Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
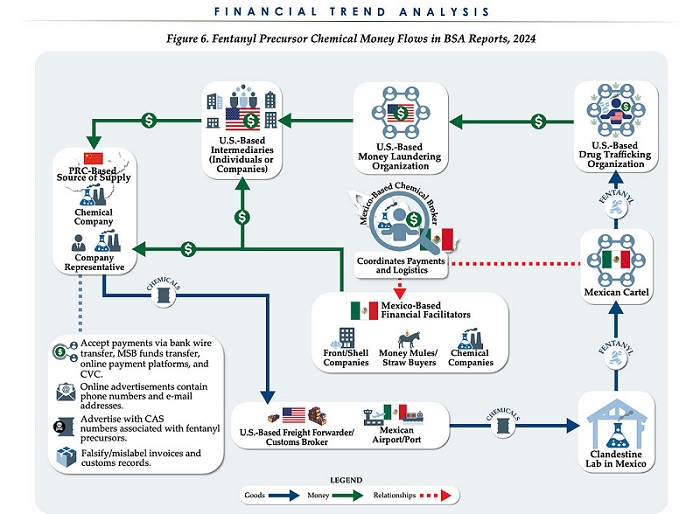
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
Business
Carney’s Ethics Test: Opposition MP’s To Challenge Prime Minister’s Financial Ties to China

Brookfield’s 2017 purchase of Teekay Offshore tied it to a corporate family whose LNG arm partnered with China’s COSCO to ship Russian Arctic gas under the shadow of Crimea-era sanctions.
In 2017, Brookfield, the investment giant that would later launch Prime Minister Mark Carney’s global business and political reach, bought control of Teekay Offshore Partners — a shipping deal that now casts a long geopolitical shadow.
On the surface, it looked like just another Brookfield deal. But behind it lies a complicated backstory, one that deepens concerns about the global-security risks lurking beneath Carney’s sprawling portfolio of more than 550 corporate holdings.
Teekay Offshore was part of the wider Teekay corporate family, which also included Teekay LNG Partners. That LNG arm entered a major joint venture with China LNG Shipping (CLNG), a subsidiary of COSCO, the Chinese state-owned shipping giant. Together, they financed and operated six ice-breaking carriers built to transport Russian natural gas from the Arctic Yamal LNG project.

