Fraser Institute
No evidence of ‘mass graves’ or ‘genocide’ in residential schools

From the Fraser Institute
” substantial pushback gradually developed among a group of retired judges, lawyers, professors, journalists and others who have had careers in researching and evaluating evidence. It’s no accident that most are retired, because that gives them some protection against attempts to silence them as “deniers.” “
The following is a summary of the 2023 book Grave Error: How the Media Misled Us (and the Truth About Residential Schools) by C.P. Champion and Tom Flanagan.
On May 27, 2021, Rosanne Casimir, Chief of the Tk’emlúps te Secwepemc (Kamloops Indian Band), announced that ground-penetrating radar (GPR) had located the remains of 215 “missing children” in an apple orchard on the site of a former residential school.
Politicians and media seized on the announcement, and stories of “mass unmarked graves” and “burials of missing children” ricocheted around Canada and indeed much of the world. Prime Minister Justin Trudeau set the tone of the public response by ordering Canadian flags to be flown at half-mast on all federal buildings to honour the “215 children whose lives were taken at the Kamloops residential school,” thus elevating the possible burials to the status of victims of foul play and making Canada sound like a charnel house of murdered children.
According to Canadian newspaper editors, the discovery of the so-called unmarked graves was the “news story of the year.” And the World Press Photo of the Year award went to a “haunting image of red dresses hung on crosses along a roadside, with a rainbow in the background, commemorating children who died at a residential school created to assimilate Indigenous children in Canada.”
These events created a narrative about the genocidal nature of residential schools, which were established in the 19th and 20th centuries by churches and the government to educate Indigenous children and assimilate them into Canadian society. That narrative went unchallenged at first. Yet substantial pushback gradually developed among a group of retired judges, lawyers, professors, journalists and others who have had careers in researching and evaluating evidence. It’s no accident that most are retired, because that gives them some protection against attempts to silence them as “deniers.” In the words of Janis Joplin, “Freedom’s just another word for nothin’ left to lose.” I published a book, which has been an Amazon Canada bestseller, proving Canadians’ desire for accurate information on this topic.
The book is a collection of some of the best pushback essays published in response to the Kamloops mythology. They analyze and critique the false narrative of unmarked graves, missing children, forced attendance and genocidal conditions at residential schools. The book’s title, Grave Error, summarizes the authors’ view of the Kamloops narrative. It is wrong, and not just wrong, but egregiously wrong. It deserves our sardonic title. And our book shows in detail just why and where the narrative is wrong.
Several of these authors, as well as others who have helped research and edit these publications, had for many years been writing for major metropolitan dailies, national magazines, academic journals, university presses and commercial publishers. However, they quickly learned that the corporate, legacy or mainstream media—in addition to religious leaders and politicians—have little desire to stand up to the narrative flow of a moral panic. They thus wrote about residential schools mainly in specialized journals such as The Dorchester Review, online daily media such as True North and the Western Standard, and online journals such as Unherd and History Reclaimed whose raison d’être is to challenge conventional wisdom.
For example, the first essay—“In Kamloops, Not One Body Has Been Found,” by Montreal historian Jacques Rouillard—has done more than any other single publication to punch holes in the false narrative of unmarked graves and missing children. Other essays punch more holes. Academic provocateur Frances Widdowson shows how the legend of murdered children and unmarked graves was spread by defrocked United Church minister Kevin Annett before it popped up at Kamloops. Retired professor Hymie Rubenstein and collaborators examine the “evidence” of unmarked graves, such as the results of the GPR, and find there’s nothing—repeat, nothing—there. Journalist Jonathan Kay explains how the media got the story completely wrong, generating the worst fake news in Canadian history. Retired professor Ian Gentles examines health conditions in the schools and shows that children were better off there than at home on reserves. My contribution criticizes the prolific but weak body of research purporting to show that attendance at residential schools created a historical trauma that’s responsible for the social pathologies in Indigenous communities. Retired professor Rodney Clifton recounts from personal experience how benign conditions could be in residential schools. And other essays explore other fallacies.
Our book demonstrates that all the major elements of the Kamloops narrative are either false or highly exaggerated. No unmarked graves have been discovered at Kamloops or elsewhere—not one. As of August 2023, there had been 20 announcements of soil “anomalies” discovered by GPR near residential schools across Canada; but most have not even been excavated, so what, if anything, lies beneath the surface remains unknown. Where excavations have taken place, no burials related to residential schools have been found.
In other words, there are no “missing children.” The fate of some children may have been forgotten with the passage of generations—forgotten by their own families, that is. But “forgotten” is not the same as “missing.” The myth of missing students arose from a failure of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission’s researchers to cross-reference the vast number of historical documents about residential schools and the children who attended them. The documentation exists, but the commissioners did not avail themselves of it.
Media stories about Indian residential schools are almost always accompanied by the frightening claim that 150,000 students were “forced to attend” these schools, but that claim is misleading at best. Children were not legally required to attend residential school unless no reserve day school was available; and even then, the law was only sporadically enforced. For students who did attend residential schools, an application form signed by a parent or other guardian was required. The simple truth is that many Indian parents saw residential schools as the best option available for their children.
Prior to 1990, residential schools enjoyed largely favourable media coverage, with many positive testimonials from former students. Indeed, alumni of residential schools comprised most of the emerging First Nations elite. But then Manitoba regional Chief Phil Fontaine appeared on a popular CBC television show hosted by Barbara Frum and claimed he had suffered sexual abuse at a residential school. He did not give details nor specify whether the alleged abusers were missionary priests, lay staff members or other students. Nonetheless, things went south quickly after Fontaine’s appearance, as claims of abuse multiplied and lawyers started to bring them to court.
To avoid clogging the justice system with lawsuits, the Liberal government of Paul Martin negotiated a settlement in 2005, which was accepted shortly afterwards by the Conservative government of Stephen Harper. Ultimately about $5 billion in compensation was paid to about 80,000 claimants, and in 2008 Prime Minister Harper publicly apologized for the existence of residential schools.
Harper might have thought that the payments and his apology would be the end of the story, but instead it became the beginning of a new chapter. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) that he appointed took off in its own direction after the initial set of commissioners resigned and were replaced on short notice. The TRC held emotional public hearings around the country where “survivors” told their stories without fact-checking or cross-examination. The TRC concluded in 2015 that the residential schools amounted to “cultural genocide.”
Cultural genocide is a metaphor, an emotive term for assimilation or integration of an ethnic minority into an encompassing society. The next step, in turned out, was to start speaking with increasing boldness of a literal physical genocide involving real deaths. The claims about missing children, unmarked burials and “mass graves” reinforced a genocide scenario.
Perhaps sensing the weakness of their evidence-free position, purveyors of the genocide narrative are beginning to double down, demanding that criticism of their ideology be made illegal. For example, in 2022, Winnipeg NDP MP Leah Gazan, introduced a resolution declaring residential schools to be genocidal—the House of Commons gave unanimous consent.
So, there we are—a narrative about genocide in residential schools firmly established in the public domain while unbelievers are called heretics (“denialists”) and threatened with criminal prosecution. But don’t believe the hype, no matter how often the propositions are repeated. As the little boy said in Hans Christian Andersen’s fairytale, “The Emperor has no clothes.”
Author: Tom Flanagan
Fraser Institute
Long waits for health care hit Canadians in their pocketbooks

