Energy
Canada badly misjudged the future of LNG
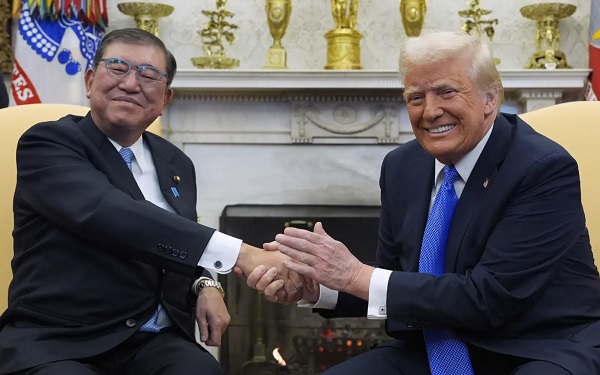
Canada’s failure to push more strongly for LNG has put us in a weaker position, but there is time to recover
Earlier this month, President Donald Trump and Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba announced a joint American-Japanese venture for the Alaska LNG Project. Once built, the $44 billion project will ship gas from northern Alaska through an 800-mile pipeline to a liquefaction facility in Nikiski for export.
It is another sign that Canada needs to step up its LNG industry.
For years, Canada has been indecisive about liquefied natural gas (LNG), while others seized the moment. Now, with global demand for LNG surging and allies like Germany, Poland, and Japan needing stable energy sources, Canada finds itself left behind, and forced to regret regulatory missteps, political foot-dragging, and underestimating LNG’s long-term value.
The warning signs have been there for years. In 2022, as Europe scrambled to replace Russian gas after the invasion of Ukraine, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz personally came to Canada to request LNG exports. Instead of seizing the moment, only to be told there was no “strong business case” for Canadian LNG exports to Europe.
The same story followed with Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida in 2023 and Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis and Polish President Andrzej Duda in 2024. Each time, Canada’s response was the same, with no commitment, no plan, and no urgency.
Meanwhile, others acted. The U.S. and Qatar ramped up their LNG exports, locking in long-term contracts with European and Asian buyers. Germany, despite its push for renewables, invested in floating LNG terminals, recognizing that natural gas would be essential for energy security. Canada, despite having some of the world’s largest natural gas reserves, failed to position itself as a global supplier.
Canada’s failure isn’t just about hesitation, it’s about active obstruction. The federal government’s Bill C-69, the so-called “no more pipelines” law, created an onerous and unpredictable regulatory process for major energy projects. The CleanBC plan made it clear that investment in the sector would face endless hurdles.
The results have been severe. Since 2015, Canada has seen $670 billion in cancelled resource projects, including multiple LNG terminals on the Atlantic and Pacific coasts. The Energy East pipeline, which could have supplied LNG facilities in New Brunswick and enabled exports to Europe, was cancelled due to regulatory delays. The proposed expansion of Repsol’s LNG terminal in Saint John faced the same fate. Investors, spooked by uncertainty and government hostility, took their money elsewhere.
While Canada dithered, the world moved. As Stewart Muir, CEO of Resource Works, has written, LNG is not just a “bridge fuel”, it’s a destination fuel for much of the world. Despite heavy investment in renewables, countries like China are building coal-fired power plants because they lack secure, low-emissions alternatives.
If Canada had been exporting LNG between 2020 and 2022, it could have displaced an entire year’s worth of Canada’s domestic emissions in coal-dependent countries. Instead, Canada chose climate protectionism, prioritizing domestic emissions cuts over global impact.
The irony is that Canada’s hesitation to embrace LNG has hurt the climate more than it has helped. As coal consumption rises in Asia and Europe, emissions continue to soar, emissions that Canadian LNG could have displaced. A National Bank of Canada report found that transitioning India from coal to natural gas could cut four times more emissions than Canada’s total annual output, a massive missed opportunity.
Beyond environmental costs, the economic consequences are enormous. LNG projects in B.C. have been job engines, revitalizing communities once dependent on fishing, mining, and forestry. The Atlantic provinces, struggling economically, could have experienced the same boom had LNG infrastructure been developed there. Instead, they’ve been left behind.
There’s still time for Canada to change course, but it will require a complete reversal of policy. The federal government must:
- Reform permitting and regulatory processes to make LNG projects viable and competitive.
- Acknowledge LNG’s role in global emissions reduction and align climate policies with global realities.
- Develop Atlantic LNG infrastructure to serve European markets, capitalizing on growing demand.
As Enbridge CEO Greg Ebel said at LNG2023, Canada’s allies have been “knocking on our door…to which we’ve said…no.” It’s time to stop saying no, to LNG, to economic growth, and to a cleaner energy future. If we don’t act now, we’ll be left behind forever.
Alberta
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith Discusses Moving Energy Forward at the Global Energy Show in Calgary

From Energy Now
At the energy conference in Calgary, Alberta Premier Danielle Smith pressed the case for building infrastructure to move provincial products to international markets, via a transportation and energy corridor to British Columbia.
“The anchor tenant for this corridor must be a 42-inch pipeline, moving one million incremental barrels of oil to those global markets. And we can’t stop there,” she told the audience.
The premier reiterated her support for new pipelines north to Grays Bay in Nunavut, east to Churchill, Man., and potentially a new version of Energy East.
The discussion comes as Prime Minister Mark Carney and his government are assembling a list of major projects of national interest to fast-track for approval.
Carney has also pledged to establish a major project review office that would issue decisions within two years, instead of five.
Alberta
Punishing Alberta Oil Production: The Divisive Effect of Policies For Carney’s “Decarbonized Oil”