The timing could hardly have been more sensitive. The Teekay-COSCO venture was launched in 2014 — the same year Russia seized Crimea and the West hit Moscow with sanctions. Five years later, in 2019, the U.S. government sanctioned a COSCO affiliate for carrying Iranian oil, which briefly caused Teekay’s joint venture with COSCO’s China LNG Shipping on the Arctic Yamal project to be treated as a “Blocked Person” under American rules.
The sanction was lifted after COSCO restructured its ownership.
Brookfield never owned Teekay LNG; its stake was in the Teekay Offshore arm, a separate division of the Teekay corporate family. But the two companies shared the Teekay brand, and as long as Brookfield remained tied to that structure, it was positioned uncomfortably close to a Sino-Russian natural gas venture that Washington had already flagged as risky.
COSCO – or China Ocean Shipping Company, a state-owned maritime giant – is a story in itself.
It has repeatedly faced U.S. scrutiny over its potential role in illicit and sensitive activities. In 1996, U.S. Customs agents seized 2,000 disassembled Chinese assault rifles hidden in containers on a COSCO ship at the Port of Oakland, allegedly bound for Mexican drug cartels. While official blame fell on Poly Technologies Inc. — a Chinese arms exporter — and the smuggling network behind the shipment, the incident heightened concerns about COSCO’s links to Beijing’s military and underground proliferation networks.
Other troubling episodes include a 1993 incident involving a COSCO vessel suspected of carrying chemical-weapons precursors to Iran, a 2015 seizure of explosives on a COSCO ship in Colombia headed for Cuba, and the 2019 U.S. sanctions on COSCO subsidiaries for violating Iran oil embargoes.
The Bureau has also reported on Canadian concerns. In December 1999, former Crown prosecutor Scott Newark wrote to an Ottawa intelligence review panel, noting that Canadian intelligence officials had long scrutinized COSCO’s activities at Vancouver’s port, citing alleged ties to both Chinese Triads and the People’s Liberation Army.
As Carney steps back into Parliament today, he is likely to face scathing questions from the Opposition not only about his Brookfield holdings and potential conflicts tied to deals like Teekay, but also over his government’s billion-dollar loan to BC Ferries for vessels built at a Chinese state-owned shipyard linked to Beijing’s civil-military fusion strategy.
This is where Carney himself enters the Brookfield story. After stepping down from the Bank of England in 2020, he joined Brookfield as Vice Chair and Head of ESG and Impact Investing. He later became Chair of Brookfield Asset Management. That means while Brookfield was still closely tied to Teekay Offshore, Carney was one of the most senior figures shaping Brookfield’s strategy — and holding significant personal stakes in its success.
Today, Brookfield has no exposure through Teekay. Teekay Offshore has since been renamed Altera Infrastructure and separated from its parent. In other words: while Brookfield has avoided direct legal risk, the reputational and geopolitical iceberg remains just beneath the waterline. Fresh controversy now looms in the case of the BC Ferries deal, in which the federal government, through the Canada Infrastructure Bank, which is overseen by Housing Minister and former Vancouver mayor Gregor Robertson, has provided a $1 billion low-interest loan to help BC Ferries purchase four hybrid vessels built by CMI Weihai, a Chinese state-owned shipyard. Opposition MPs say the loan contradicts Carney’s “Buy Canada” rhetoric and risks strengthening a PRC enterprise under civil-military fusion policy, at a moment when Beijing is openly threatening to invade Taiwan — with vessels constructed by state-owned shipbuilders such as CMI Weihai potentially part of that buildup.
As The Bureau has reported, an Ottawa democracy watchdog has already warned that Prime Minister Carney’s sprawling private investments — including substantial holdings in Brookfield as well as shares in more than 550 other companies — create a disabling conflict of interest that cannot be solved by his so-called “ethics screen,” ultimately undermining Ottawa’s credibility and weakening Carney’s capacity to confront hostile regimes, including China.
“PM Carney’s so-called ‘blind’ trust isn’t blind at all,” Democracy Watch stated this summer. “He knows exactly what he put in, he chose his own trustee, can instruct them not to sell, and can receive updates at any time. On top of that, he owns stock options in Brookfield that he can’t sell for years, guaranteeing he stays tethered to these corporate interests.”
These warnings echo The Bureau’s March 2025 pre-election investigation, which outlined in granular detail Carney’s deep entanglements with Brookfield and China. The Bureau revealed that Brookfield, the $900 billion investment giant Carney joined in 2020, held over $3 billion in politically sensitive assets connected to Chinese state-linked real estate and energy conglomerates, as well as a significant offshore banking footprint. One of its headline deals — a $750 million stake in a Shanghai commercial property project dating back to 2013 — was tied to a Hong Kong tycoon with official links to the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, a central “united front” body identified by the CIA as a tool of Beijing’s overseas influence operations.
Business
Carney Admits Deficit Will Top $61.9 Billion, Unveils New Housing Bureaucracy

