Energy
Anti-LNG activists have decided that they now actually care for LNG investors after years of calling to divest
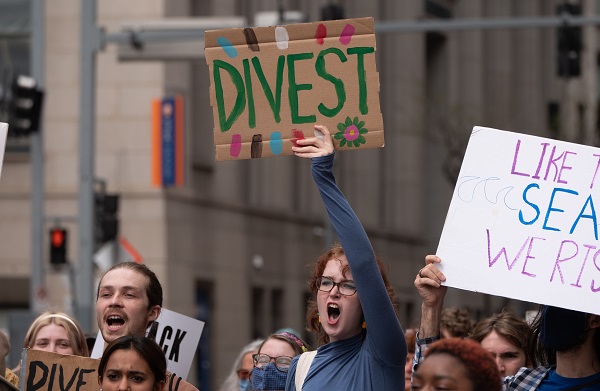
From Resource Works
Qatar is building or chartering 104 LNG carriers, and plans to double its LNG output by the end of 2030. It would then produce 142 million megatonnes of LNG a year — more than 20 times the 7 million from the LNG Canada plant.
Strange to see activists opposed to LNG development in Canada publicly worrying about whether such projects are economically viable for investors.
One group has been arguing “the reality is that in the coming years the world may no longer need BC.’s LNG” and that could mean “the risk of future stranded assets.” Of course, they aren’t at all concerned about investors; they’re just desperately throwing every brick they can think of in organized and well-funded political campaigns to influence government.
Meanwhile, two of their prime targets proceed with their government-approved plans: LNG Canada moves steadily toward overseas exports in 2025, and Woodfibre LNG is moving toward construction, and shipping pre-sold exports in 2027. BC has also approved Fortis BC’s planned marine LNG terminal on the Fraser, which would provide LNG as fuel for visiting ships, and could also handle export cargoes from an expanded FortisBC plant in Delta.
And First Nations are working on the Haisla Nation’s Cedar LNG project, and the Nisga’a Nation’s proposed Ksi Lisims LNG operation. Odd how the activists refrain from criticizing the First Nations Peoples who want to export LNG to help their communities thrive .
And, somehow, the activists’ messages fail to impress LNG developers in the U.S., Australia, the United Arab Emirates, Russia, and Qatar. For context, Qatar is building or chartering 104 LNG carriers, and plans to double its LNG output by the end of 2030. It would then produce 142 million megatonnes of LNG a year — more than 20 times the 7 million from the LNG Canada plant.
The critics’ climate issues and concerns are indeed legitimate, no argument. World emissions hit a record high in 2023, the International Energy Agency reports. Emissions in advanced economies fell to a 50-year low, but rose in China and India.
China in 2023 accounted for 35 percent of global carbon-dioxide emissions. The U.S. stood at 12.5 percent and India at 7.7 percent. While China has indeed made much progress on renewables, it and India continue to burn more and more coal.
Why Canadian groups think they can solve world issues by focussing on relatively modest LNG proposals in Canada is beyond us.
Our Canadian LNG will be environmentally cleaner than LNG from many rival suppliers. And buyers can use it to generate more of their electricity, replacing coal-powered generation that produces far more emissions. That’s an environmental plus.
LNG Canada will have an emissions intensity of 0.15 percent of carbon dioxide per tonne of LNG produced, less than half the global industry average of 0.35 percent per tonne, and 35 percent lower than the best-performing facility.
Woodfibre LNG will be the world’s first net-zero LNG export facility — 23 years ahead of government net-zero goals. Woodfibre LNG will have an emissions intensity of just 0.04 percent — and that’s less than one sixth of the global industry average.
The Haisla’s Cedar LNG project will have an emissions intensity of just 0.08 percent of CO2 per tonne of LNG. That’s less than a third of the global average. Its plans call for emissions to be near zero by 2030.
And the Nisga’a Ksi Lisims project promises to be operating with net-zero emissions within three years of the project’s first shipment.
Our LNG has another advantage over U.S. LNG: The shipping distance from BC to prime Asian buyers is about 10 days compared to 20 days from U.S. Gulf Coast LNG plants. That means 50-60 percent lower emissions from the ships carrying the LNG.
Canada produces only 1.5 percent of world greenhouse-gas emissions. As Canada’s independent parliamentary budget officer reported in 2022: “Canada’s own emissions are not large enough to materially impact climate change.”
Thus the First Nations LNG Alliance points out: “You could shut the entire country down — no energy, no industry, no jobs, no transportation, no heat, no light — and that reduction of 1.5 percent of emissions could be wiped out by new energy development and new emissions in other countries in a matter of some months or perhaps a few years.”
And so the Alliance says: “So we have government punishing taxpayers, First Nations and industry by putting on blinkers when it comes to LNG. Ottawa views Canada as a geographical silo in which we must meet our emissions targets, regardless of what others do.
“It’s long past time, indeed, to act locally — but think globally.”
Alberta
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith Discusses Moving Energy Forward at the Global Energy Show in Calgary

From Energy Now
At the energy conference in Calgary, Alberta Premier Danielle Smith pressed the case for building infrastructure to move provincial products to international markets, via a transportation and energy corridor to British Columbia.
“The anchor tenant for this corridor must be a 42-inch pipeline, moving one million incremental barrels of oil to those global markets. And we can’t stop there,” she told the audience.
The premier reiterated her support for new pipelines north to Grays Bay in Nunavut, east to Churchill, Man., and potentially a new version of Energy East.
The discussion comes as Prime Minister Mark Carney and his government are assembling a list of major projects of national interest to fast-track for approval.
Carney has also pledged to establish a major project review office that would issue decisions within two years, instead of five.
Alberta
Punishing Alberta Oil Production: The Divisive Effect of Policies For Carney’s “Decarbonized Oil”

