Business
CMHC rubberstamps $102 million in bonuses amid housing affordability crisis

From the Canadian Taxpayers Federation
Author: Ryan Thorpe
The Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation dished out more than $27 million in bonuses in 2023, according to access-to-information records obtained by the Canadian Taxpayers Federation.
That pushes the total bonuses at the CMHC to $102 million since the beginning of 2020.
“Why is the CMHC patting itself on the back and showering staff with bonuses when Canadians can’t afford homes?” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “If the CMHC’s number one goal is housing affordability, then it doesn’t make sense to hand out $100 million in bonuses during a housing affordability crisis.”
Ninety-eight per cent of the CMHC workforce took a bonus in 2023.
At least 2,283 CMHC staffers took home a bonus last year, costing taxpayers $27.2 million, with the average bonus coming in at about $11,800.
The CMHC’s 10 executives received $4.1 million in total compensation in 2023. That includes $3.1 million in salary (for an average of $311,000) and $831,000 in bonuses (for an average of $83,000).
The CMHC also paid executives $211,000 in other “benefits.”
More than 2,000 CMHC staffers, representing 89 per cent of its workforce, also got a pay raise last year. Not a single employee received a pay cut.
There are now 1,073 CMHC bureaucrats taking home a six-figure annual salary, a 15 per cent increase over 2022, representing nearly half (46 per cent) of its workforce. Those six-figure salaries cost taxpayers a combined $140 million in 2023.
“The CMHC could do more to end the housing affordability crisis by hiring a thousand carpenters, rather than paying a thousand bureaucratic pencil-pushers six-figure salaries,” Terrazzano said.
The CMHC is “driven by one goal: housing affordability for all,” according to its 2023-2027 corporate plan.
Polling from Ipsos and Global News in 2023 shows 63 per cent of Canadians who don’t own a home have “given up” on ever owning one. Nearly 70 per cent of respondents said home ownership in Canada is “only for the rich.”
In April 2024, the Royal Bank of Canada said it was the “toughest time ever to afford a home as soaring interest costs keep raising the bar.”
The RBC said ownership costs were propelled to a “new summit” in the fourth quarter of 2023, with a “household earning a median income (needing) to spend a staggering 62.5 per cent of it to cover the costs of owning an average home at market price.”
“Affordability worsened in all markets we track,” the RBC said, with the housing in Vancouver, Victoria and Toronto experiencing “the biggest deterioration,” and affordability in Ottawa, Montreal and Halifax being “at or near all-time worst levels.”
In the 2023 Budget, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said, “the government will also work with federal Crown corporations to ensure they achieve comparable spending reductions, which would account for an estimated $1.3 billion over four years.”
“The feds need to stop rewarding failure with bonuses,” Terrazzano said. “Freeland said she would find savings in Crown corporations and these bonuses should be the first thing on the chopping block.”
Business
The world is no longer buying a transition to “something else” without defining what that is

From Resource Works
Even Bill Gates has shifted his stance, acknowledging that renewables alone can’t sustain a modern energy system — a reality still driving decisions in Canada.
You know the world has shifted when the New York Times, long a pulpit for hydrocarbon shame, starts publishing passages like this:
“Changes in policy matter, but the shift is also guided by the practical lessons that companies, governments and societies have learned about the difficulties in shifting from a world that runs on fossil fuels to something else.”
For years, the Times and much of the English-language press clung to a comfortable catechism: 100 per cent renewables were just around the corner, the end of hydrocarbons was preordained, and anyone who pointed to physics or economics was treated as some combination of backward, compromised or dangerous. But now the evidence has grown too big to ignore.
Across Europe, the retreat to energy realism is unmistakable. TotalEnergies is spending €5.1 billion on gas-fired plants in Britain, Italy, France, Ireland and the Netherlands because wind and solar can’t meet demand on their own. Shell is walking away from marquee offshore wind projects because the economics do not work. Italy and Greece are fast-tracking new gas development after years of prohibitions. Europe is rediscovering what modern economies require: firm, dispatchable power and secure domestic supply.
Meanwhile, Canada continues to tell itself a different story — and British Columbia most of all.
A new Fraser Institute study from Jock Finlayson and Karen Graham uses Statistics Canada’s own environmental goods and services and clean-tech accounts to quantify what Canada’s “clean economy” actually is, not what political speeches claim it could be.
The numbers are clear:
- The clean economy is 3.0–3.6 per cent of GDP.
- It accounts for about 2 per cent of employment.
- It has grown, but not faster than the economy overall.
- And its two largest components are hydroelectricity and waste management — mature legacy sectors, not shiny new clean-tech champions.
Despite $158 billion in federal “green” spending since 2014, Canada’s clean economy has not become the unstoppable engine of prosperity that policymakers have promised. Finlayson and Graham’s analysis casts serious doubt on the explosive-growth scenarios embraced by many politicians and commentators.
What’s striking is how mainstream this realism has become. Even Bill Gates, whose philanthropic footprint helped popularize much of the early clean-tech optimism, now says bluntly that the world had “no chance” of hitting its climate targets on the backs of renewables alone. His message is simple: the system is too big, the physics too hard, and the intermittency problem too unforgiving. Wind and solar will grow, but without firm power — nuclear, natural gas with carbon management, next-generation grid technologies — the transition collapses under its own weight. When the world’s most influential climate philanthropist says the story we’ve been sold isn’t technically possible, it should give policymakers pause.
And this is where the British Columbia story becomes astonishing.
It would be one thing if the result was dramatic reductions in emissions. The provincial government remains locked into the CleanBC architecture despite a record of consistently missed targets.
Since the staunchest defenders of CleanBC are not much bothered by the lack of meaningful GHG reductions, a reasonable person is left wondering whether there is some other motivation. Meanwhile, Victoria’s own numbers a couple of years ago projected an annual GDP hit of courtesy CleanBC of roughly $11 billion.
But here is the part that would make any objective analyst blink: when I recently flagged my interest in presenting my research to the CleanBC review panel, I discovered that the “reviewers” were, in fact, two of the key architects of the very program being reviewed. They were effectively asked to judge their own work.
You can imagine what they told us.
What I saw in that room was not an evidence-driven assessment of performance. It was a high-handed, fact-light defence of an ideological commitment. When we presented data showing that doctrinaire renewables-only thinking was failing both the economy and the environment, the reception was dismissive and incurious. It was the opposite of what a serious policy review looks like.
Meanwhile our hydro-based electricity system is facing historic challenges: long term droughts, soaring demand, unanswered questions about how growth will be powered especially in the crucial Northwest BC region, and continuing insistence that providers of reliable and relatively clean natural gas are to be frustrated at every turn.
Elsewhere, the price of change increasingly includes being able to explain how you were going to accomplish the things that you promise.
And yes — in some places it will take time for the tide of energy unreality to recede. But that doesn’t mean we shouldn’t be improving our systems, reducing emissions, and investing in technologies that genuinely work. It simply means we must stop pretending politics can overrule physics.
Europe has learned this lesson the hard way. Global energy companies are reorganizing around a 50-50 world of firm natural gas and renewables — the model many experts have been signalling for years. Even the New York Times now describes this shift with a note of astonishment.
British Columbia, meanwhile, remains committed to its own storyline even as the ground shifts beneath it. This isn’t about who wins the argument — it’s about government staying locked on its most basic duty: safeguarding the incomes and stability of the families who depend on a functioning energy system.
Resource Works News
Business
High-speed rail between Toronto and Quebec City a costly boondoggle for Canadian taxpayers

