Addictions
New documentary exposes safer supply as gateway to teen drug use

By: Alexandra Keeler
In a new documentary, Port Coquitlam teens describe how safer supply drugs are diverted to the streets, contributing to youth drug use
Madison was just 15 when she first encountered “dillies” — hydromorphone pills meant for safer supply, but readily available on the streets.
“Multiple people walking up the street, down the street, saying ‘dillies, dillies,’ and that’s how you get them,” Madison said, referring to dealers in Vancouver’s Downtown Eastside.
Madison says she could get pills for $1.25 each, when purchased directly from someone receiving the drugs through safer supply — a provincial program that provides drug users with prescribed opioids. Madison would typically buy a whole bottle to last a week.
But as her tolerance grew, so did her addiction, leading her to try fentanyl.
“The dillies weren’t hitting me anymore … I tried [fentanyl] and instantly I just melted,” she said.
Kamilah Sword, Madison’s best friend, was just 14 when she died of an overdose on Aug. 20, 2022 after taking a hydromorphone pill dispensed through safer supply.
Madison, along with Kamilah’s father, Gregory Sword, are among the Port Coquitlam, B.C., residents featured in a documentary by journalist Adam Zivo. The film uncovers how safer supply drugs — intended as a harm reduction measure — contribute to harm among youth by being highly accessible, addictive and dangerous.
Through emotional interviews with teens and their families, the film links these drugs to overdose deaths and explores how they can act as a gateway to stronger substances like fentanyl.
Some last names are omitted to respect the victims’ desire for privacy.
Subscribe for free to get BTN’s latest news and analysis, or donate to our journalism fund.
‘Not a myth’
Safer supply aims to reduce overdose deaths by providing individuals with substance use disorders access to pharmaceutical-grade alternatives, such as hydromorphone.
But some policy experts, health officials and journalists are concerned these drugs are being diverted onto the streets — particularly hydromorphone, which is often sold under the brand name Dilaudid and nicknamed “dillies.”
Zivo, the film’s director, points out the disinformation surrounding safer supply diversion, highlighting that some drug legalization activists downplay the issue of diversion.
In 2023, B.C.’s then-chief coroner Lisa Lapointe dismissed claims that individuals were collecting their safer supply medications and selling them to youth, thereby creating new opioid dependencies and contributing to overdose deaths. She labeled such claims an “urban myth.”
In the film, Madison describes how teen substance users would occasionally accompany people enrolled in the safer supply program to the pharmacy, where they would fill their prescriptions and then sell the drugs to the teens.
“It’s not a myth, because my best friend died from it,” she says in the film.
Fiona Wilson, deputy chief of the Vancouver Police Department, testified on April 15 to the House of Commons health committee studying Canada’s opioid crisis that about 50 per cent of hydromorphone seizures by police are linked to safer supply.
 |
Deputy Chief of the Vancouver Police Department, Fiona Wilson, testified on April 15 during the House of Commons ‘Opioid Epidemic and Toxic Drug Crisis in Canada’ health committee meeting.
Additionally, Ottawa Police Sergeant Paul Stam previously confirmed to Canadian Affairs that similar reports of diverted safer supply drugs have been observed in Ottawa.
“Hopefully, by giving these victims a platform and bringing their stories to life, the film can impress upon Canadians the urgent need for reform,” Zivo told Canadian Affairs.
‘Creating addicts’
The teens featured in the film share their experiences with the addictive nature of dillies.
“After doing them for like a month, it felt like I needed them everyday,” says Amelie North, one teen featured in the documentary. “I felt like I couldn’t stand being alive without being on dillies.”
Madison explains how tolerance builds quickly. “You just keep doing them until it’s not enough at all.”
Madison started using fentanyl at the age of 12, leading to a near-fatal overdose after just one hit at a SkyTrain station. “It took five Narcan kits to save my life,” she says in the film.
Many of her friends use dillies or have tried fentanyl, she says. She estimates half the students at her school do.
