the Carney and Smith governments as per the MOU.
Finally, the agreement ignores a basic law of economics. The first lesson in the very first class of any economics program is that resources are limited. At any given point in time, we only have so much labour, raw materials, time, etc. In other words, when we choose to do one project, the real cost is foregoing the other projects that could have been undertaken. Economics is mostly about trying to understand how to maximize the use of limited resources.
The MOU requires massive, literally hundreds of billions of dollars to be used to create nuclear power, other zero-emitting power sources and transmission systems all in the name of being able to produce low or even zero-emitting oil and gas while also moving to towards net zero.
These resources cannot be used for other purposes and it’s impossible to imagine what alternative companies or industries would have been invested in. What we do know is that workers, entrepreneurs, businessowners and investors are not making these decisions. Rather, politicians and bureaucrats in Ottawa and Edmonton are making these decisions but they won’t pay any price if they’re wrong. Canadians pay the price. Just consider the financial fiasco unfolding now with Ottawa, Ontario and Quebec’s subsidies (i.e. corporate welfare) for electric vehicle batteries.
Understanding the fundamentally flawed commitment to Canadian net zero rather than understanding a larger global context of GHG emissions lays at the heart of the recent MOU and unfortunately for Canadians will continue to guide flawed and expensive policies. Until we get the net zero policies right, we’re going to continue to spend enormous resources on projects with limited returns, costing all Canadians.
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoCanada’s free speech record is cracking under pressure
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoTanker ban politics leading to a reckoning for B.C.
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoMeet REEF — the massive new export engine Canadians have never heard of
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTaxpayers Federation calls on politicians to reject funding for new Ottawa Senators arena
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoClaims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny
-
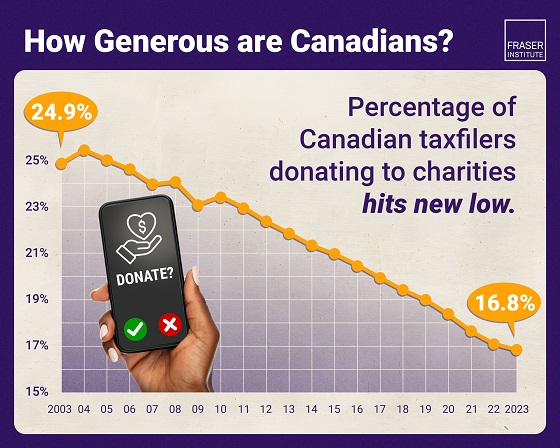
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAlbertans give most on average but Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
-

 Energy9 hours ago
Energy9 hours agoCanada’s future prosperity runs through the northwest coast
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoToo nice to fight, Canada’s vulnerability in the age of authoritarian coercion