From the Fraser Institute
Canadians continue to endure long wait times for health care. And while waiting for care can obviously be detrimental to your health and wellbeing, it can also hurt your pocketbook.
In 2024, the latest year of available data, the median wait—from referral by a family doctor to treatment by a specialist—was 30 weeks (including 15 weeks waiting for treatment after seeing a specialist). And last year, an estimated 1.5 million Canadians were waiting for care.
It’s no wonder Canadians are frustrated with the current state of health care.
Again, long waits for care adversely impact patients in many different ways including physical pain, psychological distress and worsened treatment outcomes as lengthy waits can make the treatment of some problems more difficult. There’s also a less-talked about consequence—the impact of health-care waits on the ability of patients to participate in day-to-day life, work and earn a living.
According to a recent study published by the Fraser Institute, wait times for non-emergency surgery cost Canadian patients $5.2 billion in lost wages in 2024. That’s about $3,300 for each of the 1.5 million patients waiting for care. Crucially, this estimate only considers time at work. After also accounting for free time outside of work, the cost increases to $15.9 billion or more than $10,200 per person.
Of course, some advocates of the health-care status quo argue that long waits for care remain a necessary trade-off to ensure all Canadians receive universal health-care coverage. But the experience of many high-income countries with universal health care shows the opposite.
Despite Canada ranking among the highest spenders (4th of 31 countries) on health care (as a percentage of its economy) among other developed countries with universal health care, we consistently rank among the bottom for the number of doctors, hospital beds, MRIs and CT scanners. Canada also has one of the worst records on access to timely health care.
So what do these other countries do differently than Canada? In short, they embrace the private sector as a partner in providing universal care.
Australia, for instance, spends less on health care (again, as a percentage of its economy) than Canada, yet the percentage of patients in Australia (33.1 per cent) who report waiting more than two months for non-emergency surgery was much higher in Canada (58.3 per cent). Unlike in Canada, Australian patients can choose to receive non-emergency surgery in either a private or public hospital. In 2021/22, 58.6 per cent of non-emergency surgeries in Australia were performed in private hospitals.
But we don’t need to look abroad for evidence that the private sector can help reduce wait times by delivering publicly-funded care. From 2010 to 2014, the Saskatchewan government, among other policies, contracted out publicly-funded surgeries to private clinics and lowered the province’s median wait time from one of the longest in the country (26.5 weeks in 2010) to one of the shortest (14.2 weeks in 2014). The initiative also reduced the average cost of procedures by 26 per cent.
Canadians are waiting longer than ever for health care, and the economic costs of these waits have never been higher. Until policymakers have the courage to enact genuine reform, based in part on more successful universal health-care systems, this status quo will continue to cost Canadian patients.
Business
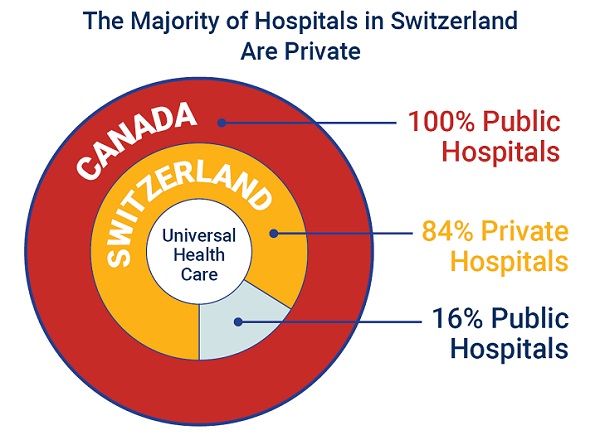
84% of Swiss hospitals and 60% of hospitalizations are in private facilities, and they face much lower wait times
From the Fraser Institute
If Canada reformed to emulate Switzerland’s approach to universal health care, including its much greater use of private sector involvement, the country would deliver far better results to patients and reduce wait times, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian policy think-tank.
“The bane of Canadian health care is lack of access to timely care, so it’s critical to look to countries like Switzerland with more successful universal health care,” said Yanick Labrie, senior fellow at the Fraser Institute and author of Integrating Private Health Care Into Canada’s Public System: What We Can Learn from Switzerland. The study highlights how Switzerland successfully integrates the private sector into their universal health-care system, which consistently outperforms Canada on most health-care metrics, including wait times.
For example, in 2022, the percentage of patients who waited less than two months for a specialist appointment was 85.3 per cent in Switzerland compared to just 48.3 per cent in Canada.
In Switzerland, 84.2 per cent of all hospitals are private (either for-profit or not-for profit) institutions, and the country’s private hospitals provide 60.2 per cent of all hospitalizations, 60.9 per cent of all births, and 67.1 per cent of all operating rooms.
Crucially, Swiss patients can obtain treatment at the hospital of their choice, whether located inside or outside their geographic location, and hospitals cannot discriminate against patients, based on the care required.
“Switzerland shows that a universal health-care system can reconcile efficiency and equity–all while being more accessible and responsive to patients’ needs and preferences,” Labrie said.
“Based on the success of the Swiss model, provinces can make these reforms now and help improve Canadian health care.”

