conflict
China Poised To Cut Off US Military From Key Mineral As America’s Own Reserves Lay Buried Under Red Tape

 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Nick Pope
China is planning to restrict exports of a key mineral needed to make weapons while a U.S. company that could be reducing America’s reliance on foreign suppliers is languishing in red tape, energy experts told the Daily Caller News Foundation.
The Chinese government announced on August 15 that it will restrict exports of antimony, a critical mineral that dominates the production of weapons globally and is essential for producing equipment like munitions, night vision goggles and bullets that are essential to national security, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS). Perpetua Resources, an American mining company, has been navigating red tape for years to develop a mine in Valley County, Idaho, that could decrease reliance on the Chinese supply of antimony, but the slow permitting process is getting in the way, energy experts told the DCNF.
It can take years to secure all the necessary approvals and permits to develop a mine like the one Perpetua Resources is trying to operate. One of the key permitting laws in place is the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), which also applies to federal land management actions and the construction of certain public infrastructure projects like highways.
“After six years of planning and early engagement, we began the [NEPA] permitting process in 2016. We are now eight years into NEPA,” a Perpetua Resources spokesperson told the DCNF. The company is hoping to extract antimony from the largest known deposit in the U.S., and Perpetua Resources’ development could also produce millions of ounces of gold as well.
Diana Furchtgott-Roth, director of the Heritage Foundation’s Center for Energy, Climate and Environment, argues that the Perpetua Resources mine poses real environmental considerations that should be addressed, but production in the U.S. is almost certainly cleaner than production that takes place in China. Moreover, depending on China for raw materials needed to produce key defense equipment poses a clear national security risk, Furchtgott-Roth said.
“The United States has the highest environmental standards in the world for its mines, as well as for some other things, too,” Furchtgott-Roth told the DCNF. “It’s a huge national security risk. Given what we’ve seen with Russia cutting off supplies of natural gas to Europe, we know that countries can cut off important supplies to other countries.”
“If the administration wants to pursue policies that push electric vehicles, green energy and other mineral-intensive technologies, it should look to streamline the permitting process across the board rather than selectively pursuing reform for some favored types of development and not for others,” Furchtgott-Roth added.
Steve Coonen, a former Department of Defense (DOD) official who focused on technology exports to China, agreed that relying on China for raw materials needed to produce crucial technologies presents a clear national security risk.
“The United States has all the rare earth elements it needs, not too dissimilar from its energy requirements,” Coonen told the DCNF. “However, Democrats have enchained U.S. industry by prohibiting the extraction of these materials for misplaced and ill-informed ecological reasons at a significant risk to national security and the United States’ long-term economic health.”
China is responsible for just under 50% of the world’s antimony production, and it is also the source of 63% of the U.S.’ current antimony imports, according to CSIS. The U.S., meanwhile, did not mine any “marketable” antimony in 2023, according to CNBC.
China’s recently announced export restrictions for antimony will take effect on Sept. 15, according to CNBC. To many in the industry, China moving to curb antimony exports would have come as a surprise just a few months ago, so the country’s decision to take action comes across as “quite confrontational in that regard,” Lewis Black, CEO of Canadian mining company Almonty Industries, told the outlet.
In addition to antimony, China has also flexed its muscles by restricting exports of other critical minerals that it dominates globally, like germanium and gallium, since 2023.
“The United States has some of the highest permitting standards in the world, and that’s something to be proud of. But NEPA gets criticism for being inefficient, and much of that criticism is justified,” the Perpetua Resources spokesperson told the DCNF. “When we are talking about minerals we need for America’s national and economic security — not to mention our clean energy future — we need an efficient regulatory process that still maintains robust protections for communities and the environment.”
The company is anticipating that the process — from initial deposit identification to the beginning of mineral extraction from the mine site — will take 18 years, the Perpetua Resources spokesperson told the DCNF. However, the spokesperson added that NEPA has been beneficial for transparency with the public and allowing stakeholder communities to weigh in about the project.
