Energy
Indigenous communities await Trans Mountain pipeline share
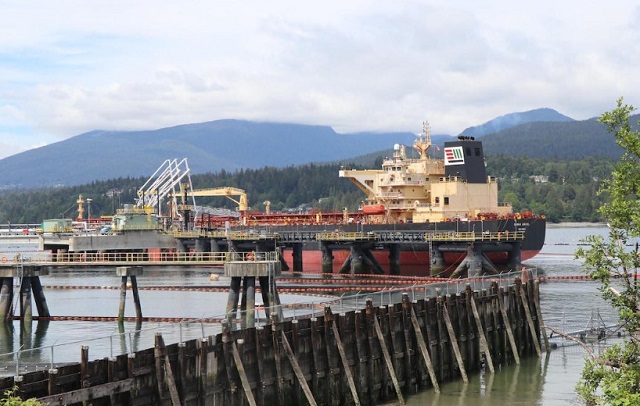

Tanker Dubai Angel at the Trans Mountain terminal, Burnaby
(Photo: Radio-Canada / Georgie Smyth / CBC)
From Resource Works
Ottawa’s Commitment to 30 percent Indigenous Stake in Trans Mountain Pipeline Still Awaiting Confirmation.
Indigenous leaders in Western Canada have been waiting for months for confirmation that the federal government will indeed enable Indigenous Peoples to get a 30 percent share in the Trans Mountain oil pipeline system.
That Ottawa has such a share in mind has been confirmed by Alberta Premier Danielle Smith. She says Ottawa is looking at possibly offering a loan guarantee to First Nations.
“They wanted to get the Indigenous partners to own 30 per cent. . . . It’s going to be a great source of income for the Indigenous partners.”
With the pipeline system’s capacity set to almost triple through the expansion project known as TMX, the federal government first announced in 2019, its intention to explore the possibility of the economic participation of 129 affected Indigenous Peoples.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland sent Indigenous leaders a letter last August outlining a plan to sell a stake in the pipeline system to eligible communities through a special-purpose vehicle. It said they would not have to risk any of their own money to participate.
But since then Indigenous groups have been awaiting further word from federal authorities on how and when the equity promise will be kept.
All Ottawa has said publicly is this on May 1: “The federal government will launch a divestment process in due course.”
Two key groups have aired proposals for acquiring equity in the oil pipeline:
- The Western Indigenous Pipeline Group was formed in 2018 “ to acquire a major stake in Trans Mountain for the benefit of Indigenous communities who live along the pipeline.” It’s been working behind the scenes, and, with Pembina Pipelines Corporation, developed in 2021 the Chinook Pathways operating partnership.
“Chinook Pathways is finance ready. There are no capital contributions required for Indigenous communities. We will structure the transaction so that participating communities will make zero financial contribution.”
- Project Reconciliation, also founded in 2018, proposed a ”framework” that would give ownership of the pipeline system to 129 Indigenous Peoples.
“We are poised to facilitate Indigenous ownership of up to 100 percent, fostering economic autonomy and environmental responsibility.”
And: “A portion of revenue generated (portion directed by each Indigenous community) will be used to establish the Indigenous Sovereign Wealth Fund, supporting investment in infrastructure, clean energy projects and renewable technologies.”
- A third group, the Alberta-based Iron Coalition, announced interest in TMX in 2019, but apparently dropped out in 2020.
In Alberta, the pipeline system spans the territories of Treaty 6, Treaty 8, and the Métis Nation of Alberta (Zone 4). In British Columbia, the system crosses numerous traditional territories and 15 First Nation reserves.
Commentator Joseph Quesnel writes: “According to Trans Mountain, there have been 73,000 points of contact with Indigenous communities throughout Alberta and British Columbia as the expansion was developed and constructed. . . .
“Beyond formal Indigenous engagement, the project proponent conducted numerous environmental and engineering field studies. These included studies drawing on deep Indigenous input, such as traditional ecological knowledge studies, traditional land use studies, and traditional marine land use studies.”
And Alberta’s Canadian Energy Centre reported: “In addition to $4.9 billion in contracts with Indigenous businesses during construction, the project leaves behind more than $650 million in benefit agreements and $1.2 billion in skills training with Indigenous communities.”
Not all First Nations have been happy with the expansion project.