“Government-supplied hydromorphone is a dangerous domino in the cascade of an addict’s downward spiral to ever more risky behaviour,” said Madison’s mother, Beth, to Canadian Affairs.
“The safe drug supply is creating addicts, not helping addicts,” Denise Fenske, North’s mother, told Canadian Affairs.
“I’m not sure when politicians talk about all the beds they have opened up for youth with drug or alcohol problems, where they actually are and how do we access them?”
Sword, Kamilah’s father, expressed his concern in an email to Canadian Affairs. “I want the people [watching the film] to understand how easy this drug is to get for the kids and how many kids it is affecting, the pain it causes the loved ones, [with] no answers or help for them.”
 |
Screenshot: Dr. Matthew Orde reviewing Kamilah Sword’s toxicology report during his interview for the filming of ‘Government Heroin 2: The Invisible Girls’ in March 2024.
Autopsy
Kamilah’s death raises further concerns.
According to Dr. Matthew Orde, a forensic pathologist featured in the film, Kamilah’s toxicology report revealed a mix of depressants and stimulants, including flualprazolam (a benzo), benzoylecgonine (a cocaine byproduct), MDMA and hydromorphone.
Orde criticizes the BC Coroners Service for not following best practices by focusing solely on cardiac arrhythmia caused by cocaine and MDMA, while overlooking the potential role of benzos and hydromorphone.
Orde notes that in complex poly-drug deaths, an autopsy is typically performed to determine the cause more accurately. He says he was shocked that Kamilah’s case did not receive this level of investigation.
B.C. has one of the lowest autopsy rates in Canada.
Zivo told Canadian Affairs he thinks a public inquiry into Kamilah’s case and other youth deaths involving hydromorphone since 2020 is needed to assess if the province is accurately reporting the harms of safer supply.
“That just angers me that our coroners did not do what most of Canada would have done,” Sword told Canadian Affairs.
“It also makes me question why they didn’t do an autopsy, what is our so-called government hiding?”
Government Heroin 2: The Invisible Girls is available for free on YouTube.
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle. Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism, consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Addictions
Why B.C.’s new witnessed dosing guidelines are built to fail
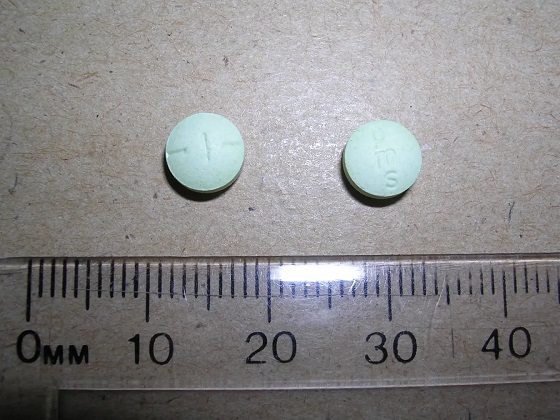
Photo by Acceptable at English Wikipedia, ‘Two 1 mg pills of Hydromorphone, prescribed to me after surgery.’ [Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons]
By Alexandra Keeler
B.C. released new witnessed dosing guidelines for safer supply opioids. Experts say they are vague, loose and toothless
This February, B.C pledged to reintroduce witnessed dosing to its controversial safer supply program.
Safer supply programs provide prescription opioids to people who use drugs. Witnessed dosing requires patients to consume those prescribed opioids under the supervision of a health-care professional, rather than taking their drugs offsite.
The province said it was reintroducing witnessed dosing to “prevent the diversion of prescribed opioids and hold bad actors accountable.”
But experts are saying the government’s interim guidelines, released April 29, are fundamentally flawed.
“These guidelines — just as any guidelines for safer supply — do not align with addiction medicine best practices, period,” said Dr. Leonara Regenstreif, a primary care physician specializing in substance use disorders. Regenstreif is a founding member of Addiction Medicine Canada, an advocacy group that represents 23 addiction specialists.
Addiction physician Dr. Michael Lester, who is also a founding member of the group, goes further.
“Tweaking a treatment protocol that should not have been implemented in the first place without prior adequate study is not much of an advancement,” he said.