Nevertheless, Perpetua Resources “absolutely supports a commonsense, bipartisan approach to permitting reform” because “good projects should not wither in red tape.”
The antimony curbs may be even more pressing given existing concerns about the strength of America’s defense-industrial base amid wars in the Middle East and Europe, as well as rising tensions with China over Taiwan. Many experts have cautioned that the U.S. is allowing itself to become too dependent on an adversarial China’s mineral supplies at a time when those minerals are playing a much larger role in the American economy, thanks in part to the Biden administration’s massive green energy agenda.
“In the mid-twentieth century, domestic mining accounted for 90% of the U.S.’s antimony consumption. Today, the U.S. no longer mines antimony; instead, it relies on China, its chief geopolitical rival, for over 60% of its antimony imports,” Quill Robinson, an associate fellow in CSIS’ Energy Security and Climate Change Program, told the DCNF. “Effective China de-risking requires reducing reliance up and down the value chain.”
Independent West Virginia Sen. Joe Manchin and Republican Wyoming Sen. John Barrasso teamed up to introduce a major permitting reform bill in July, designing the package to simplify the regulatory hurdles that major infrastructure and development projects must clear and expedite timelines without totally defanging regulators’ ability to ensure that environmental concerns and considerations are addressed. That bill has not yet come up for a vote in the Senate.
“There are legitimate environmental challenges that need to be mitigated for projects like this,” Arnab Datta, the Institute for Progress’ director of infrastructure policy, told the DCNF. However, government agencies are more strongly incentivized to avoid legal challenges of their reviews from third parties than they are to thoroughly review the more significant environmental concerns, meaning that regulators tend to chew up lots of time on those minor points and ultimately extend the timelines for permitting, Datta explained.
“The uncertainty from permitting and litigation compounds the challenge of reaching production in what’s often a volatile and uncertain market environment for these commodities,” Datta, who also works for Employ America as a managing director of policy implementation, continued. “These companies need a process with certainty and reasonable timelines and also support that helps mitigate the volatility that arises from China’s actions in the market.”
Featured Image: Photo by Dominik Vanyi on Unsplash
conflict
US airstrike on Iran’s nuclear facilities. Was it obliteration?

A satellite image of the Isfahan nuclear research center in Iran shows visible damage to structures and nearby tunnel entrances from recent US airstrikes. / Satellite image (c) 2025 Maxar Technologies.
 Seymour Hersh
Seymour Hersh
The US attack on Iran may not have wiped out its nuclear ambitions but it did set them back years
I started my career in journalism during the early 1960s as a reporter for the City News Bureau of Chicago, a now long-gone local news agency that was set up by the Chicago newspapers in the 1890s to cover the police and fire departments, City Hall, the courts, the morgue, and so on. It was a training ground, and the essential message for its aspiring reporters was: “If your mother says she loves you, check it out.”
It was a message I wish our cable networks would take to heart. CNN and MSNBC, basing their reporting on an alleged Defense Intelligence Agency analysis, have consistently reported that the Air Force raids in Iran on June 22 did not accomplish their primary goal: total destruction of Iran’s nuclear-weapons capacity. US newspapers also joined in, but it was the two nominally liberal cable channels, with their dislike—make that contempt—for President Donald Trump, that drove the early coverage.
There was no DIA analysis per se. All US units that engage in combat must file an “after-action report” to the DIA after a military engagement. In this case, the report would have come from the US Central Command, located at MacDill Air Force base in Tampa, Florida. CENTCOM is responsible for all US military operations in the Middle East, Egypt, Central Asia, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. One US official involved in the process told me that “the first thing out of the box is you have to tell your boss what happened.” It was that initial report of the bombing attack that was forwarded to DIA headquarters along the Potomac River in Washington and copied or summarized by someone not authorized to do so and sent to the various media outlets.