In 2018, the federal appeal court ruled that Ottawa had failed to consider the concerns of several nations that challenged the project. In 2019, the project was re-approved by Ottawa, and again several nations (including the Squamish and Tsleil-Waututh) appealed. That appeal was dismissed in 2020. The nations then went to the Supreme Court of Canada, but it declined to hear the case.
Private company Kinder Morgan originally proposed the expansion project, but when it threatened to back out in 2018, the federal government stepped in and bought the existing pipeline, and the expansion project, for $4.5-billion. Ottawa said it was “a necessary and serious investment in the national interest.”
Ottawa at that time estimated that the total cost of the expansion project would come in around $7.4 billion. But cost overruns have since driven the final price to some $34 billion.
On the other hand, Ernst & Young found that between 2024 and 2043, the expanded Trans Mountain system will pay $3.7 billion in wages, generate $9.2 billion in GDP, and pay $2.8 billion in government taxes.
The TMX expansion twinned the 1953 Trans Mountain pipeline from near Edmonton to Burnaby (1,150 km) and increased the system’s capacity to 890,000 barrels a day from 300,000 barrels a day.
The original pipeline will carry refined products, synthetic crude oils, and light crude oils with the capability for heavy crude oils. The new pipeline will primarily carry heavier oils but can also transport lighter oils.
And the Alberta Energy Regulator says it expects oilsands production to grow by more than 17 per cent by 2033 (increasing to four million barrels a day from 3.4 million in 2023). And it expects global oil prices will continue to rise.
The TMX expansion finally opened and began to fill on May 1 this year.
And, as our CEO Stewart Muir noted, there was a quick reduction of eight cents a litre in gasoline prices for Vancouver due to completion of the project.
From Trans Mountain’s Westridge Marine Terminal at Burnaby, around three million barrels of oil have been shipped to China or India since the TMX expansion opened.
But because the port of Vancouver can handle only smaller Aframax tankers, more than half the oil has first been shipped to California, where it is then transferred to much larger VLCC (Very Large Crude Carrier) tankers. That makes for a longer but potentially cheaper journey.
At Westridge, because of limited tanker size, cargoes are limited to about 600,000 barrels per Aframax vessel. The largest VLCCs can carry two million barrels of oil. Westridge now can handle 34 Aframax tankers per month.
Some 20 tankers loaded oil there in June, a couple fewer than TMX had hoped for.
“This first month is just shy of the 350,000-400,000 bpd (barrels a day) we expected ahead of the startup,” said shipping analyst Matt Smith. “We are still in the discovery phase, with kinks being ironed out . . . but in the grand scheme of things, this has been a solid start.”
The Dubai Angel became the first Aframax tanker to load at Westridge. It took on 550,000 barrels of Alberta crude in the last week of May, and headed for the port of Zhoushan, China.
Now the Dubai Angel is headed to Burnaby for another load, and is expected to arrive there on July 8.
Energy
Canada’s oilpatch shows strength amid global oil shakeup

This article supplied by Troy Media.
Global oil markets are stumbling under too much supply and too little demand but Canada’s energy sector is managing to hold its own
Oil prices are sliding under the weight of global oversupply and weakening demand, but Canada’s oilpatch is holding steady—perhaps even thriving—as others flounder.
Crude is piling up in tankers, major producers are flooding the system, and demand is fading fast. According to a Windward report cited by Oilprice.com, the amount of oil held in floating storage—tankers sitting offshore waiting for buyers —has hit record highs. Sanctions on Russian and Iranian crude have sidelined entire fleets. Meanwhile, Middle East cargoes continue to pour in, keeping global supply bloated.
Gunvor CEO Torbjorn Tornqvist called the scale “unprecedented,” warning the market would be flooded overnight if sanctions against Russian and Iran were lifted.
And there’s more coming. U.S. crude production has hit a new record of 13.8 million barrels per day in August. And China’s Changqing oilfield just surpassed 20 million tonnes in cumulative output, and national totals have topped 400 million tonnes of oil equivalent this year. More barrels. More pressure. Less price support.
At the same time, demand is slipping. U.S. gasoline use is down. Global shipping activity has slowed. JPMorgan just trimmed its 2025 oil demand forecast by 300,000 barrels per day. China’s manufacturing sector shrank for the seventh month in a row.
Japan’s purchasing index dropped to an 18-month low. And recession fears are back in the headlines.
