Business
Carney government needs stronger ‘fiscal anchors’ and greater accountability

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Grady Munro
Following the recent release of the Carney government’s first budget, Fitch Ratings (one of the big three global credit rating agencies) issued a warning that the “persistent fiscal expansion” outlined in the budget—characterized by high levels of spending, borrowing and debt accumulation—will erode the health of Canada’s finances and could lead to a downgrade in Canada’s credit rating.
Here’s why this matters. Canada’s credit rating impacts the federal government’s cost of borrowing money. If the government’s rating gets downgraded—meaning Canadian federal debt is viewed as an increasingly risky investment due to fiscal mismanagement—it will likely become more expensive for the government to borrow money, which ultimately costs taxpayers.
The cost of borrowing (i.e. the interest paid on government debt) is a significant part of the overall budget. This year, the federal government will spend a projected $55.6 billion on debt interest, which is more than one in every 10 dollars of federal revenue, and more than the government will spend on health-care transfers to the provinces. By 2029/30, interest costs will rise to a projected $76.1 billion or more than one in every eight dollars of revenue. That’s taxpayer money unavailable for programs and services.
Again, if Canada’s credit rating gets downgraded, these costs will grow even larger.
To maintain a good credit rating, the government must prevent the deterioration of its finances. To do this, governments establish and follow “fiscal anchors,” which are fiscal guardrails meant to guide decisions regarding spending, taxes and borrowing.
Effective fiscal anchors ensure governments manage their finances so the debt burden remains sustainable for future generations. Anchors should be easily understood and broadly applied so that government cannot get creative with its accounting to only technically abide by the rule, but still give the government the flexibility to respond to changing circumstances. For example, a commonly-used rule by many countries (including Canada in the past) is a ceiling/target for debt as a share of the economy.
The Carney government’s budget establishes two new fiscal anchors: balancing the federal operating budget (which includes spending on day-to-day operations such as government employee compensation) by 2028/29, and maintaining a declining deficit-to-GDP ratio over the years to come, which means gradually reducing the size of the deficit relative to the economy. Unfortunately, these anchors will fail to keep federal finances from deteriorating.
For instance, the government’s plan to balance the “operating budget” is an example of creative accounting that won’t stop the government from borrowing money each year. Simply put, the government plans to split spending into two categories: “operating spending” and “capital investment” —which includes any spending or tax expenditures (e.g. credits and deductions) that relates to the production of an asset (e.g. machinery and equipment)—and will only balance operating spending against revenues. As a result, when the government balances its operating budget in 2028/29, it will still incur a projected deficit of $57.9 billion when spending on capital is included.
Similarly, the government’s plan to reduce the size of the annual deficit relative to the economy each year does little to prevent debt accumulation. This year’s deficit is expected to equal 2.5 per cent of the overall economy—which, since 2000, is the largest deficit (as a share of the economy) outside of those run during the 2008/09 financial crisis and the pandemic. By measuring its progress off of this inflated baseline, the government will technically abide by its anchor even as it runs relatively large deficits each and every year.
Moreover, according to the budget, total federal debt will grow faster than the economy, rising from a projected 73.9 per cent of GDP in 2025/26 to 79.0 per cent by 2029/30, reaching a staggering $2.9 trillion that year. Simply put, even the government’s own fiscal plan shows that its fiscal anchors are unable to prevent an unsustainable rise in government debt. And that’s assuming the government can even stick to these anchors—which, according to a new report by the Parliamentary Budget Officer, is highly unlikely.
Unfortunately, a federal government that can’t stick to its own fiscal anchors is nothing new. The Trudeau government made a habit of abandoning its fiscal anchors whenever the going got tough. Indeed, Fitch Ratings highlighted this poor track record as yet another reason to expect federal finances to continue deteriorating, and why a credit downgrade may be on the horizon. Again, should that happen, Canadian taxpayers will pay the price.
Much is riding on the Carney government’s ability to restore Canada’s credibility as a responsible fiscal manager. To do this, it must implement stronger fiscal rules than those presented in the budget, and remain accountable to those rules even when it’s challenging.
Business
Parliamentary Budget Officer begs Carney to cut back on spending

PBO slices through Carney’s creative accounting
The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on Prime Minister Mark Carney to cut spending following today’s bombshell Parliamentary Budget Officer report that criticizes the government’s definition of capital spending and promise to balance the operating budget.
“The reality is that Carney is continuing on a course of unaffordable borrowing and the PBO report shows government messaging about ‘balancing the operating budget’ is not credible,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Carney is using creative accounting to hide the spiralling debt.”
Carney’s Budget 2025 splits the budget into operating and capital spending and promises to balance the operating budget by 2028-29.
However, today’s PBO budget report states that Carney’s definition of capital spending is “overly expansive.” Without using that “overly expansive” definition of capital spending, the government would run an $18 billion operating deficit in 2028-29, according to the PBO.
“Based on our definition, capital investments would total $217.3 billion over 2024-25 to 2029-30, which is approximately 30 per cent ($94 billion) lower compared to Budget 2025,” according to the PBO. “Moreover, based on our definition, the operating balance in Budget 2025 would remain in a deficit position over 2024-25 to 2029-30.”