The view of many who were involved in the planning and execution of the mission is that the report was summarized and leaked “for political purposes”—to cast immediate doubt on the success of the mission. The early reports went so far as to suggest that Iran’s nuclear program has survived incapacitation by the attack. Seven US B-2 “Spirit” bombers, each carrying two deep-penetration “bunker-busters” weighing 30,000 pounds, had flown without challenge from their base in Missouri to the primary target: Iran’s Fordo nuclear facility, concealed deep inside a mountain twenty miles north of the city of Qom.
The planning for the attack began with the knowledge that the main target—the working area of the nuclear program—was buried at least 260 feet below the rocky surface at Fordo. The gas centrifuges spinning there were repeatedly enriching uranium, in what is known as a cascade, not to weapons-grade level—uranium-235 isotopes enriched to 90 percent—but to 60 percent. Further processing to create weapons grade uranium, if Iran chose to do so, could be done in a matter of weeks, or less. The Air Force planning group had also been informed before the bombing raid, most likely by the Israelis, who have a vast spy network in Iran, that more than 450 pounds of the enriched gas stored at Fordo had been shipped to safety at another vital Iranian nuclear site at Isfahan, 215 miles south of Tehran. Isfahan was the only known facility in Iran capable of converting the Fordo gas into a highly enriched metal—a critical early stage of building the bomb. Isfahan also was a separate target of the US attack on Fordo, and was pulverized by Tomahawk missiles fired by a U.S. submarine operating in the Gulf of Aden, off Yemen.
As a journalist who for decades has covered the nascent nuclear crisis in the Middle East, it seemed clear to me and to informed friends I have in Washington and Israel that if Fordo somehow survived its bunker-buster attack, as was initially suggested, and continued to enrich more uranium, Isfahan would not. No enrichment, no Iranian bomb.
I’ve been frustrated and angry at cable news coverage for years, and that includes Fox News, too, and decided to try and find the real story. If your mother says she loves you, check it out. And I checked out enough of it to share.
I was told that “the first question for the American planners was how big was the actual workspace at Fordo? Was it a structure? We had to find that out before we got rid of it.” Some of the planners estimated that the working space “was the size of two hockey rinks: 200 feet long and 85 feet wide.” It came to 34,000 square feet. The height of the underground working space was assumed to be ten-and-a-half feet—I was not told the genesis of that assumption—and the size of the target was determined to be 357,000 cubic feet.
The next step was to measure the power of the dozen or more bunker-busters that were planned to be “carefully spaced and dropped” by the US B-2 bombers, using the most advanced guidance systems. (During one high-level session in Washington, one of the Air Force planners was asked what would happen if the B-2’s guidance systems were corrupted by an outside signal. “We’d miss the target” was the answer.)
I was assured that even if the rough estimate of the working space at Fordo was far off, the bombers targeting Fordo each carried a 30,000-pound bomb with an explosive payload of as much as five thousand pounds, which was more than enough to pulverize the mythical hockey rinks, or even a much larger working space.
Some of the bombs were also outfitted with what is known as a hard target void sensing fuze, which enabled the bombs to penetrate multiple layers of a site like Fordo before detonating. This would maximize the destructive effect. Each bomb, dropped in sequence, would create a force of rubble that would cause increasing havoc in the working areas deep inside the mountain.
“The bombs made their own hole. We built a 30,000-pound steel bullet,” the official told me, referring with pride to the bunker-busters.
Most important, he said, was that there were no post-strike hints detected of radioactivity—more evidence that the 450 pounds of enriched uranium had been moved from Fordo to the reprocessing site at Isfahan prior to the US attack there, which was code-named “Midnight Hammer.” That operation included a third US strike at yet another nuclear facility at Natanz.
“The Air Force got everything on the hit list,” the official told me. “Even if Iran rebuilds some centrifuges, it will still need Isfahan. There is no conversion capability without it.”
Why not, I asked, tell the public about the success of the raid and the fact that Iran no longer has a potential nuclear weapon?