OPEC+ tried to calm the chaos by announcing a modest increase in output this December, with a pause on future hikes. But the move didn’t move markets. Then Saudi Arabia cut its selling prices to Asia, a clear signal that the kingdom sees weak demand ahead.
In short, it’s messy out there. But not everywhere.
Amid this global downturn, Canada’s energy sector stands out for one rare quality: resilience. While other producers are scaling back or scrambling to adapt, Canada’s oilpatch is quietly outperforming.
A recent CBC News report highlighted the sector’s staying power and why it’s better positioned than its U.S. counterparts. “The companies that have survived here are the companies that have been able to adapt,” said Patrick O’Rourke, managing director at ATB Capital Markets. “It’s effectively Darwinism.”
It’s also smart design. Canada’s oilsands—primarily in Alberta—are expensive to build but cheap to run. Once the upfront costs are covered, producers can keep pumping for decades with relatively low reinvestment. That means even in a
downturn, output stays strong.
Dane Gregoris of Enverus says Canada’s conventional sector is holding up better than the U.S. shale patch. Why? Canadian oil producers operate more efficiently, with fewer legal and logistical barriers tied to land access and ownership than their U.S. shale counterparts. They also benefit from lower operating costs and are less dependent on relentless drilling just to maintain output.
And now, they finally have a way to get more oil out.
The long-delayed Trans Mountain pipeline expansion is finally complete. It delivers Alberta crude to B.C.’s tidewater and, from there, to Asian markets. That access, once a significant limitation for Canadian producers, is now a strategic advantage. It’s already helping offset lower global prices.
Canada’s energy sector also benefits from long-life assets, slow decline rates and political stability. We have a reputation for responsible regulation, but that same system can slow development and limit how quickly we respond to shifting global demand. We can offer a stable, secure supply but only if infrastructure and regulatory hurdles don’t block access to it.
And for Canadians, that matters. Oil prices don’t just fuel industry headlines; they shape provincial and national budgets, drive investment and underpin jobs across the country. Most producers around the world are bracing for pain but Canada may be bracing for opportunity to expand its presence in Asian markets, secure long-term export contracts and position itself as a reliable supplier in a turbulent global landscape.
None of this means Canada is immune. If demand collapses or sanctions lift, prices could sink further. But in a volatile global landscape, Canada isn’t scrambling—it’s competing.
While others slash forecasts, shut wells or hope for an OPEC rescue, Canada’s energy producers are doing something rare in today’s oil market: holding the line.
Toronto-based Rashid Husain Syed is a highly regarded analyst specializing in energy and politics, particularly in the Middle East. In addition to his contributions to local and international newspapers, Rashid frequently lends his expertise as a speaker at global conferences. Organizations such as the Department of Energy in Washington and the International Energy Agency in Paris have sought his insights on global energy matters.
Troy Media empowers Canadian community news outlets by providing independent, insightful analysis and commentary. Our mission is to support local media in helping Canadians stay informed and engaged by delivering reliable content that strengthens community connections and deepens understanding across the country
Alberta
How economic corridors could shape a stronger Canadian future

Ship containers are stacked at the Panama Canal Balboa port in Panama City, Saturday, Sept. 20, 2025. The Panama Canals is one of the most significant trade infrastructure projects ever built. CP Images photo
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Q&A with Gary Mar, CEO of the Canada West Foundation
Building a stronger Canadian economy depends as much on how we move goods as on what we produce.
Gary Mar, CEO of the Canada West Foundation, says economic corridors — the networks that connect producers, ports and markets — are central to the nation-building projects Canada hopes to realize.
He spoke with CEC about how these corridors work and what needs to change to make more of them a reality.
CEC: What is an economic corridor, and how does it function?
Gary Mar: An economic corridor is a major artery connecting economic actors within a larger system.
Consider the road, rail and pipeline infrastructure connecting B.C. to the rest of Western Canada. This infrastructure is an important economic corridor facilitating the movement of goods, services and people within the country, but it’s also part of the economic corridor connecting western producers and Asian markets.
Economic corridors primarily consist of physical infrastructure and often combine different modes of transportation and facilities to assist the movement of many kinds of goods.
They also include social infrastructure such as policies that facilitate the easy movement of goods like trade agreements and standardized truck weights.
The fundamental purpose of an economic corridor is to make it easier to transport goods. Ultimately, if you can’t move it, you can’t sell it. And if you can’t sell it, you can’t grow your economy.