The PBO states that the Carney government is using “a definition of capital investment that expands beyond the current treatment in the Public Accounts and international practice.” The report specifically points out that “by including corporate income tax expenditures, investment tax credits and operating (production) subsidies, the framework blends policy measures with capital formation.”
The federal government plans to borrow about $80 billion this year, according to Budget 2025. Carney has no plan stop borrowing money and balance the budget. Debt interest charges will cost taxpayers $55.6 billion this year, which is more than the federal government will send to the provinces in health transfers ($54.7 billion) or collect through the GST ($54.4 billion).
“Carney isn’t balancing anything when he borrows tens of billions of dollars every year,” Terrazzano said. “Instead of applying creative accounting to the budget numbers, Carney needs to cut spending and debt.”
Business
P.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
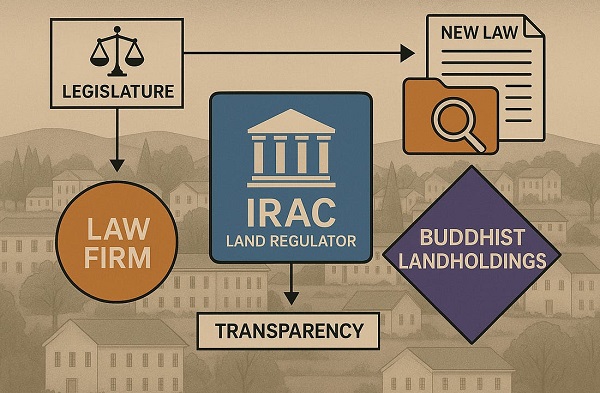
Following an exclusive report from The Bureau detailing transparency concerns at Prince Edward Island’s land regulator — and a migration of lawyers from firms that represented the Buddhist land-owning entities the regulator had already probed — the P.E.I. Legislature has passed a new law forcing the Island Regulatory and Appeals Commission (IRAC) to make its land-investigation reports public.
The bill — introduced by Green Party Leader Matt MacFarlane — passed unanimously on Wednesday, CTV News reported. It amends the Lands Protection Act to require IRAC to table final investigation reports and supporting documents in the Legislature within 15 days of completion.
MacFarlane told CTV the reform was necessary because “public trust … is at an all-time low in the system,” adding that “if Islanders can see that work is getting done, that the (LPA) is being properly administered and enforced, that will get some trust rebuilt in this body.”
The Bureau’s report last week underscored that concern, showing how lawyers from Cox & Palmer — the firm representing the Buddhist landholders — steadily moved into senior IRAC positions after the regulator quietly shut down its mandated probe into those same entities. The issue exploded this fall when a Legislative Committee subpoena confirmed that IRAC’s oft-cited 2016–2018 investigation had never produced a final report at all.
There have been reports, including from CBC, that the Buddhist landholders have ties to a Chinese Communist Party entity, which leaders from the group deny.
In the years following IRAC’s cancelled probe into the Buddhist landholders, The Bureau reported, Cox & Palmer’s general counsel and director of land joined IRAC, and the migration of senior former lawyers culminated this spring, with former premier Dennis King appointing his own chief of staff, longtime Cox & Palmer partner Pam Williams, as IRAC chair shortly after the province’s land minister ordered the regulator to reopen a probe into Buddhist landholdings.
The law firm did not respond to questions, while IRAC said it has strong measures in place to guard against any conflicted decision-making.
Reporting on the overall matter, The Bureau wrote that:
“The integrity of the institution has, in effect, become a test of public confidence — or increasingly, of public disbelief. When Minister of Housing, Land and Communities Steven Myers ordered IRAC in February 2025 to release the 2016–2018 report and reopen the investigation, the commission did not comply … Myers later resigned in October 2025. Days afterward, the Legislative Committee on Natural Resources subpoenaed IRAC to produce the report. The commission replied that no formal report had ever been prepared.”
The Bureau’s investigation also showed that the Buddhist entities under review control assets exceeding $480 million, and there is also a planned $185-million campus development in the Town of Three Rivers, citing concerns that such financial power, combined with a revolving door between key law firms, political offices and the regulator, risks undermining confidence in P.E.I.’s land-oversight regime.
Wednesday’s new law converts the expectation for transparency at IRAC, voiced loudly by numerous citizens in this small province of about 170,000, into a statutory obligation.
Housing, Land and Communities Minister Cory Deagle told CTV the government supported the bill: “We do have concerns about some aspects of it, but the main principles of what you’re trying to achieve are a good thing.”
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoRichmond Mayor Warns Property Owners That The Cowichan Case Puts Their Titles At Risk
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoHow economic corridors could shape a stronger Canadian future
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoLaura Ingraham’s Viral Clash With Trump Prompts Her To Tell Real Reasons China Sends Students To US
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoP.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
-
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoMajor new studies link COVID shots to kidney disease, respiratory problems
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoCanada’s oilpatch shows strength amid global oil shakeup
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex16 hours ago
Censorship Industrial Complex16 hours agoEU’s “Democracy Shield” Centralizes Control Over Online Speech
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSluggish homebuilding will have far-reaching effects on Canada’s economy