The answer: “There will be a top-secret report about all of this, but we don’t tell people how hard we work. We tell the public what we think it wants to hear.”
The US official, asked about the future of the Iranian nuclear program, quickly acknowledged that “there is a communication problem” when it comes to the fate of the program.
The intent of the strike planners, he said, “was to prevent the Iranians from building a nuclear weapon in the near term—a year or so—with the hope they would not try again. The clear understanding was that there was no expectation to ‘obliterate’ every aspect of their nuclear program. We don’t even know what that is.
“Obliteration means the glass—[eliminating] Iran’s nuclear program—is full. The planning and the results are the glass is half-full. For Trump critics, the results are the glass is half-empty—the centrifuges may have survived and four hundred pounds of 60 percent enriched uranium are missing. The bombs could not be assured to penetrate the centrifuge chamber . . . too deep, but they could cover them up [with rocks and other bomb debris] and in the process cause unknown damage to them.
“Whether the 60 percent [enriched uranium] was there or not is irrelevant because without centrifuges they cannot refine it to weapons grade. Add to this the research and refinement and conversion from gas to metal—required for a bomb—at Isfahan are also gone.
“Results? Glass is half-full . . . a couple of years of respite and uncertain future. So now Trump’s defense is Full Glass. Critics? Half-empty. Reality? Half-full. There you are.”
The immediate beneficiary of the use of US force in Iran will not be a more placid Middle East, but Israel, and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. The Israeli Air Force and army are still killing massive numbers of Palestinians in Gaza.
There remains no evidence that Iran was on the cusp of becoming a nuclear power. But as the world has known for decades, Israel maintains a significant nuclear arsenal that it officially claims does not exist.
This is a story not about the bigger picture, which is muddled, but about a successful US mission that was the subject of a lot of sloppy reporting because of a reviled president. It would have been a breakthrough had anyone in the mainstream press spoken or written about the double standard that benefits Israel and its nuclear umbrella, but in America that remains a taboo.
Subscribe to Seymour Hersh.
For the full experience, upgrade your subscription.
conflict
Obama Dropped Over 26K Bombs Without Congressional Approval
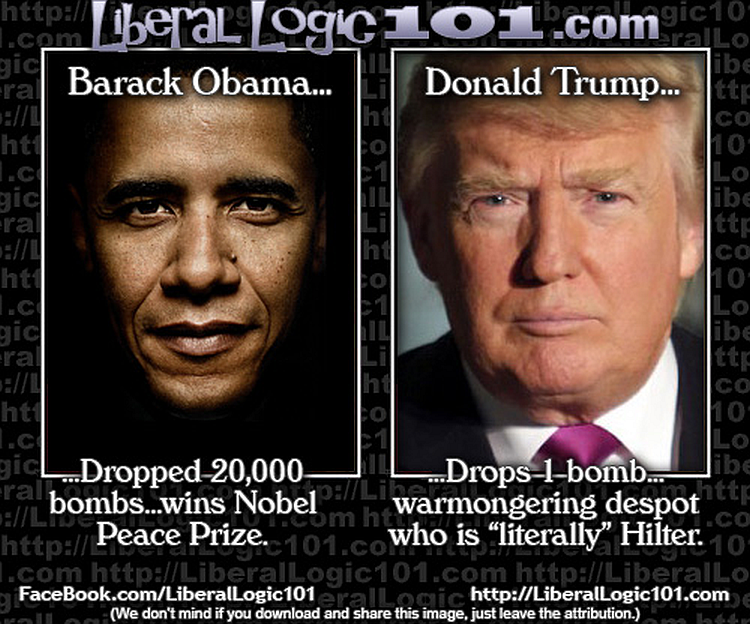
@miss_stacey_ Biden, Clinton, Obama & Harris on Iran #biden #clinton #obama #harris #trump #iran #nuclear
Iran has been the target for decades. Biden, Harris, and Clinton—all the Democrats have said that they would attack Iran if given the opportunity. It appears that Donald Trump is attempting to mitigate a potentially irresolvable situation. As he bluntly told reporters: We basically — we have two countries that have been fighting so long and so hard that they don’t know what the f‑‑‑ they’re doing.”