CEC: Which resources make the strongest case for transport through economic corridors, and why?
Gary Mar: Economic corridors usually move many different types of goods.
Bulk commodities are particularly dependent on economic corridors because of the large volumes that need to be transported.
Some of Canada’s most valuable commodities include oil and gas, agricultural commodities such as wheat and canola, and minerals such as potash.
CEC: How are the benefits of an economic corridor measured?
Gary Mar: The benefits of economic corridors are often measured via trade flows.
For example, the upcoming Roberts Bank Terminal 2 in the Port of Vancouver will increase container trade capacity on Canada’s west coast by more than 30 per cent, enabling the trade of $100 billion in goods annually, primarily to Asian markets.
Corridors can also help make Canadian goods more competitive, increasing profits and market share across numerous industries. Corridors can also decrease the costs of imported goods for Canadian consumers.
For example, after the completion of the Trans Mountain Expansion in May 2024 the price differential between Western Canada Select and West Texas Intermediate narrowed by about US$8 per barrel in part due to increased competition for Canadian oil.
This boosted total industry profits by about 10 per cent, and increased corporate tax revenues to provincial and federal governments by about $3 billion in the pipeline’s first year of operation.
CEC: Where are the most successful examples of these around the world?
Gary Mar: That depends how you define success. The economic corridors transporting the highest value of goods are those used by global superpowers, such as the NAFTA highway that facilitates trade across Canada, the United States and Mexico.
The Suez and Panama canals are two of the most significant trade infrastructure projects ever built, facilitating 12 per cent and five per cent of global trade, respectively. Their success is based on their unique geography.
Canada’s Asia-Pacific Gateway, a coordinated system of ports, rail lines, roads, and border crossings, primarily in B.C., was a highly successful initiative that contributed to a 48 per cent increase in merchandise trade with Asia from $44 million in 2006 to $65 million in 2015.
China’s Belt and Road initiative to develop trade infrastructure in other countries is already transforming global trade. But the project is as much about extending Chinese influence as it is about delivering economic returns.

Piles of coal awaiting export and gantry cranes used to load and unload containers onto and from cargo ships are seen at Deltaport, in Tsawwassen, B.C., on Monday, September 9, 2024. CP Images photo
CEC: What would need to change in Canada in terms of legislation or regulation to make more economic corridors a reality?
Gary Mar: A major regulatory component of economic corridors is eliminating trade barriers.
The federal Free Trade and Labour Mobility in Canada Act is a good start, but more needs to be done at the provincial level to facilitate more internal trade.
Other barriers require coordinated regulatory action, such as harmonizing weight restrictions and road bans to streamline trucking.
By taking a systems-level perspective – convening a national forum where Canadian governments consistently engage on supply chains and trade corridors – we can identify bottlenecks and friction points in our existing transportation networks, and which investments would deliver the greatest return on investment.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoRichmond Mayor Warns Property Owners That The Cowichan Case Puts Their Titles At Risk
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoHow economic corridors could shape a stronger Canadian future
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoProtesters Storm Elite Climate Summit In Chaotic Scene
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoLaura Ingraham’s Viral Clash With Trump Prompts Her To Tell Real Reasons China Sends Students To US
-
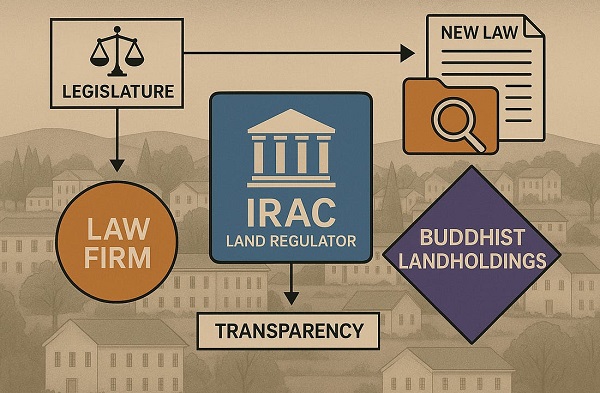
 Business23 hours ago
Business23 hours agoP.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoWhen Teachers Say Your Child Has Nowhere Else to Go
-

 Energy23 hours ago
Energy23 hours agoCanada’s oilpatch shows strength amid global oil shakeup
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSluggish homebuilding will have far-reaching effects on Canada’s economy