From Energy Now
By Ron Wallace
The federal government has doubled down on its commitment to “responsibly produced oil and gas”. These terms are apparently carefully crafted to maintain federal policies for Net Zero. These policies include a Canadian emissions cap, tanker bans and a clean electricity mandate.
Following meetings in Saskatoon in early June between Prime Minister Mark Carney and Canadian provincial and territorial leaders, the federal government expressed renewed interest in the completion of new oil pipelines to reduce reliance on oil exports to the USA while providing better access to foreign markets. However Carney, while suggesting that there is “real potential” for such projects nonetheless qualified that support as being limited to projects that would “decarbonize” Canadian oil, apparently those that would employ carbon capture technologies. While the meeting did not result in a final list of potential projects, Alberta Premier Danielle Smith said that this approach would constitute a “grand bargain” whereby new pipelines to increase oil exports could help fund decarbonization efforts. But is that true and what are the implications for the Albertan and Canadian economies?
The federal government has doubled down on its commitment to “responsibly produced oil and gas”. These terms are apparently carefully crafted to maintain federal policies for Net Zero. These policies include a Canadian emissions cap, tanker bans and a clean electricity mandate. Many would consider that Canadians, especially Albertans, should be wary of these largely undefined announcements in which Ottawa proposes solely to determine projects that are “in the national interest.”
The federal government has tabled legislation designed to address these challenges with Bill C-5: An Act to enact the Free Trade and Labour Mobility Act and the Building Canada Act (the One Canadian Economy Act). Rather than replacing controversial, and challenged, legislation like the Impact Assessment Act, the Carney government proposes to add more legislation designed to accelerate and streamline regulatory approvals for energy and infrastructure projects. However, only those projects that Ottawa designates as being in the national interest would be approved. While clearer, shorter regulatory timelines and the restoration of the Major Projects Office are also proposed, Bill C-5 is to be superimposed over a crippling regulatory base.
It remains to be seen if this attempt will restore a much-diminished Canadian Can-Do spirit for economic development by encouraging much-needed, indeed essential interprovincial teamwork across shared jurisdictions. While the Act’s proposed single approval process could provide for expedited review timelines, a complex web of regulatory processes will remain in place requiring much enhanced interagency and interprovincial coordination. Given Canada’s much-diminished record for regulatory and policy clarity will this legislation be enough to persuade the corporate and international capital community to consider Canada as a prime investment destination?
As with all complex matters the devil always lurks in the details. Notably, these federal initiatives arrive at a time when the Carney government is facing ever-more pressing geopolitical, energy security and economic concerns. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development predicts that Canada’s economy will grow by a dismal one per cent in 2025 and 1.1 per cent in 2026 – this at a time when the global economy is predicted to grow by 2.9 per cent.
It should come as no surprise that Carney’s recent musing about the “real potential” for decarbonized oil pipelines have sparked debate. The undefined term “decarbonized”, is clearly aimed directly at western Canadian oil production as part of Ottawa’s broader strategy to achieve national emissions commitments using costly carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects whose economic viability at scale has been questioned. What might this mean for western Canadian oil producers?
The Alberta Oil sands presently account for about 58% of Canada’s total oil output. Data from December 2023 show Alberta producing a record 4.53 million barrels per day (MMb/d) as major oil export pipelines including Trans Mountain, Keystone and the Enbridge Mainline operate at high levels of capacity. Meanwhile, in 2023 eastern Canada imported on average about 490,000 barrels of crude oil per day (bpd) at a cost estimated at CAD $19.5 billion. These seaborne shipments to major refineries (like New Brunswick’s Irving Refinery in Saint John) rely on imported oil by tanker with crude oil deliveries to New Brunswick averaging around 263,000 barrels per day. In 2023 the estimated total cost to Canada for imported crude oil was $19.5 billion with oil imports arriving from the United States (72.4%), Nigeria (12.9%), and Saudi Arabia (10.7%). Since 1988, marine terminals along the St. Lawrence have seen imports of foreign oil valued at more than $228 billion while the Irving Oil refinery imported $136 billion from 1988 to 2020.
What are the policy and cost implication of Carney’s call for the “decarbonization” of western Canadian produced, oil? It implies that western Canadian “decarbonized” oil would have to be produced and transported to competitive world markets under a material regulatory and financial burden. Meanwhile, eastern Canadian refiners would be allowed to import oil from the USA and offshore jurisdictions free from any comparable regulatory burdens. This policy would penalize, and makes less competitive, Canadian producers while rewarding offshore sources. A federal regulatory requirement to decarbonize western Canadian crude oil production without imposing similar restrictions on imported oil would render the One Canadian Economy Act moot and create two market realities in Canada – one that favours imports and that discourages, or at very least threatens the competitiveness of, Canadian oil export production.
Ron Wallace is a former Member of the National Energy Board.
-

 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoIran nuclear talks were ‘coordinated deception’ between US and Israel: report
-

 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days agoLA protests continue as judge pulls back CA National Guard ahead of ‘No Kings Day’
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoIsrael strikes Iran, targeting nuclear sites; U.S. not involved in attack
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoPunishing Alberta Oil Production: The Divisive Effect of Policies For Carney’s “Decarbonized Oil”
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoIsrael’s Decapitation Strike on Iran Reverberates Across Global Flashpoints
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoCanada is no energy superpower
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump: ‘Changes are coming’ to aggressive immigration policy after business complaints
-
 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoJust 3 Days Left to Win the Dream Home of a Lifetime!