Witnessed dosing
Initially, B.C.’s safer supply program was generally administered through witnessed dosing. But in 2020, to facilitate access amidst pandemic restrictions, the province moved to “take-home dosing,” allowing patients to take their prescription opioids offsite.
After pandemic restrictions were lifted, the province did not initially return to witnessed dosing. Rather, it did so only recently, after a bombshell government report alleged more than 60 B.C. pharmacies were boosting sales by encouraging patients to fill unnecessary opioid prescriptions. This incentivized patients to sell their medications on the black market.
B.C.’s interim guidelines, developed by the BC Centre on Substance Use at the government’s request, now require all new safer supply patients to begin with witnessed dosing.
But for existing patients, the guidelines say prescribers have discretion to determine whether to require witnessed dosing. The guidelines define an existing patient as someone who was dispensed prescription opioids within the past 30 days.
The guidelines say exemptions to witnessed dosing are permitted under “extraordinary circumstances,” where witnessed dosing could destabilize the patient or where a prescriber uses “best clinical judgment” and determines diversion risk is “very low.”
Holes
Clinicians say the guidelines are deliberately vague.
Regenstreif described them as “wordy, deliberately confusing.” They enable prescribers to carry on as before, she says.
Lester agrees. Prescribers would be in compliance with these guidelines even if “none of their patients are transferred to witnessed dosing,” he said.
In his view, the guidelines will fail to meet their goal of curbing diversion.
And without witnessed dosing, diversion is nearly impossible to detect. “A patient can take one dose a day and sell seven — and this would be impossible to detect through urine testing,” Lester said.
He also says the guidelines do not remove the incentive for patients to sell their drugs to others. He cites estimates from Addiction Medicine Canada that clients can earn up to $20,000 annually by selling part of their prescribed supply.
“[Prescribed safer supply] can function as a form of basic income — except that the community is being flooded with addictive and dangerous opioids,” Lester said.
Regenstreif warns that patients who had been diverting may now receive unnecessarily high doses. “Now you’re going to give people a high dose of opioids who don’t take opioids,” she said.
She also says the guidelines leave out important details on adjusting doses for patients who do shift from take-home to witnessed dosing.
“If a doctor followed [the guidelines] to the word, and the patient followed it to the word, the patient would go into withdrawal,” she said.
The guidelines assume patients will swallow their pills under supervision, but many crush and inject them instead, Regenstreif says. Because swallowing is less potent, a higher dose may be needed.
“None of that is accounted for in this document,” she said.
Survival strategy
Some harm reduction advocates oppose a return to witnessed dosing, saying it will deter people from accessing a regulated drug supply.
Some also view diversion as a life-saving practice.
Diversion is “a harm reduction practice rooted in mutual aid,” says a 2022 document developed by the National Safer Supply Community of Practice, a group of clinicians and harm reduction advocates.
The group supports take-home dosing as part of a broader strategy to improve access to safer supply medications. In their document, they say barriers to accessing safer supply programs necessitate diversion among people who use drugs — and that the benefits of diversion outweigh the risks.
However, the risks — and harms — of diversion are mounting.
People can quickly develop a tolerance to “safer” opioids and then transition to more dangerous substances. Some B.C. teenagers have said the prescription opioid Dilaudid was a stepping stone to them using fentanyl. In some cases, diversion of these drugs has led to fatal overdoses.
More recently, a Nanaimo man was sentenced to prison for running a highly organized drug operation that trafficked diverted safer supply opioids. He exchanged fentanyl and other illicit drugs for prescription pills obtained from participants in B.C.’s safer supply program.
Recovery
Lester, of Addiction Medicine Canada, believes clinical discretion has gone too far. He says take-home dosing should be eliminated.
“Best practices in addiction medicine assume physicians prescribing is based on sound and thorough research, and ensuring that their prescribing does not cause harm to the broader community, as well as the patient,” he said.
“[Safer supply] for opioids fails in both these regards.”
He also says safer supply should only be offered as a short-term bridge to patients being started on proven treatments like buprenorphine or methadone, which help reduce drug cravings and manage withdrawal symptoms.