Integrating Private Health Care into Canada’s Public System: What We Can Learn from Switzerland
- Access to timely care remains the Achilles’ heel of Canada’s health systems. To reduce wait times, some provinces have partnered with private clinics for publicly funded surgeries—a strategy that has proven effective, but continues to spark debate in Canada.
- This study explores how Switzerland successfully integrates private health care into a universal public system and considers what Canada can learn from this model.
- In Switzerland, universal coverage is delivered through a system of managed competition among 44 non-profit private insurers, while decentralized governance allows each of the 26 cantons to coordinate and oversee hospital services in ways that reflect local needs and priorities.
- Nearly two-thirds of Swiss hospitals are for-profit institutions; they provide roughly half of all hospitalizations, births, and hospital beds across the country.
- All hospitals are treated equally—regardless of legal status—and funded through the same activity-based model, implemented nationwide in 2012.
- The reform led to a significant increase in the number of cases treated without a corresponding rise in expenditures per case, suggesting improved efficiency, better use of resources, and expanded access to hospital care.
- The average length of hospital stay steadily decreased over time and now stands at 4.87 days in for-profit hospitals versus 5.53 days in public ones, indicating faster patient turnover and more streamlined care pathways.
- Hospital-acquired infection rates are significantly lower in private hospitals (2.7%) than in public hospitals (6.2%), a key indicator of care quality.
- Case-mix severity is as high or higher in private hospitals, countering the notion that they only take on simpler or less risky cases.
- Patient satisfaction is slightly higher in private hospitals (4.28/5) than in public ones (4.17/5), reflecting strong user experience across multiple dimensions.
- Canada could benefit from regulated competition between public and private providers and activity-based funding, without breaching the Canada Health Act.

-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoIran nuclear talks were ‘coordinated deception’ between US and Israel: report
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoPunishing Alberta Oil Production: The Divisive Effect of Policies For Carney’s “Decarbonized Oil”
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoIsrael’s Decapitation Strike on Iran Reverberates Across Global Flashpoints
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCanada is no energy superpower
-
 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoJust 3 Days Left to Win the Dream Home of a Lifetime!
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Premier Danielle Smith Discusses Moving Energy Forward at the Global Energy Show in Calgary
-

 Fraser Institute2 days ago
Fraser Institute2 days agoLong waits for health care hit Canadians in their pocketbooks
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoOne dead, over 60 injured after Iranian missiles pierce Iron Dome