From Energy Now
By Ron Wallace
The federal government has doubled down on its commitment to “responsibly produced oil and gas”. These terms are apparently carefully crafted to maintain federal policies for Net Zero. These policies include a Canadian emissions cap, tanker bans and a clean electricity mandate.
Following meetings in Saskatoon in early June between Prime Minister Mark Carney and Canadian provincial and territorial leaders, the federal government expressed renewed interest in the completion of new oil pipelines to reduce reliance on oil exports to the USA while providing better access to foreign markets. However Carney, while suggesting that there is “real potential” for such projects nonetheless qualified that support as being limited to projects that would “decarbonize” Canadian oil, apparently those that would employ carbon capture technologies. While the meeting did not result in a final list of potential projects, Alberta Premier Danielle Smith said that this approach would constitute a “grand bargain” whereby new pipelines to increase oil exports could help fund decarbonization efforts. But is that true and what are the implications for the Albertan and Canadian economies?
The federal government has doubled down on its commitment to “responsibly produced oil and gas”. These terms are apparently carefully crafted to maintain federal policies for Net Zero. These policies include a Canadian emissions cap, tanker bans and a clean electricity mandate. Many would consider that Canadians, especially Albertans, should be wary of these largely undefined announcements in which Ottawa proposes solely to determine projects that are “in the national interest.”
The federal government has tabled legislation designed to address these challenges with Bill C-5: An Act to enact the Free Trade and Labour Mobility Act and the Building Canada Act (the One Canadian Economy Act). Rather than replacing controversial, and challenged, legislation like the Impact Assessment Act, the Carney government proposes to add more legislation designed to accelerate and streamline regulatory approvals for energy and infrastructure projects. However, only those projects that Ottawa designates as being in the national interest would be approved. While clearer, shorter regulatory timelines and the restoration of the Major Projects Office are also proposed, Bill C-5 is to be superimposed over a crippling regulatory base.
It remains to be seen if this attempt will restore a much-diminished Canadian Can-Do spirit for economic development by encouraging much-needed, indeed essential interprovincial teamwork across shared jurisdictions. While the Act’s proposed single approval process could provide for expedited review timelines, a complex web of regulatory processes will remain in place requiring much enhanced interagency and interprovincial coordination. Given Canada’s much-diminished record for regulatory and policy clarity will this legislation be enough to persuade the corporate and international capital community to consider Canada as a prime investment destination?
As with all complex matters the devil always lurks in the details. Notably, these federal initiatives arrive at a time when the Carney government is facing ever-more pressing geopolitical, energy security and economic concerns. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development predicts that Canada’s economy will grow by a dismal one per cent in 2025 and 1.1 per cent in 2026 – this at a time when the global economy is predicted to grow by 2.9 per cent.
It should come as no surprise that Carney’s recent musing about the “real potential” for decarbonized oil pipelines have sparked debate. The undefined term “decarbonized”, is clearly aimed directly at western Canadian oil production as part of Ottawa’s broader strategy to achieve national emissions commitments using costly carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects whose economic viability at scale has been questioned. What might this mean for western Canadian oil producers?
The Alberta Oil sands presently account for about 58% of Canada’s total oil output. Data from December 2023 show Alberta producing a record 4.53 million barrels per day (MMb/d) as major oil export pipelines including Trans Mountain, Keystone and the Enbridge Mainline operate at high levels of capacity. Meanwhile, in 2023 eastern Canada imported on average about 490,000 barrels of crude oil per day (bpd) at a cost estimated at CAD $19.5 billion. These seaborne shipments to major refineries (like New Brunswick’s Irving Refinery in Saint John) rely on imported oil by tanker with crude oil deliveries to New Brunswick averaging around 263,000 barrels per day. In 2023 the estimated total cost to Canada for imported crude oil was $19.5 billion with oil imports arriving from the United States (72.4%), Nigeria (12.9%), and Saudi Arabia (10.7%). Since 1988, marine terminals along the St. Lawrence have seen imports of foreign oil valued at more than $228 billion while the Irving Oil refinery imported $136 billion from 1988 to 2020.
What are the policy and cost implication of Carney’s call for the “decarbonization” of western Canadian produced, oil? It implies that western Canadian “decarbonized” oil would have to be produced and transported to competitive world markets under a material regulatory and financial burden. Meanwhile, eastern Canadian refiners would be allowed to import oil from the USA and offshore jurisdictions free from any comparable regulatory burdens. This policy would penalize, and makes less competitive, Canadian producers while rewarding offshore sources. A federal regulatory requirement to decarbonize western Canadian crude oil production without imposing similar restrictions on imported oil would render the One Canadian Economy Act moot and create two market realities in Canada – one that favours imports and that discourages, or at very least threatens the competitiveness of, Canadian oil export production.
Ron Wallace is a former Member of the National Energy Board.
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoIran nuclear talks were ‘coordinated deception’ between US and Israel: report
-

 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days agoLA protests continue as judge pulls back CA National Guard ahead of ‘No Kings Day’
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoIsrael strikes Iran, targeting nuclear sites; U.S. not involved in attack
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoIsrael’s Decapitation Strike on Iran Reverberates Across Global Flashpoints
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoCanada is no energy superpower
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoPunishing Alberta Oil Production: The Divisive Effect of Policies For Carney’s “Decarbonized Oil”
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump: ‘Changes are coming’ to aggressive immigration policy after business complaints
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta Premier Danielle Smith Discusses Moving Energy Forward at the Global Energy Show in Calgary