B.C.’s witnessed dosing guidelines say prescribers can discuss such treatment options with patients. However, the guidelines remain neutral on whether safer supply is intended as a transitional step toward longer-term treatment.
Regenstreif says this neutrality undermines care.
“[M]ost patients I’ve seen with opioid use disorder don’t want to have [this disorder],” she said. “They would rather be able to set goals and do other things.”
Oversight gaps
Currently, about 3,900 people in B.C. participate in the safer supply program — down from 5,200 in March 2023.
The B.C. government has not provided data on how many have been transitioned to witnessed dosing. Investigative journalist Rob Shaw recently reported that these data do not exist.
“The government … confirmed recently they don’t have any mechanism to track which ‘safe supply’ participants are witnessed and which [are] not,” said Elenore Sturko, a Conservative MLA for Surrey-Cloverdale, who has been a vocal critic of safer supply.
“Without a public report and accountability there can be no confidence.”
The BC Centre on Substance Use, which developed the interim guidelines, says it does not oversee policy decisions or data tracking. It referred Canadian Affairs’ questions to B.C.’s Ministry of Health, which has yet to clarify whether it will track and publish transition data. The ministry did not respond to requests for comment by deadline.
B.C. has also not indicated when or whether it will release final guidelines.
Regenstreif says the flawed guidelines mean many people may be misinformed, discouraged or unsupported when trying to reduce their drug use and recover.
“We’re not listening to people with lived experience of recovery,” she said.
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle
Addictions
More young men want to restrict pornography: survey

From LifeSiteNews
Nearly 64% of American men now believe online pornography should be more difficult to access, with even higher numbers of women saying the same thing.
A new survey has shown that an increasing number of young men want more restrictions on online pornography.
According to a survey by the American Enterprise Institute’s Survey Center on American Life, nearly 7 in 10 (69 percent) of Americans support the idea of making online pornography less accessible. In 2013, 65 percent expressed support for policies restricting internet pornography.
The most substantial increase in the support for restrictive measures on pornography could be observed in young men (age 18-24). In 2013, about half of young men favored restrictions, while 40 percent actively opposed such policies. In 2025, 64 percent of men believe accessing online pornography should be made more difficult.
The largest support for restriction on internet pornography overall could be measured among older men (65+), where 73 percent favored restrictions. An even larger percentage of women in each age group supported making online pornography less accessible. Seventy-two percent of young women (age 18-24) favored restriction, while 87 percent of women 55 years or older expressed support for less accessibility of internet pornography.
Viewing pornography is highly addictive and can lead to serious health problems. Studies have shown that children often have their first encounter with pornography at around 12 years old, with boys having a lower average age of about 10-11, and some encountering online pornography as young as 8. Studies have also shown that viewing pornography regularly rewires humans brains and that children, adolescents, and younger men are especially at risk for becoming addicted to online pornography.
According to Gary Wilson’s landmark book on the matter, “Your Brain on Porn,” pornography addiction frequently leads to problems like destruction of genuine intimate relationships, difficulty forming and maintaining real bonds in relationship, depression, social anxiety, as well as reduction of gray matter, leading to desensitization and diminished pleasure from everyday activities among many others.
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCarney government should apply lessons from 1990s in spending review
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTrump to impose 30% tariff on EU, Mexico
-

 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days agoICE raids California pot farm, uncovers illegal aliens and child labor
-

 Entertainment1 day ago
Entertainment1 day agoStudy finds 99% of late-night TV guests in 2025 have been liberal
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoLNG Export Marks Beginning Of Canadian Energy Independence
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy14 hours ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy14 hours agoCanada’s New Border Bill Spies On You, Not The Bad Guys
-

 Uncategorized14 hours ago
Uncategorized14 hours agoCNN’s Shock Climate Polling Data Reinforces Trump’s Energy Agenda
-

 Opinion6 hours ago
Opinion6 hours agoPreston Manning: Three Wise Men from the East, Again