“It’s a good a bet that high-speed rail between Toronto and Quebec City isn’t even among the top 1,000 priorities for most Canadians.”
The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is criticizing Prime Minister Mark Carney for borrowing billions more for high-speed rail between Toronto and Quebec City.
“Canadians need help paying for basics, they don’t need another massive bill from the government for a project that only benefits one corner of the country,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “It’s a good a bet that high-speed rail between Toronto and Quebec City isn’t even among the top 1,000 priorities for most Canadians.
“High-speed rail will be another costly taxpayer boondoggle.”
The federal government announced today that the first portion of the high-speed rail line will be built between Ottawa and Montreal with constructing starting in 2029. The entire high-speed rail line is expected to go between Toronto and Quebec City.
The federal Crown corporation tasked with overseeing the project “estimated that the full line will cost between $60 billion and $90 billion, which would be funded by a mix of government money and private investment,” the Globe and Mail reported.
The government already owns a railway company, VIA Rail. The government gave VIA Rail $1.9 billion over the last five years to cover its operating losses, according to the Crown corporation’s annual report.
The federal government is borrowing about $78 billion this year. The federal debt will reach $1.35 trillion by the end of this year. Debt interest charges will cost taxpayers $55.6 billion this year, which is more than the federal government will send to the provinces in health transfers ($54.7 billion) or collect through the GST ($54.4 billion).
“The government is up to its eyeballs in debt and is already spending hundreds of millions of dollars bailing out its current train company, the last thing taxpayers need is to pay higher debt interest charges for a new government train boondoggle,” Terrazzano said. “Instead of borrowing billions more for pet projects, Carney needs to focus on making life more affordable and paying down the debt.”
-

 National2 days ago
National2 days agoCanada’s free speech record is cracking under pressure
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoTanker ban politics leading to a reckoning for B.C.
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoMeet REEF — the massive new export engine Canadians have never heard of
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTaxpayers Federation calls on politicians to reject funding for new Ottawa Senators arena
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoClaims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoOttawa’s New Hate Law Goes Too Far
-
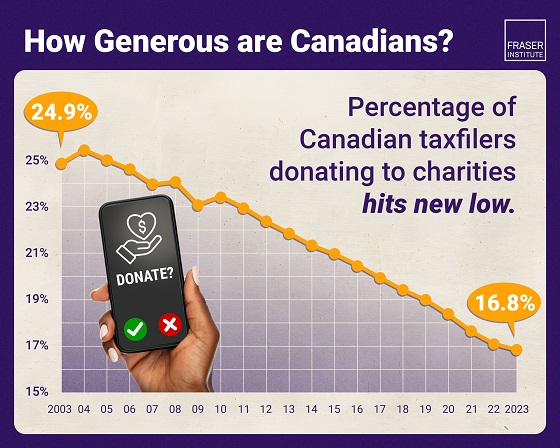
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAlbertans give most on average but Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoToo nice to fight, Canada’s vulnerability in the age of authoritarian coercion