The Prime Minister said this year’s shortfall will exceed last year’s $61.9B as Ottawa creates Build Canada Homes to expand affordable housing.
Prime Minister Mark Carney just admitted that this year’s federal budget deficit will be “substantial” larger than last year’s $61.9 billion shortfall. Speaking in Nepean ahead of Parliament’s return yesterday, Carney defended the red ink as the cost of what he called “nation-building” investments in housing, defense, and protection from global trade shocks.
Lets recap for those at home not keeping score, the federal government ran a $61.9 billion deficit last year. It was supposed to be closer to $40 billion, but like every Liberal promise, the reality was far worse. That single number, that $61.9 billion hole, was a turning point. It destroyed what little credibility Justin Trudeau had left, and it forced his own finance minister, Chrystia Freeland, to walk away.
Now, let’s pause here. Chrystia Freeland didn’t just “move on.” She resigned in December 2024 after a bitter clash with Trudeau. She couldn’t defend the runaway spending anymore, couldn’t keep pretending the numbers added up. And when your own finance minister, the person who signed off on the books, decides she can’t be part of the game, and yet she’s ok with Carney spending more???
But here’s the part that’s truly insane. Just last week, those same media outlets were floating headlines about the Liberals preparing an “austerity budget.” The Globe and Mail literally told us Carney was weighing “austerity” alongside “investments.” CTV reported the government’s own House Leader was warning Canadians about “tough choices” ahead of the fall budget. Austerity! After sixty billion dollars in red ink.
And these idiots actually had the gall to use that word, “austerity” while the country drowns in debt, while the deficit is climbing even higher, and while Carney is out there hiring new bureaucrats and creating brand-new agencies with billions of your dollars. You can’t make this up.
And speaking of spin, let’s get to the real show. Because once Carney slipped and admitted the deficit was going to be bigger, he launched into the propaganda portion of the presser, the part where he pretends to be solving the housing crisis. And what’s the solution? You guessed it. Another federal agency. A brand-new bureaucracy carved out of CMHC. Because in Carney’s Canada, the answer to too much red tape is… more red tape.
They’re calling it Build Canada Homes. Sounds nice. It gets $13 billion of your money on day one. It has a mandate to “plan, finance, and build homes.” And who’s running it? Anna Belo — a former Toronto deputy mayor turned private-sector consultant. Because nothing says “housing affordability” like another revolving-door insider cashing a taxpayer-funded paycheck.
The agency’s first big ideas? Modular housing, a $1.5 billion “rental protection fund,” and lots of partnerships with provinces, municipalities, and Indigenous groups. In other words: buzzwords. More meetings. More layers of government. More bureaucracy.
And then, as if to drive the joke home, Carney rolled out his housing minister. Who is it? Gregor Robertson. Yes, the same Gregor Robertson who, as mayor of Vancouver, presided over one of the worst housing affordability collapses in Canadian history. The man under whose watch prices skyrocketed, taxes doubled, and working families were driven out of the city. That’s the expert. That’s the guy they put in charge. Yeah, he’s got “experience” all right. Eye roll.
Even Pierre Poilievre saw straight through it. Speaking to his caucus on Parliament Hill ahead of the fall sitting, the Conservative leader mocked Carney’s shiny new agency as just another layer of government that won’t build homes.
“After six months in office, not a single home has been built. Instead, he’s created another bureaucracy. Meanwhile, CMHC’s own forecast shows homebuilding will fall 13%. In the GTA, it’s already down by half. That is the Carney record.”
Poilievre tied the criticism to Carney’s broader record of announcements without results, comparing the “nation-building” pitch to the agency’s empty promise: new logos, new titles, no shovels in the ground.
This is the Liberal solution in a nutshell: take a crisis they helped create, build another layer of bureaucracy, and put the very people who caused the problem in charge of fixing it. And then tell you, with a straight face, that this time, it’ll be different.
And here’s the kicker. Every dollar of this so-called “nation-building” deficit is a dollar borrowed against your future. Last year alone, interest payments on the debt blew past PBO’s estimate of $49.1 billion… THAT’S MORE than Ottawa spends on health care transfers.
Lets be clear, thank God the fall session is back. Because here’s the truth: these Liberals only shine when the press is playing duck and cover for them. When it’s just press conferences, glossy slogans, and clapping seals, they look untouchable. But the moment Parliament is sitting, the moment committees start pulling threads, the whole show falls apart.
Remember what happened when they had just two days of committee hearings on that ferry contract? Over a billion dollars, handed to China, while they were busy telling Canadians “Canada First.” They were humiliated. Because when the facts are out in the open, when the spin stops working, this government has nothing left to stand on.
This fall will be no different. Mark Carney can rebrand deficits as “nation-building,” he can launch new bureaucracies and hire insiders at half a million dollars a year, but once Question Period starts, none of that will save him. The reality is simple: this government is not long for the world. And soon enough, we’ll see real austerity… Not because they choose it, but because they’ve run out of money and credibility to keep the game going.
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoInside Xi’s Fifth Column: How Beijing Uses Gangsters to Wage Political Warfare in Taiwan — and the West
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoDecision expected soon in case that challenges Alberta’s “safe spaces” law
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoThe IEA’s Peak Oil Fever Dream Looks To Be In Full Collapse
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoTransgender Roomate of Alleged Charlie Kirk Assassin Cooperating with Investigation
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoWhy FDA Was Right To Say No To COVID-19 Vaccines For Healthy Kids
-
 Crime22 hours ago
Crime22 hours agoDown the Charlie Kirk Murder Rabbit Hole
-

 Business12 hours ago
Business12 hours agoCarney Admits Deficit Will Top $61.9 Billion, Unveils New Housing Bureaucracy
-

 Business20 hours ago
Business20 hours agoIt’s time to finally free the beer