A portion of the nation believes Trump acted like a dictator by attacking Iran without Congressional approval. I explained how former President Barack Obama decimated the War Powers Resolution Act when he decided Libya was overdue for a regime change. The War Powers Act, or War Powers Resolution of 1973, grants the POTUS the ability to send American troops into battle if Congress receives a 48-hour notice. The stipulation here is that troops cannot remain in battle for over 60 days unless Congress authorizes a declaration of war. Congress could also remove US forces at any time by passing a resolution.
Libya is one of seven nations that Obama bombed without Congressional approval, yet no one remembers him as a wartime president, as the United States was not technically at war. Over 26,000 bombs were deployed across 7 nations under his command in 2016 alone. Libya, Afghanistan, Syria, Yemen, Somalia, Iraq, and Pakistan were attacked without a single vote. Donald Trump’s recent orders saw 36 bombs deployed in Iran.
The majority of those bombings happened in Syria, Libya, and Iraq under the premise of targeting extremist groups like ISIS. Drone strikes were carried out across Somalia, Yemen, and Pakistan as the Obama Administration accused those nations of hosting al-Qaeda affiliated groups. Coincidentally, USAID was also providing funding to those groups.
The 2001 Authorization for Use of Military Force (AUMF) was initially implemented to hunt down the Taliban and al-Qaeda after the 9/11 terrorist attacks. Obama broadened his interpretation of the AUMF and incorporated newly formed militant groups that were allegedly expanding across the entire Middle East. The Bureau of Investigative Journalism believes there were up to 1,100 civilian casualties in Pakistan, Yemen, and Somalia. Thousands of civilians died in Syria and Iraq but the death toll was never calculated. At least 100 innocent people died in the 2016 attacks in Afghanistan alone.
The government will always augment the law for their personal agenda. The War Powers Resolution was ignored and the AUMF was altered. Congress was, however, successful in preventing Obama from putting US troops on the ground and fighting a full-scale war. In 2013, Obama sought congressional approval for military action in Syria but was denied. Obama again attempted to deploy troops in 2015 but was denied. Congress has to redraft the AUMF to specifically prevent Obama from deploying troops in the Middle East. “The authorization… does not authorize the use of the United States Armed Forces on the ground in Syria for the purpose of combat operations.” Obama attempted to redraft the AUMF on his own by insisting he would prohibit “enduring offensive ground combat operations” or long-term deployment of troops. He was met with bipartisan disapproval as both sides believed he was attempting to drag the United States into another unnecessary war.
The United States should not be involved in any of these battles, but here we are. Those living in fear that Donald Trump is a dictator fail to recognize that past leadership had every intention of sending American men and women into battle unilaterally without a single vote cast.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCOWBOY UP! Pierre Poilievre Promises to Fight for Oil and Gas, a Stronger Military and the Interests of Western Canada
-

 MAiD1 day ago
MAiD1 day agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is already killing the disabled. It’s about to get worse
-
 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days agoEyebrows Raise as Karoline Leavitt Answers Tough Questions About Epstein
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta and Ontario sign agreements to drive oil and gas pipelines, energy corridors, and repeal investment blocking federal policies
-

 Fraser Institute24 hours ago
Fraser Institute24 hours agoBefore Trudeau average annual immigration was 617,800. Under Trudeau number skyrocketted to 1.4 million from 2016 to 2024
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex13 hours ago
Censorship Industrial Complex13 hours agoCanadian pro-freedom group sounds alarm over Liberal plans to revive internet censorship bill
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days ago‘I Know How These People Operate’: Fmr CIA Officer Calls BS On FBI’s New Epstein Intel
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoChicago suburb purchases childhood home of Pope Leo XIV



